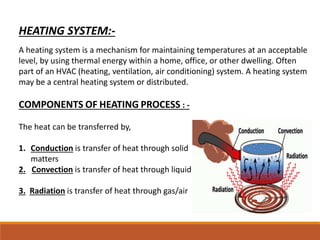
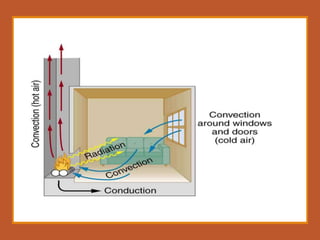
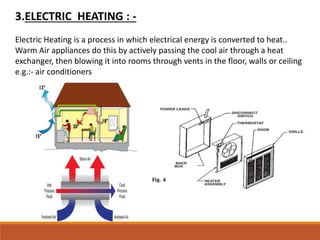
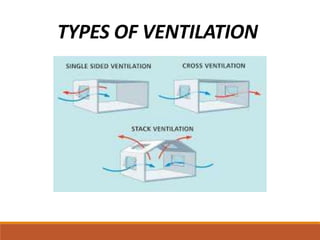
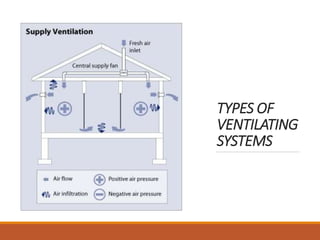
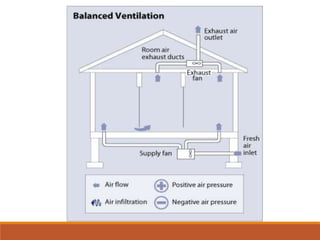
The document discusses heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. It describes the basic components and processes of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning. For heating, it discusses central heating systems using hot water or steam, and electric heating. For ventilation, it covers natural ventilation using windows and mechanical ventilation using fans. For air conditioning, it explains the basic operations of removing heat from indoor air and transferring it outside using a refrigerant in a compressor, condenser, evaporator coil, and blower. In summary, the document provides an overview of the key components, processes, and general effects of HVAC systems.