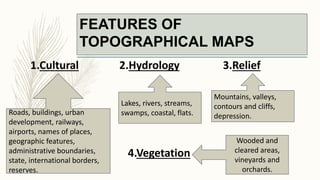
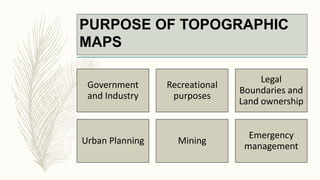
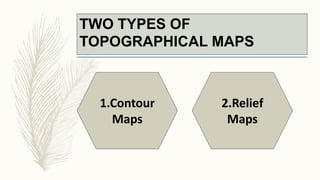
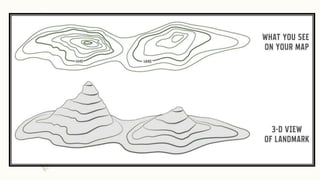
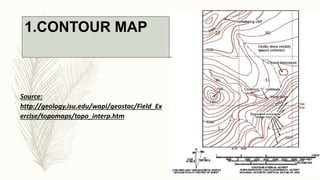
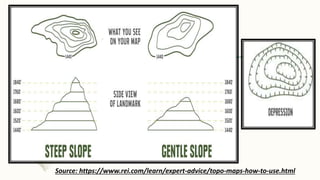
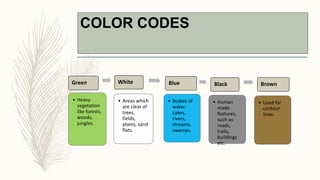
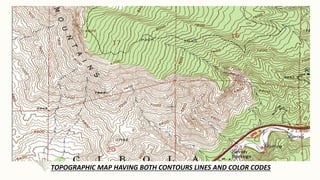
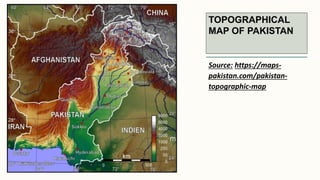
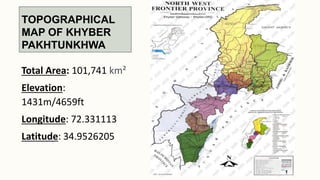
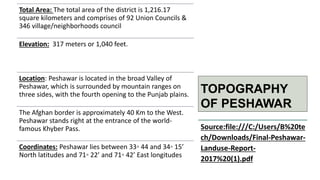
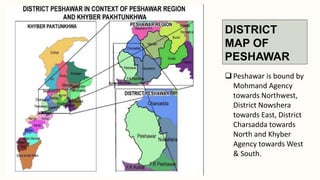
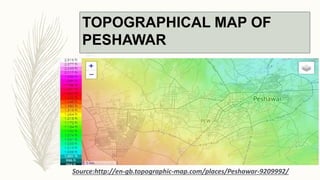
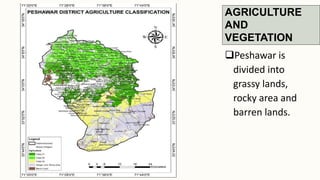
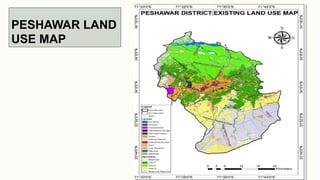
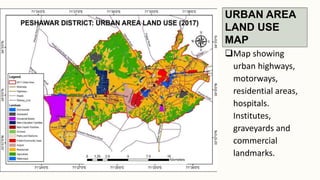
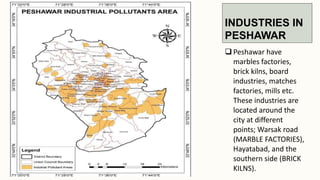
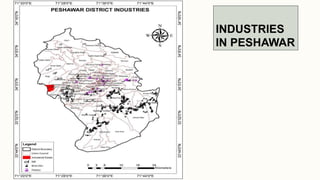
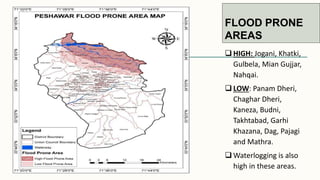
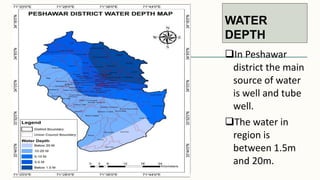
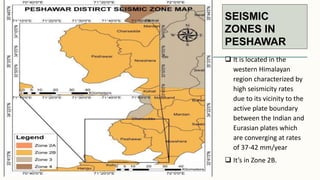
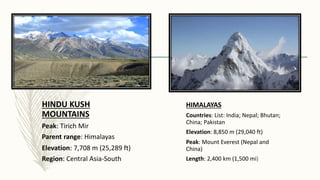
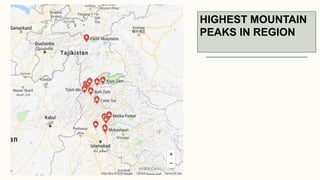
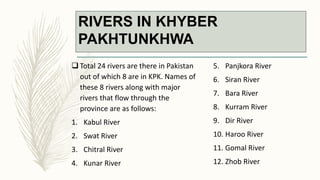
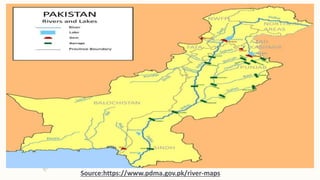
