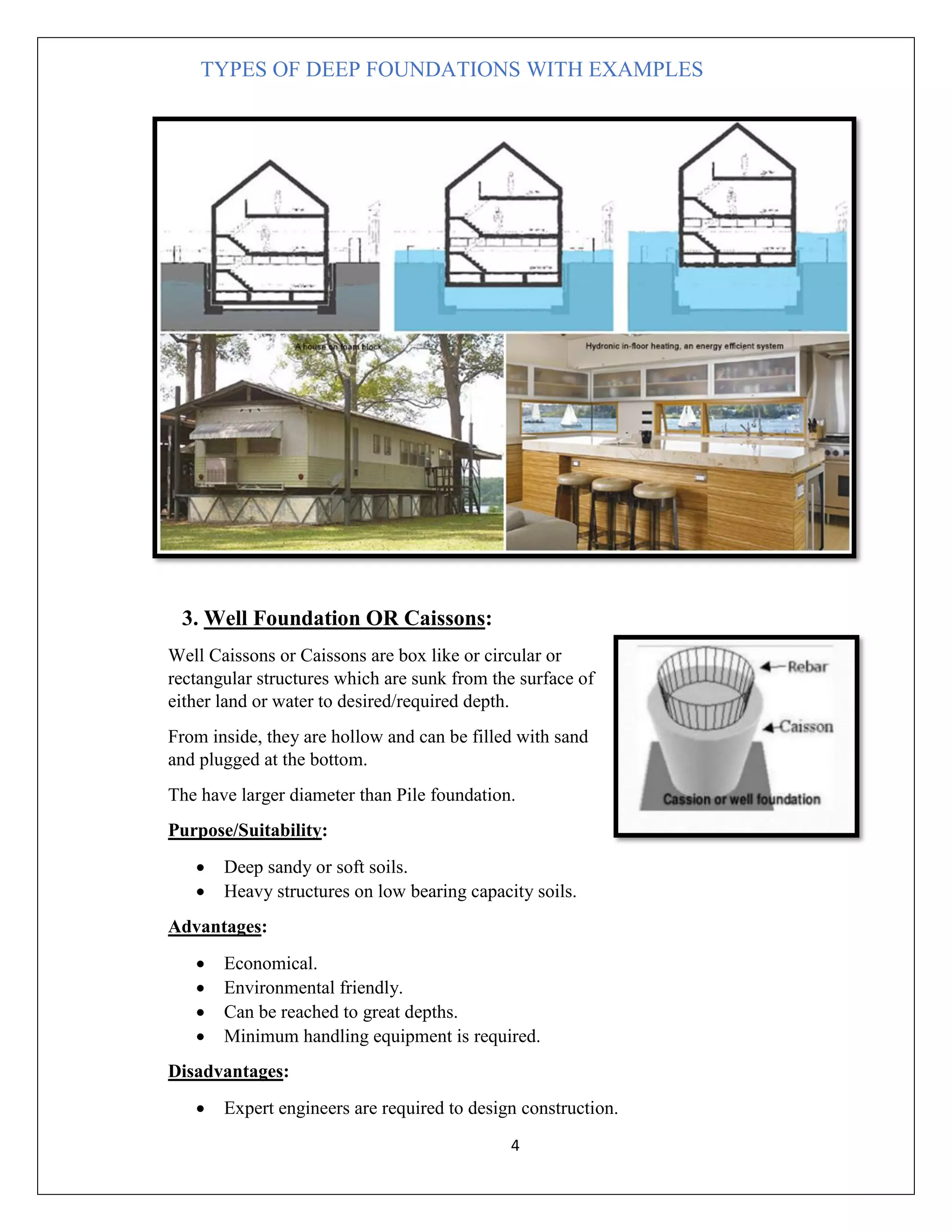
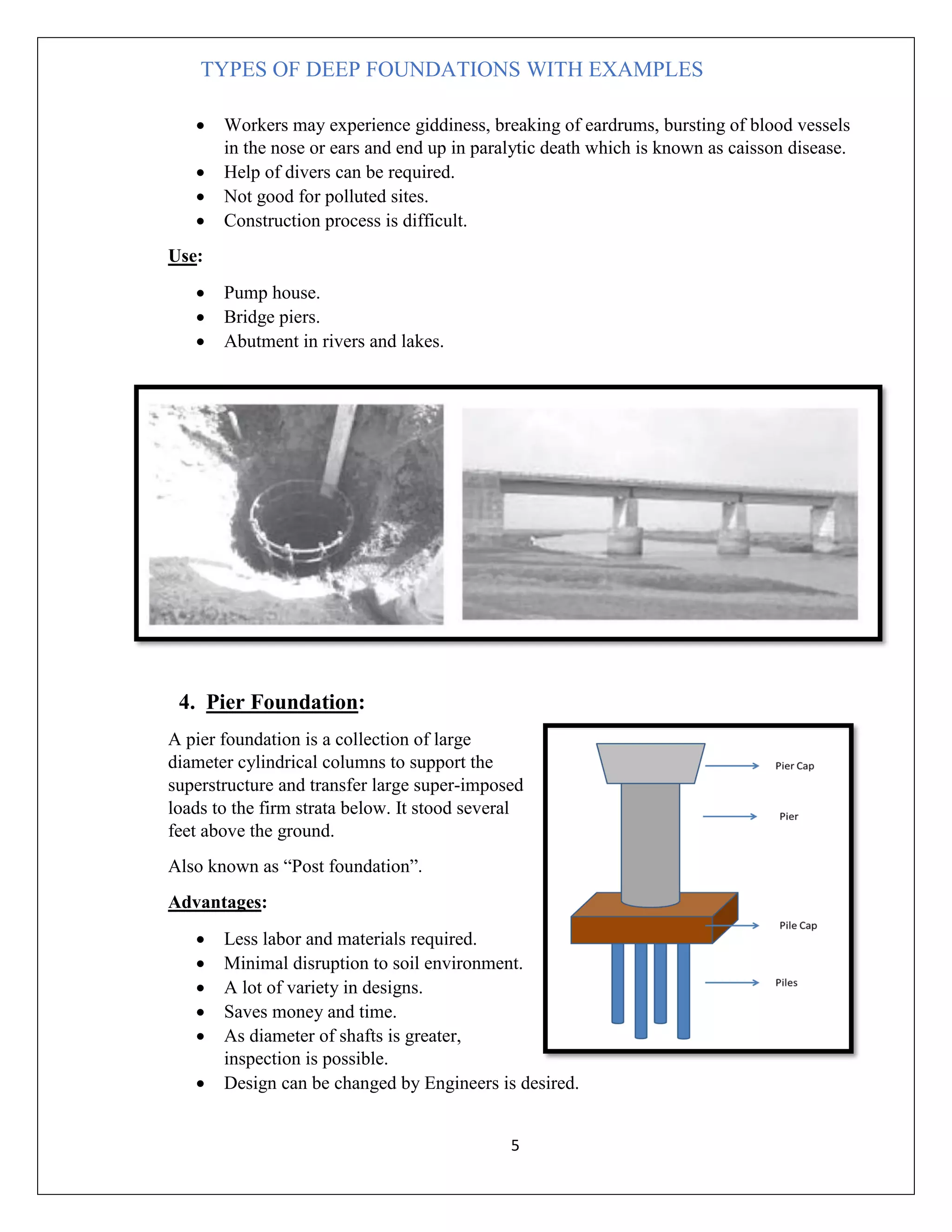
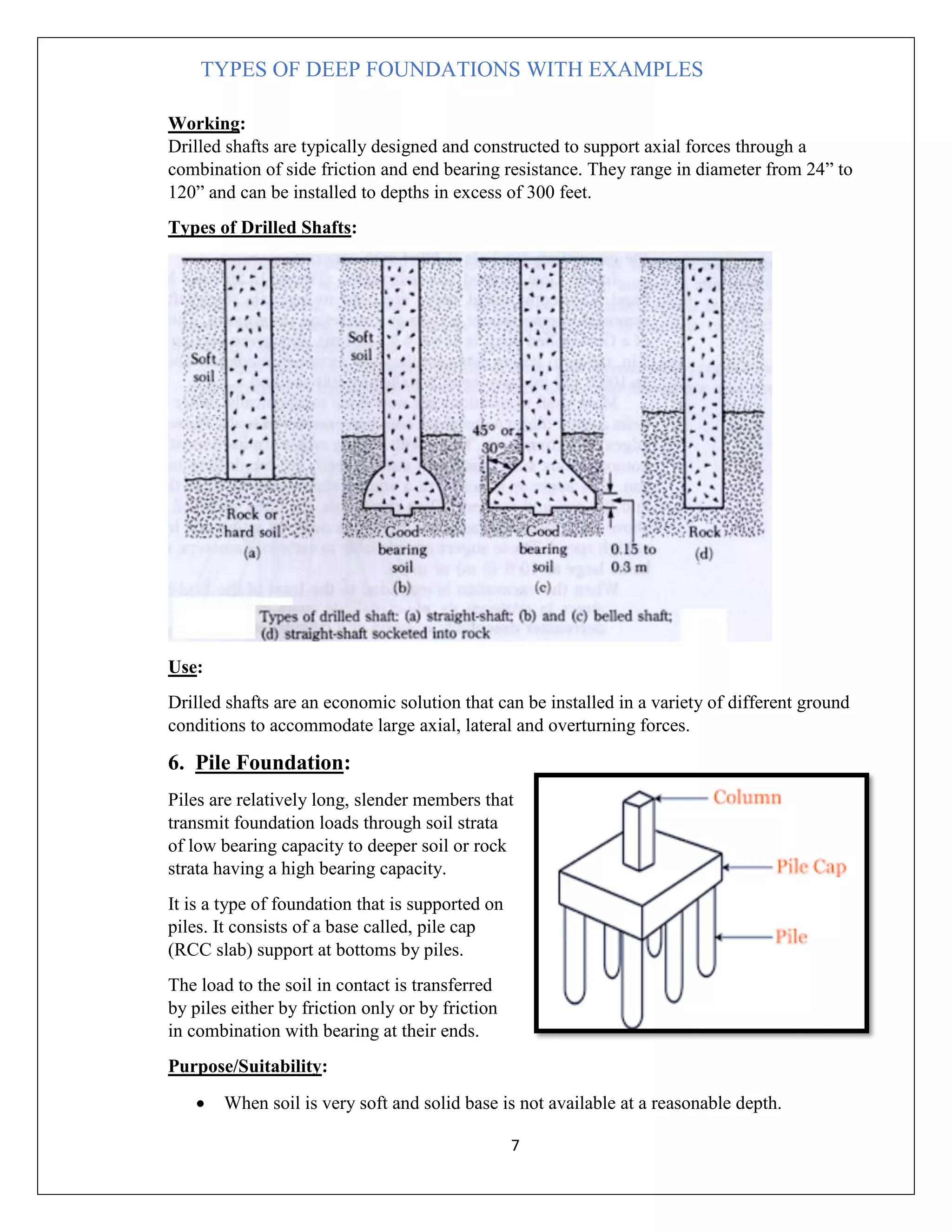
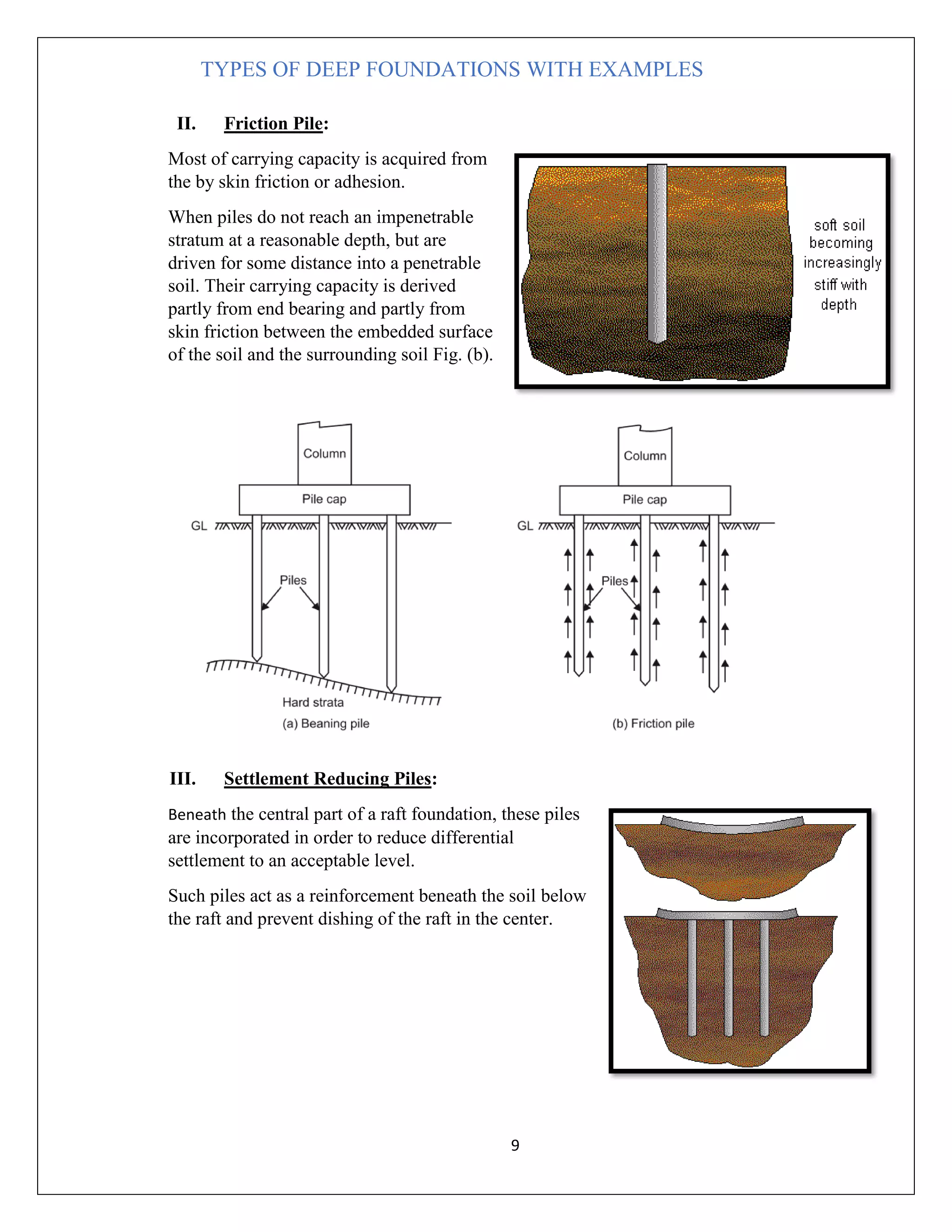
There are several types of deep foundations that can be used depending on the soil conditions and load requirements. These include basement foundations, buoyancy raft or hollow box foundations, well/caisson foundations, pier foundations, drilled shaft foundations, and pile foundations. Each type has advantages and disadvantages related to cost, construction difficulty, and suitability for different soil and loading conditions. Common examples of deep foundations used include caissons for bridge piers, drilled shafts for structures with large axial and lateral loads, and piles beneath structures with high groundwater or compressible soils. The type of deep foundation selected depends on the project needs and subsurface environment.