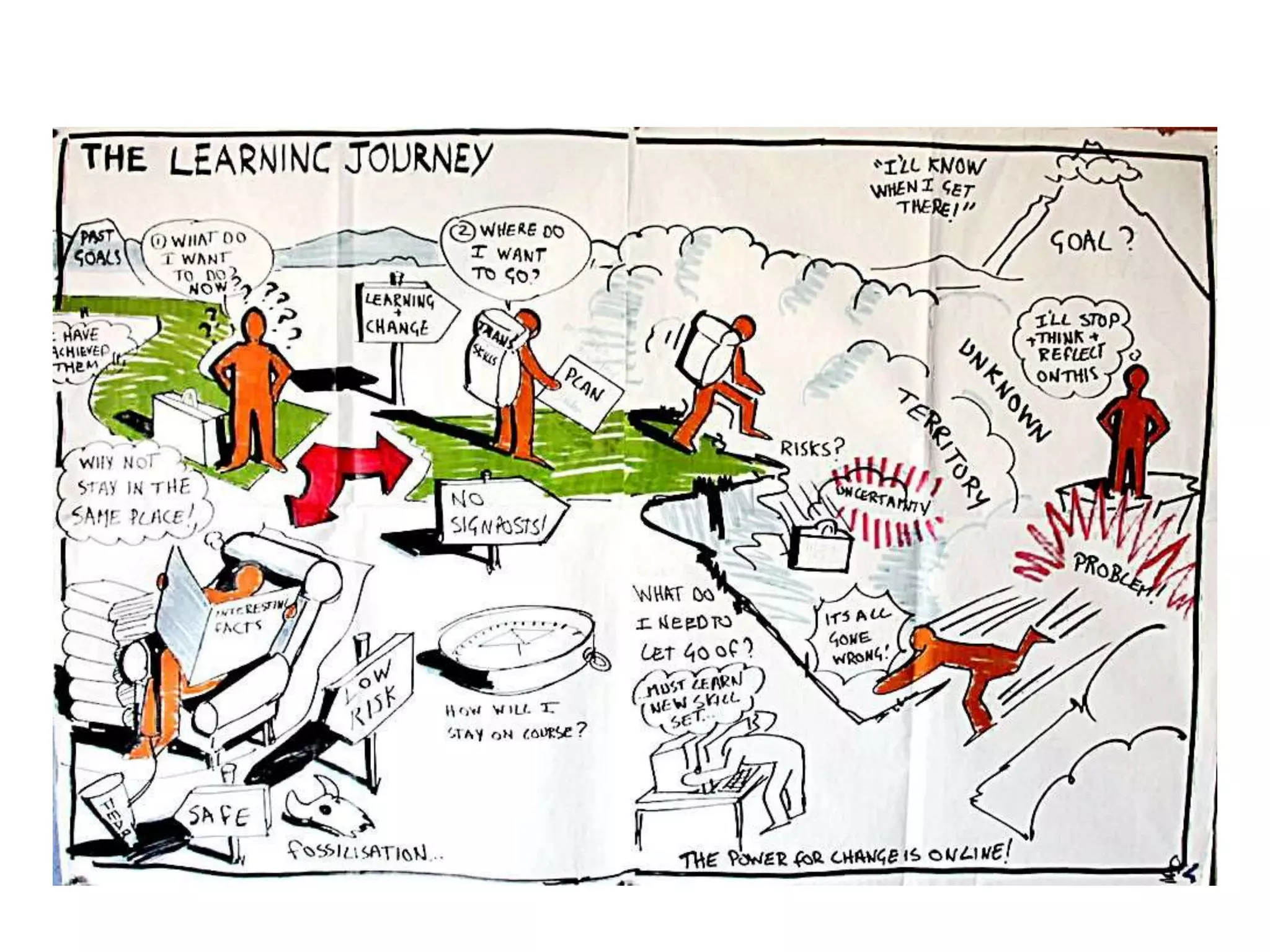
