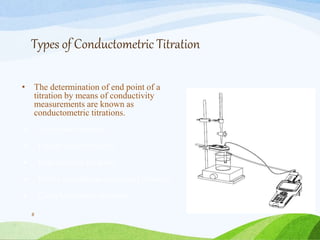
The document discusses various electrochemical methods of analysis in pharmaceutical chemistry, focusing on conductometry and its applications. It details the principles of conductometric titration, instrumentation, and various types of titrations, including acid-base and redox titrations. Key concepts such as conductivity, electrolites, and cell types are also explained.








![Precipitation Titration
• [K++Cl-]+[Ag++No3
_]
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conductometry-200131052802/85/Conductometry-10-320.jpg)


