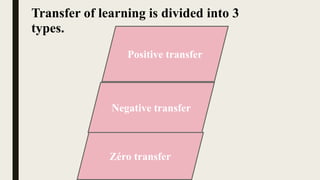
The document discusses the concept of transfer of learning, which refers to applying knowledge or skills acquired in one context to another. It categorizes transfer into three types: positive transfer, where previous learning aids new learning; negative transfer, where past knowledge hinders learning; and zero transfer, where there is no impact. Factors influencing transfer include learner intelligence, study habits, and teaching methods, and it emphasizes the importance of drawing connections between learning situations for effective transfer.