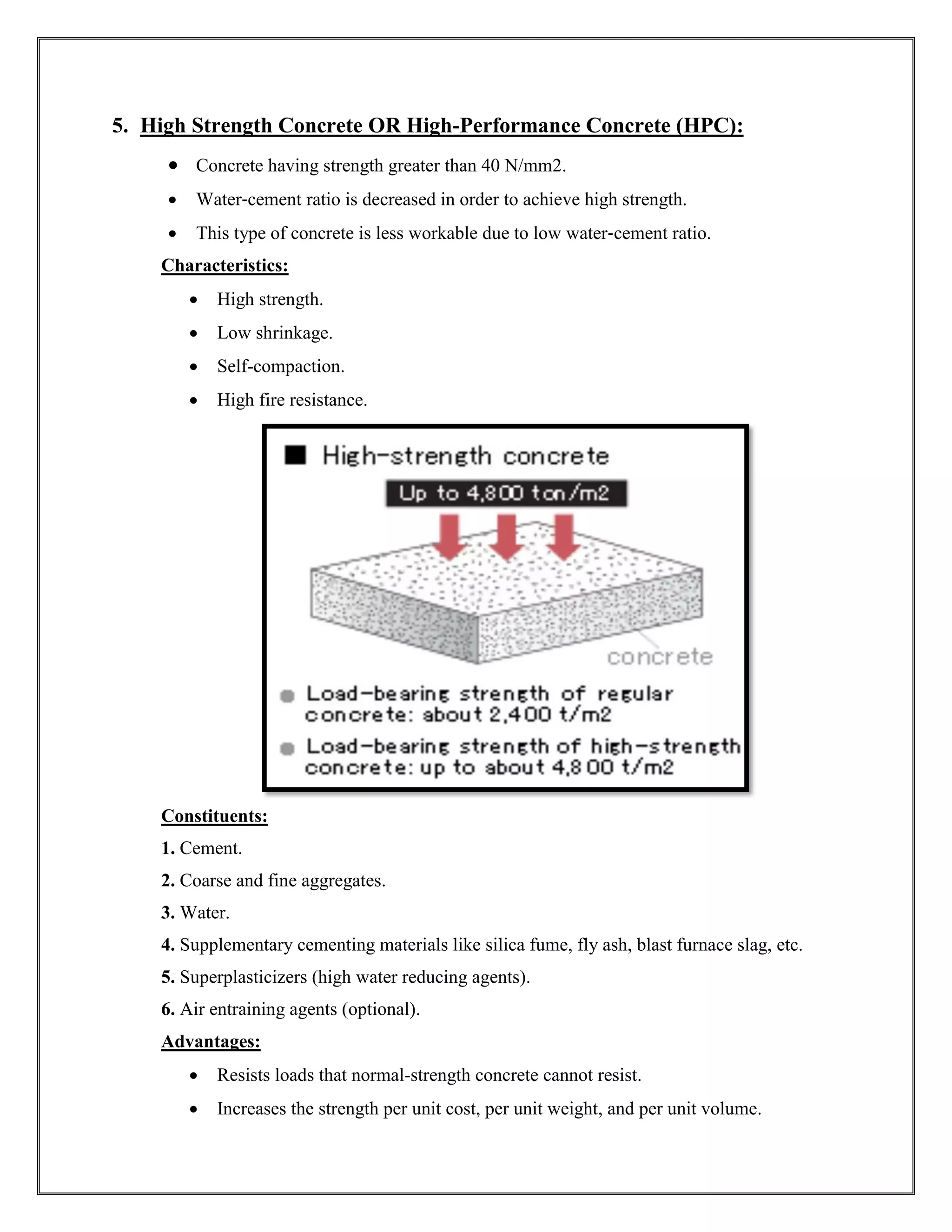
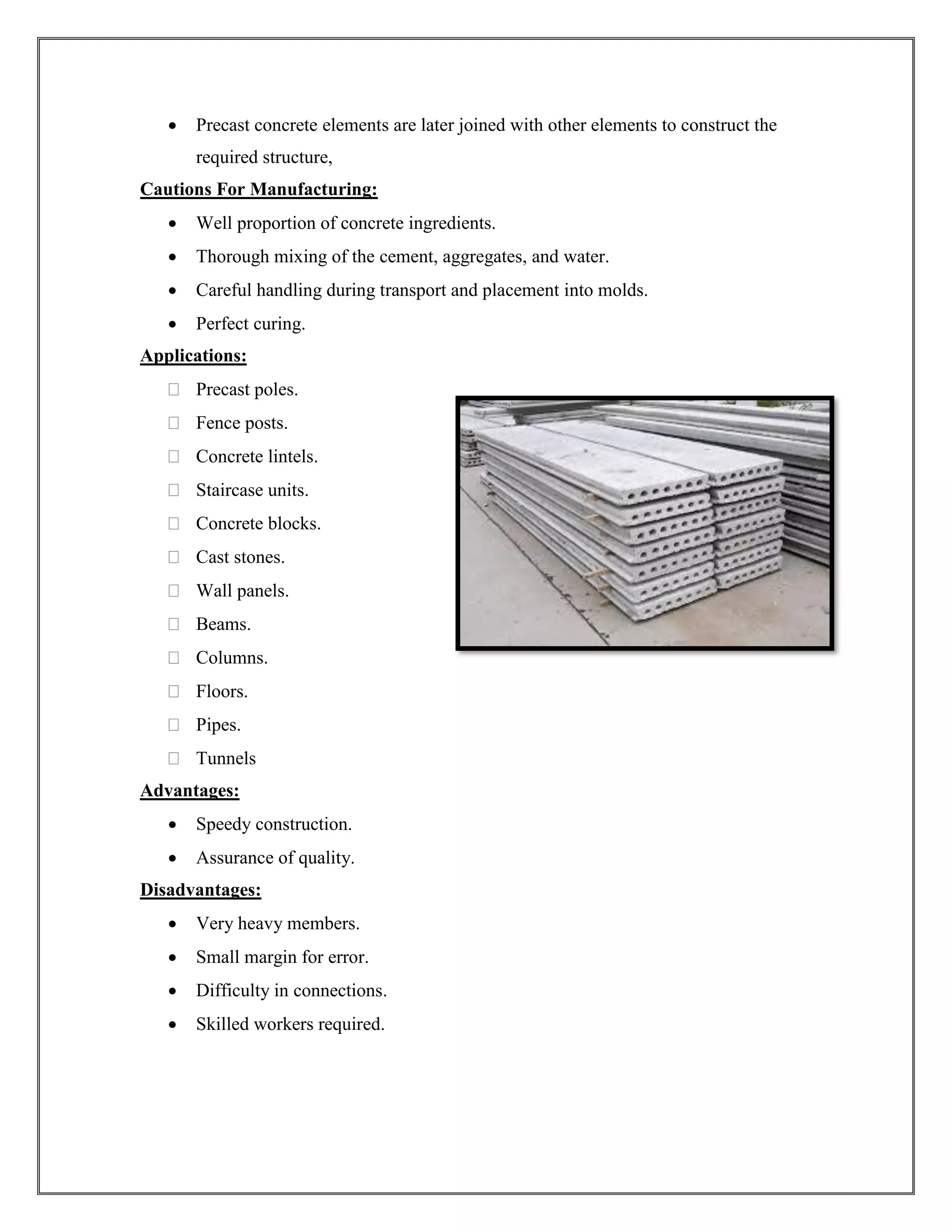
The document discusses 12 commonly used types of concrete, each with unique properties and applications, such as plain, lightweight, high-density, normal strength, and high-strength concrete. It details the composition, advantages, and disadvantages of each type, highlighting their suitability for different construction purposes, including pavements, high-performance structures, and precast elements. Emphasis is placed on the advantages of specific types, such as lightweight concrete's thermal insulation and rapid strength concrete's quick setting time.