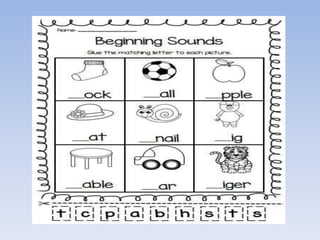
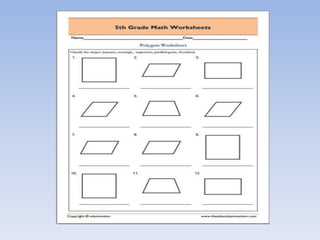
This document discusses various techniques for assessing student learning, including observation, projects, assignments, and worksheets. Observation allows assessing practical skills but requires time and can be subjective. Projects promote higher-order thinking but are not suitable for all subjects. Assignments develop important skills but take time to grade. Worksheets are efficient but not for collaboration. Overall, different techniques are suited to different purposes and content areas when evaluating student understanding.