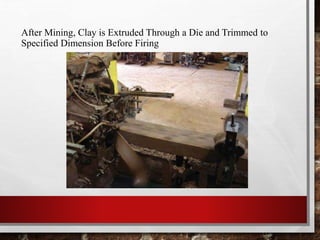
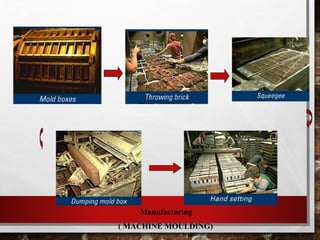
Bricks are small, hard blocks made from clay and used in construction, with their history dating back to 7000 BC in southern Turkey. The manufacturing processes have evolved to include modern machinery, and bricks come in various types, such as clay, concrete, and high alumina, each suited for different uses. Bricks have distinct properties like compressive strength, moisture regulation, and fire resistance, making them essential in both structural and decorative applications.