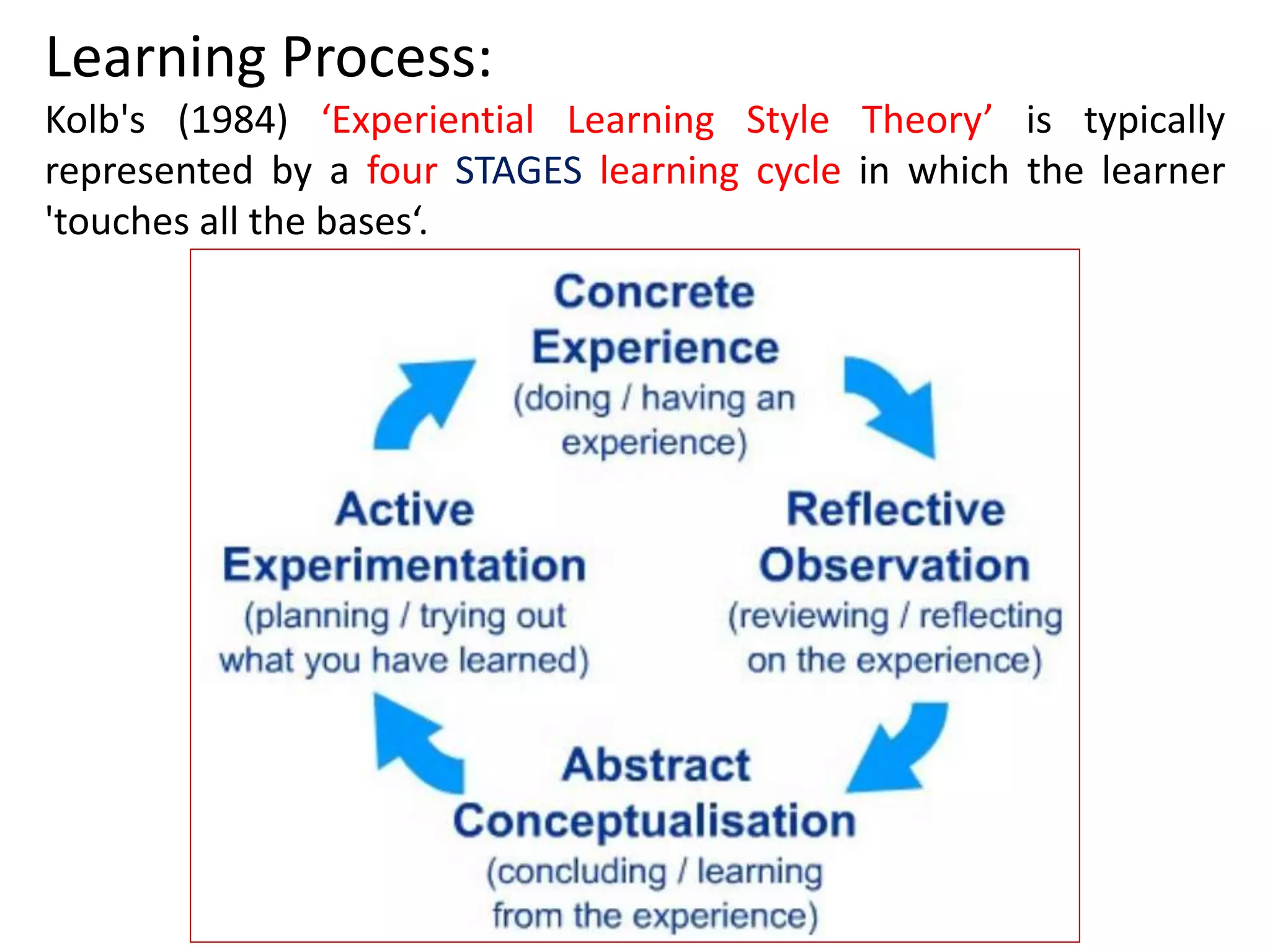