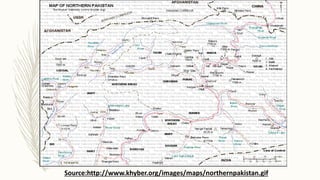
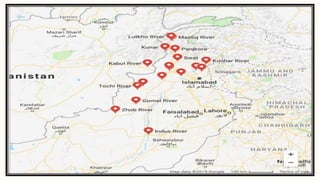
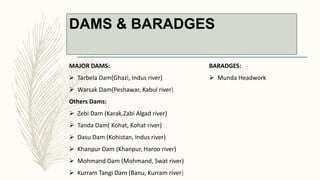
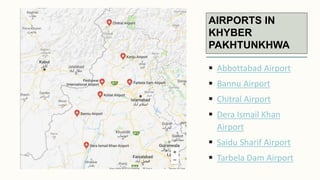
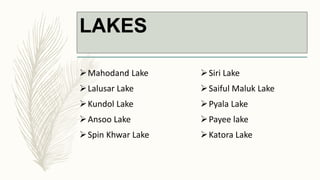
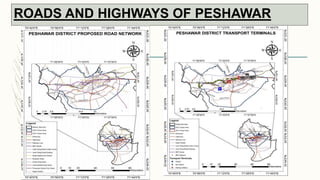
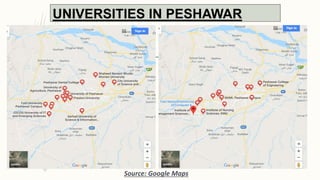
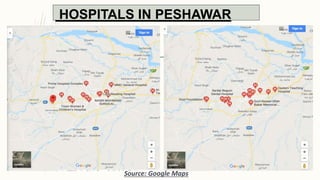
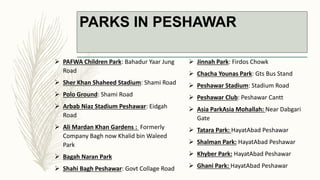
The document summarizes key topographical features of Peshawar, Pakistan through maps and descriptions. It outlines that Peshawar sits in a valley surrounded by mountain ranges, with an elevation of 317 meters. Topographical maps of Peshawar show its cultural, hydrological, relief, and vegetation features, including cities, rivers, contours, and wooded areas. Contour maps and relief maps are two types used to represent Peshawar's elevation details. The document also maps out Peshawar's industrial areas, flood zones, seismic activity, agricultural regions, airports, universities, hospitals and other infrastructure.