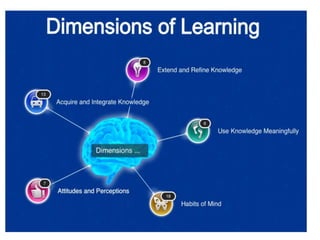
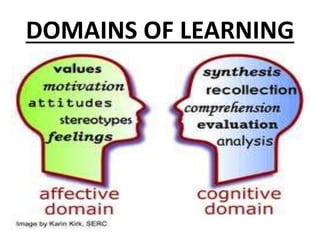
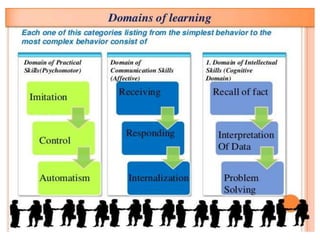
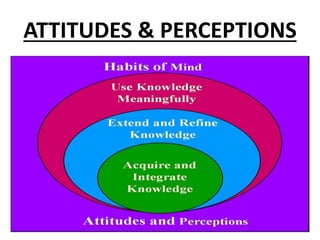
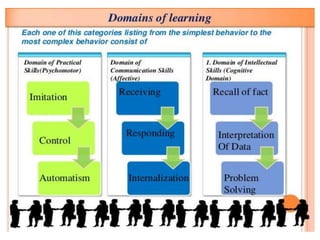
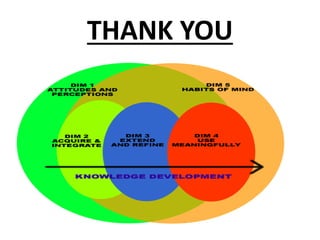
This document discusses the three main dimensions of learning: ideational, skill, and emotional learning.
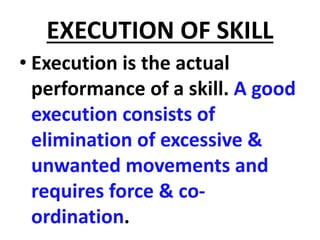
Ideational learning occurs in the cognitive domain and involves acquiring knowledge through concepts, facts, principles, and generalizations. Skill learning takes place in the psychomotor domain and involves forming and executing skills through practice, demonstration, and overcoming mistakes. Emotional learning is related to the affective domain and results in the development of attitudes, values, and ideals that shape a person's character.