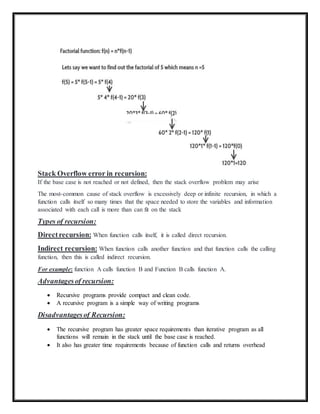
Recursion is a process where a function calls itself repeatedly until a base condition is met. A recursive function calls itself during its own execution. To prevent infinite recursion, an if/else statement can check for a base condition. The purpose of recursion is to divide a problem into smaller sub-problems until the base condition is reached. Recursion uses function calls and returns which require additional memory and time compared to iteration. An example is calculating the factorial of a number recursively by calling itself with decreasing arguments until the base case of 1 is reached.