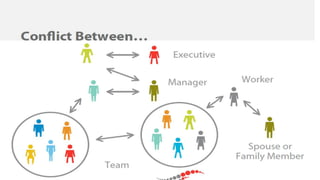
The document outlines conflict management, defining conflict as an active disagreement and emphasizing that it can be both harmful and beneficial. It discusses various views of conflict, its types, sources, components, and the differences between functional and dysfunctional conflict, along with ways to effectively manage it. The conclusion highlights the importance of self-awareness and understanding personal triggers for better handling conflict in the workplace.