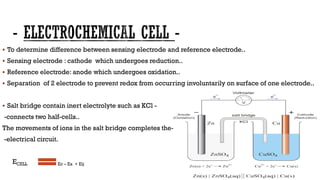
Potentiometric methods of analysis measure the potential of electrochemical cells under conditions of zero current. The potential difference between a sensing electrode and a reference electrode is measured. A salt bridge containing an inert electrolyte connects the two half-cells and allows ionic movement to complete the electrical circuit. Common reference electrodes include the standard hydrogen electrode, saturated calomel electrode, and silver-silver chloride electrode. Potentiometry is used for applications such as determining electrode potentials, measuring pH, and analyzing samples in clinical chemistry, environmental chemistry, agriculture, and food processing.


![▪ It has a standard potential on its own and it’s potential does not change to solution it is
dipped..
▪ Always treated as the anode electrode..
▪ Examples- [a]. Standard hydrogen electrode.
▪ [b]. Saturated calomel electrode.
▪ [c]. Silver-silver chloride electrode.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/potentiometric-200108161845/85/Potentiometric-Pharmaceutical-Analysis-101T-4-320.jpg)




![▪ Metal electrodes are system that use specific metal electrodes as the electrodes in an
electrochemical measurement..
▪ Ecell = Eind. + Eref + Ej
▪ There are two kinds of metal electrodes..
▪ [a].The electrodes potential responds directly in relationship to the concentration of the
metal ion ..
▪ cu 2+ + 2e- = cu
▪ [b]. Metal analyte ion is equilivrium with the target analyte..
Cu2+ + 2l- = cul2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/potentiometric-200108161845/85/Potentiometric-Pharmaceutical-Analysis-101T-9-320.jpg)