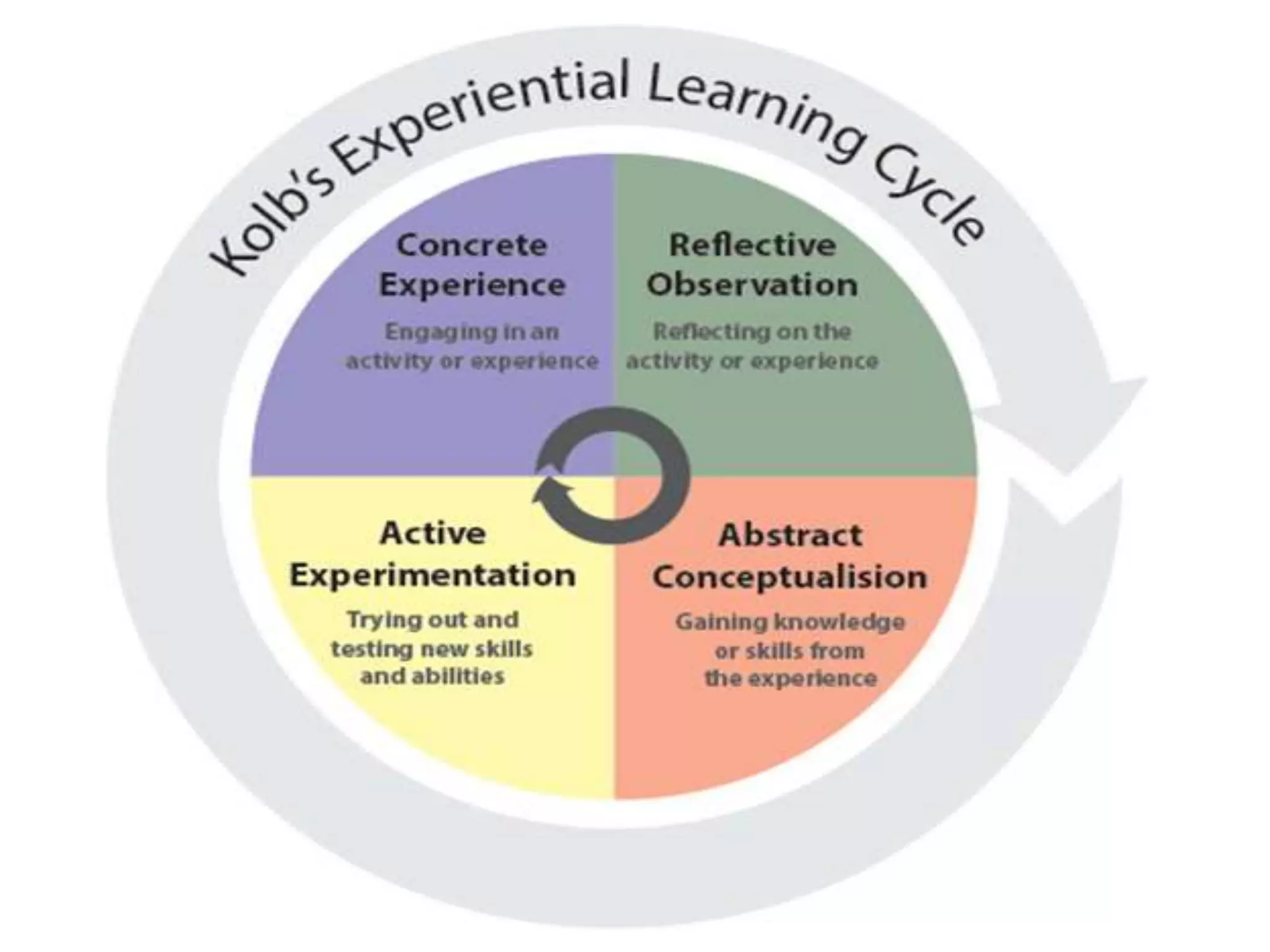
