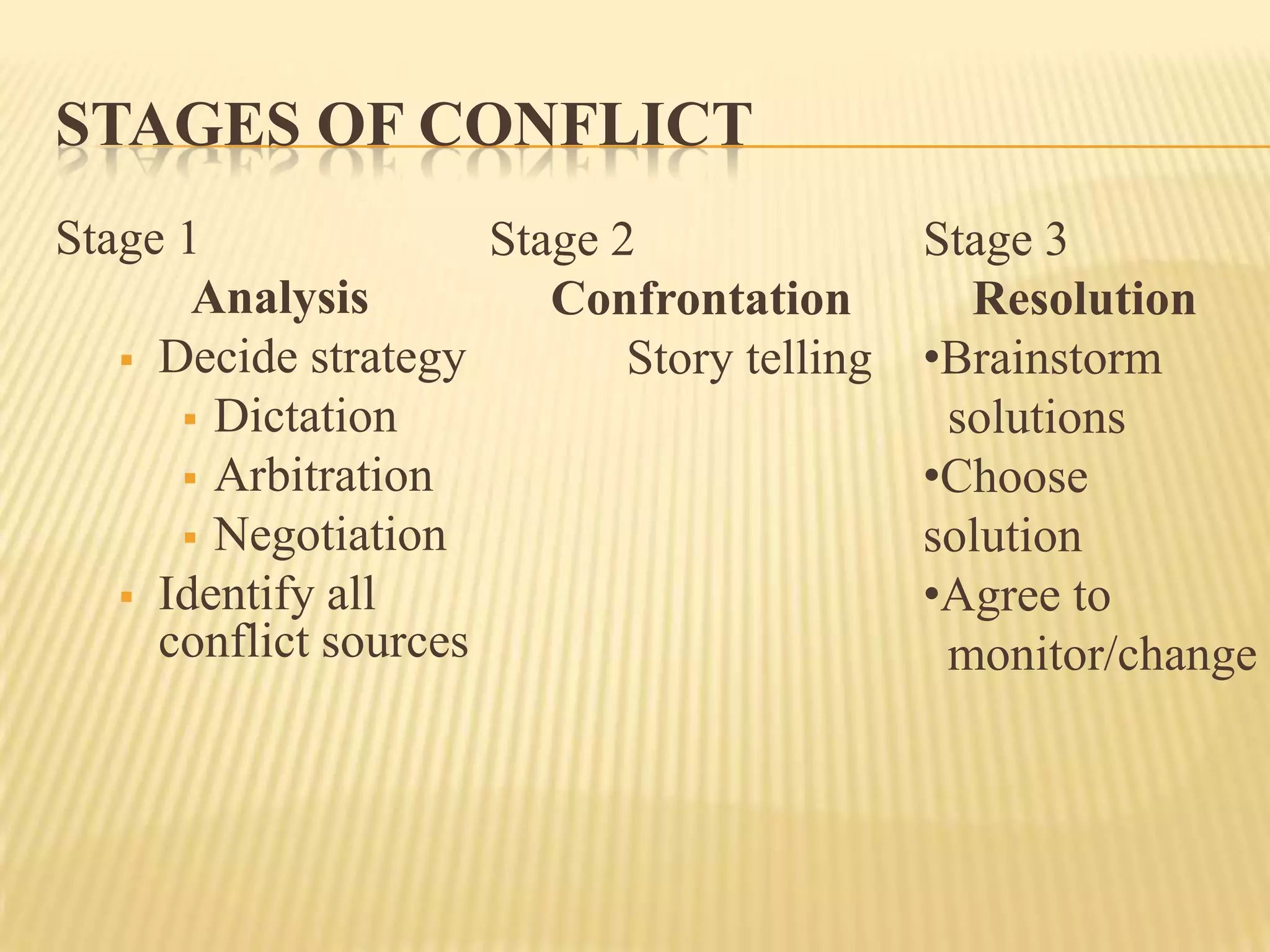
The document discusses the causes and stages of conflict. It defines conflict as an expressed struggle between parties with incompatible goals, scarce resources, or interference. The main causes of conflict discussed are conflicting resources, styles, perceptions, goals, pressures, roles, personality differences, and misunderstandings. The stages of conflict are analysis, confrontation, and resolution. In analysis, the best strategy is determined and sources identified. Confrontation involves storytelling. Resolution includes brainstorming solutions, choosing one, and agreeing to monitor changes.