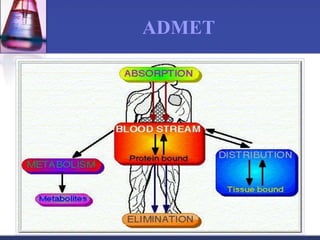
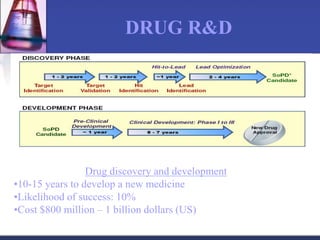
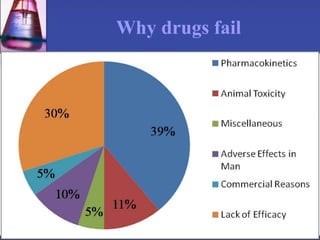
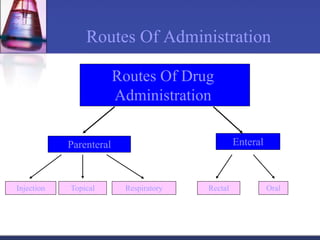
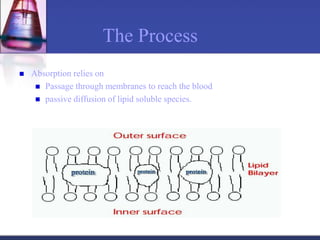
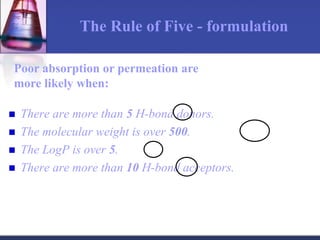
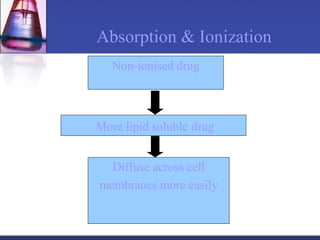
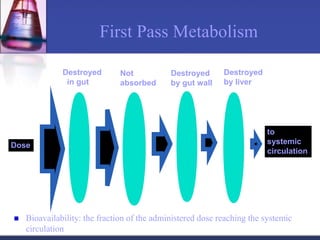
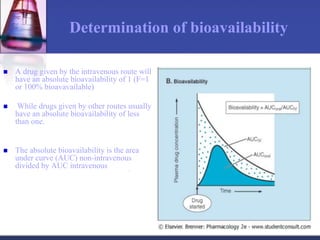
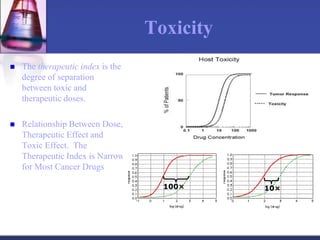
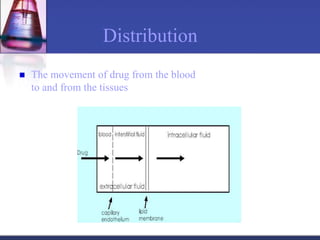
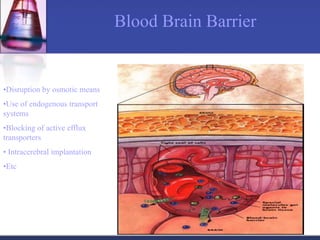
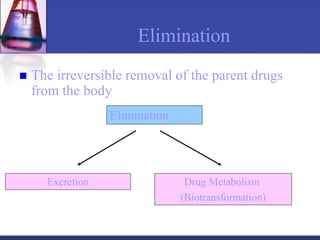
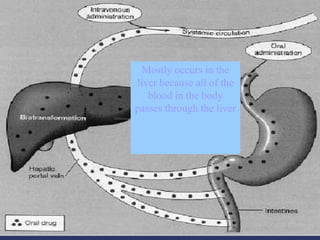
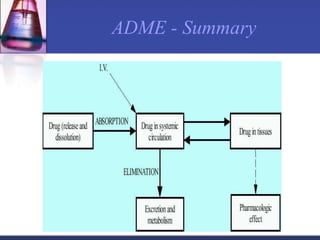
The document discusses pharmacokinetics, which is the study of drug disposition in the body, encompassing absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). It highlights the significance of pharmacokinetic studies in drug development and patient safety, noting that unsuccessful drug development can lead to toxic accumulation or ineffective treatment. The document outlines various factors influencing drug absorption, metabolism phases, and elimination processes.