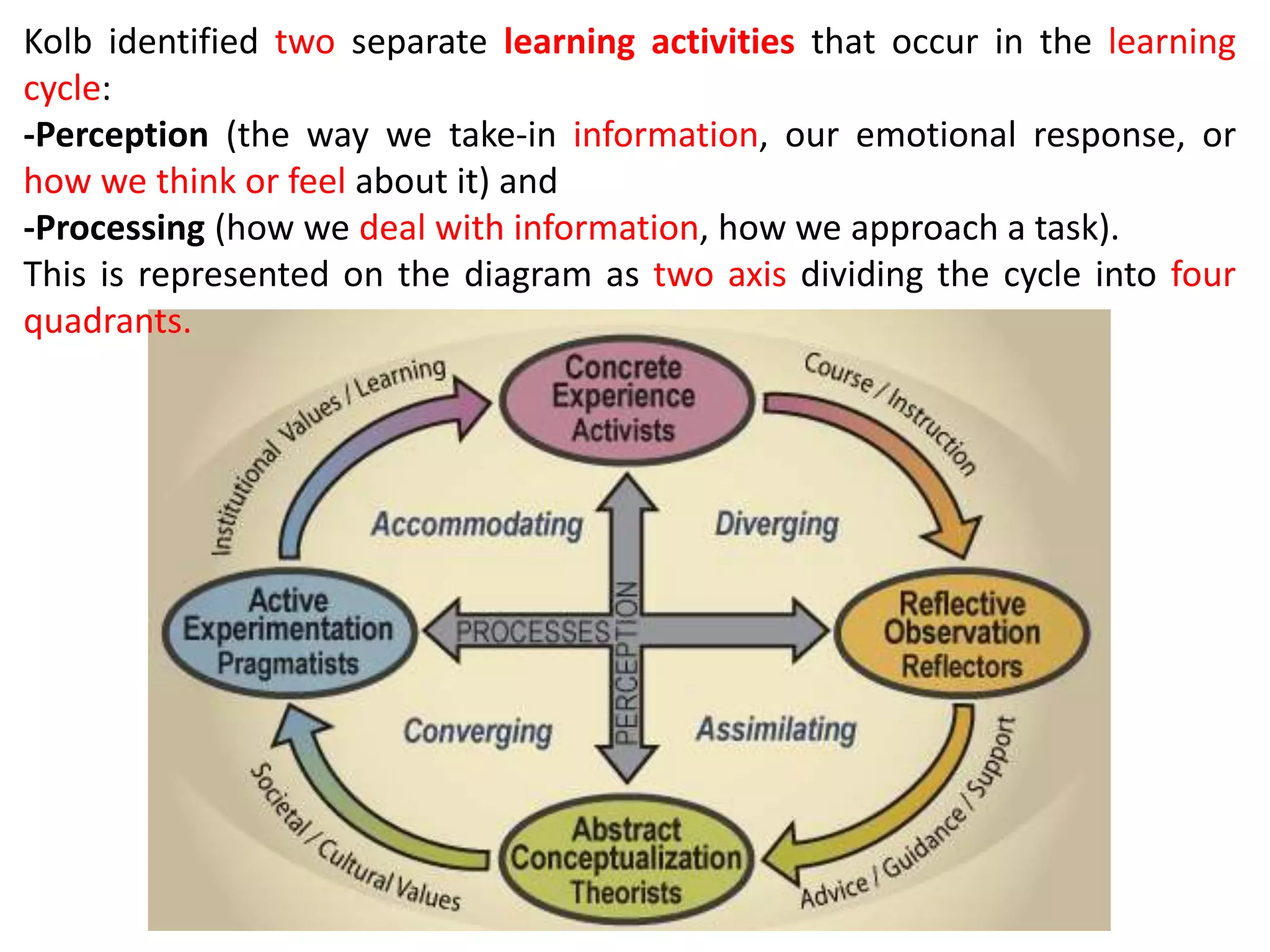
