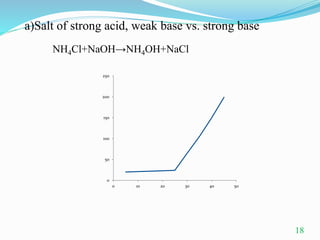
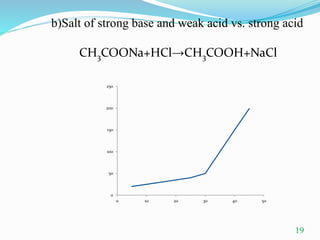
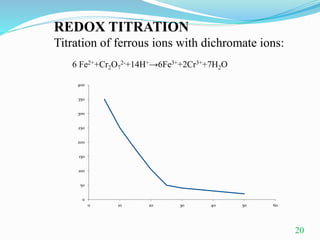
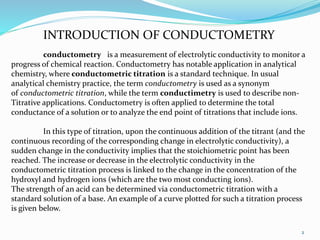
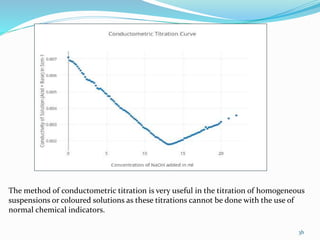
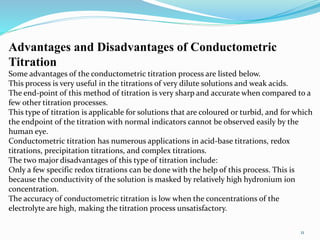
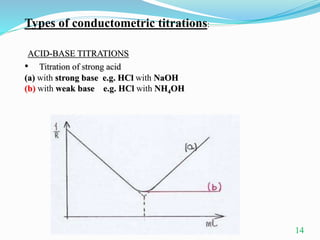
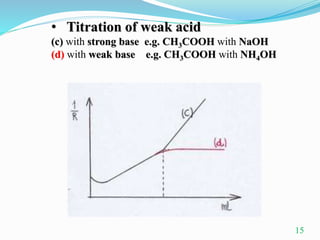
Conductometric titration is a technique used in analytical chemistry that measures electrolytic conductivity to determine chemical reaction endpoints, particularly for solutions that are turbid or colored. The method relies on the change in conductivity due to the replacement of ions during the titration process and can be applied to various types of titrations, including acid-base and redox titrations. Its advantages include sharp and accurate endpoints, while its limitations involve reduced accuracy at high electrolyte concentrations.







![PRECIPITATION TITRATIONS:-
[K++Cl-]+[Ag++No3
_]
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/12588396345772453964187501-200429134956/85/DONDUCTOMETRIC-TITRATION-16-320.jpg)