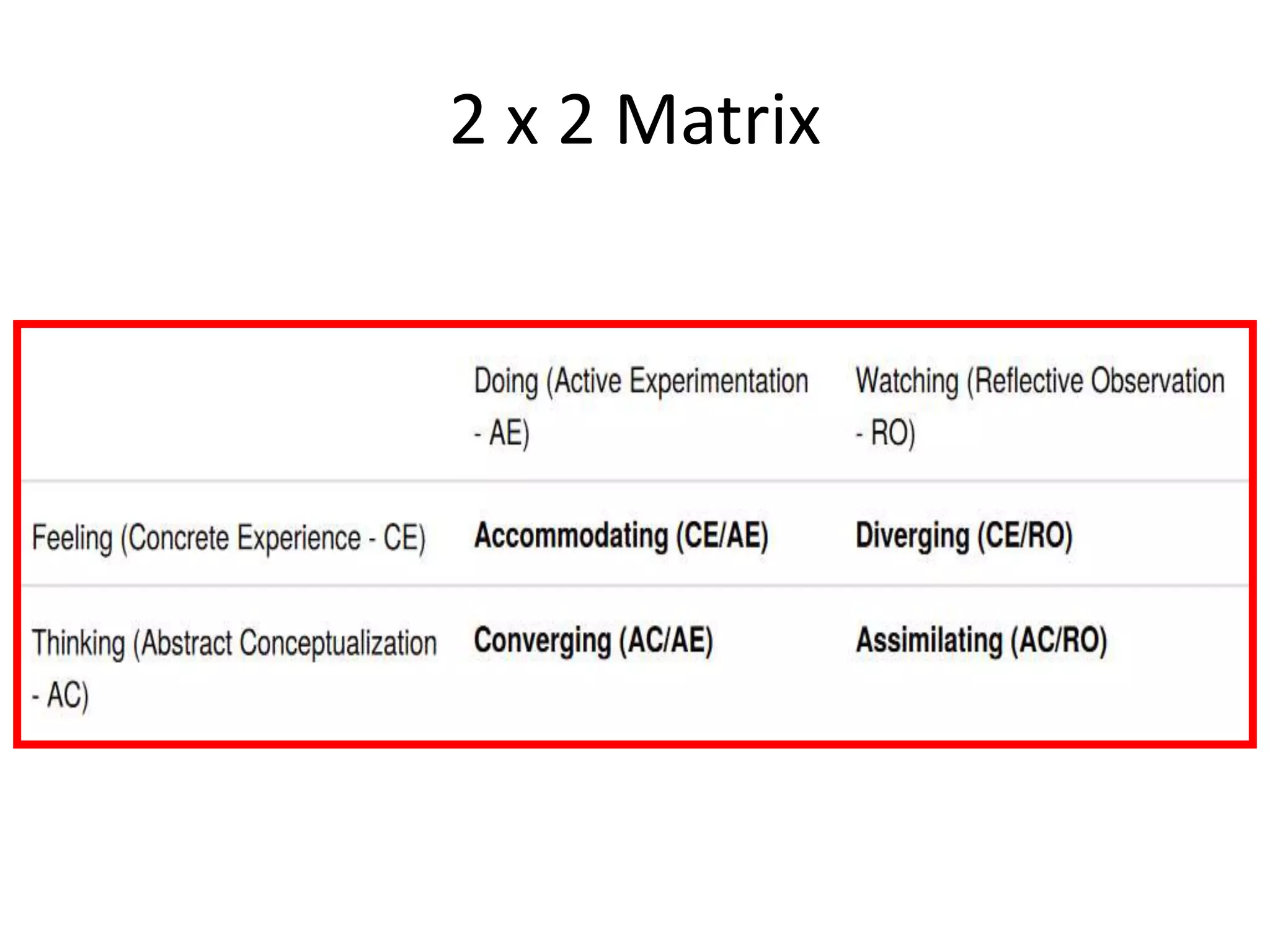
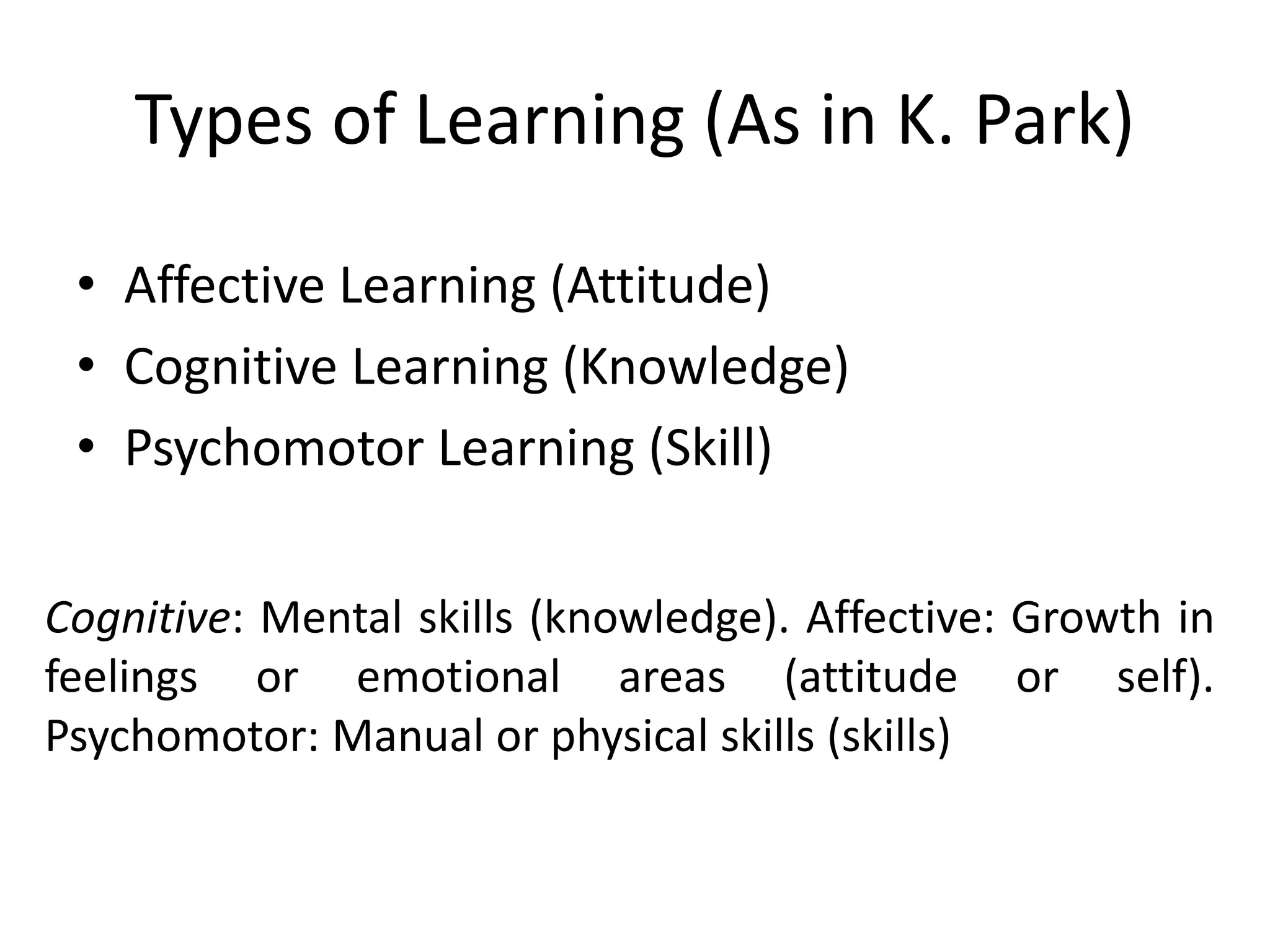
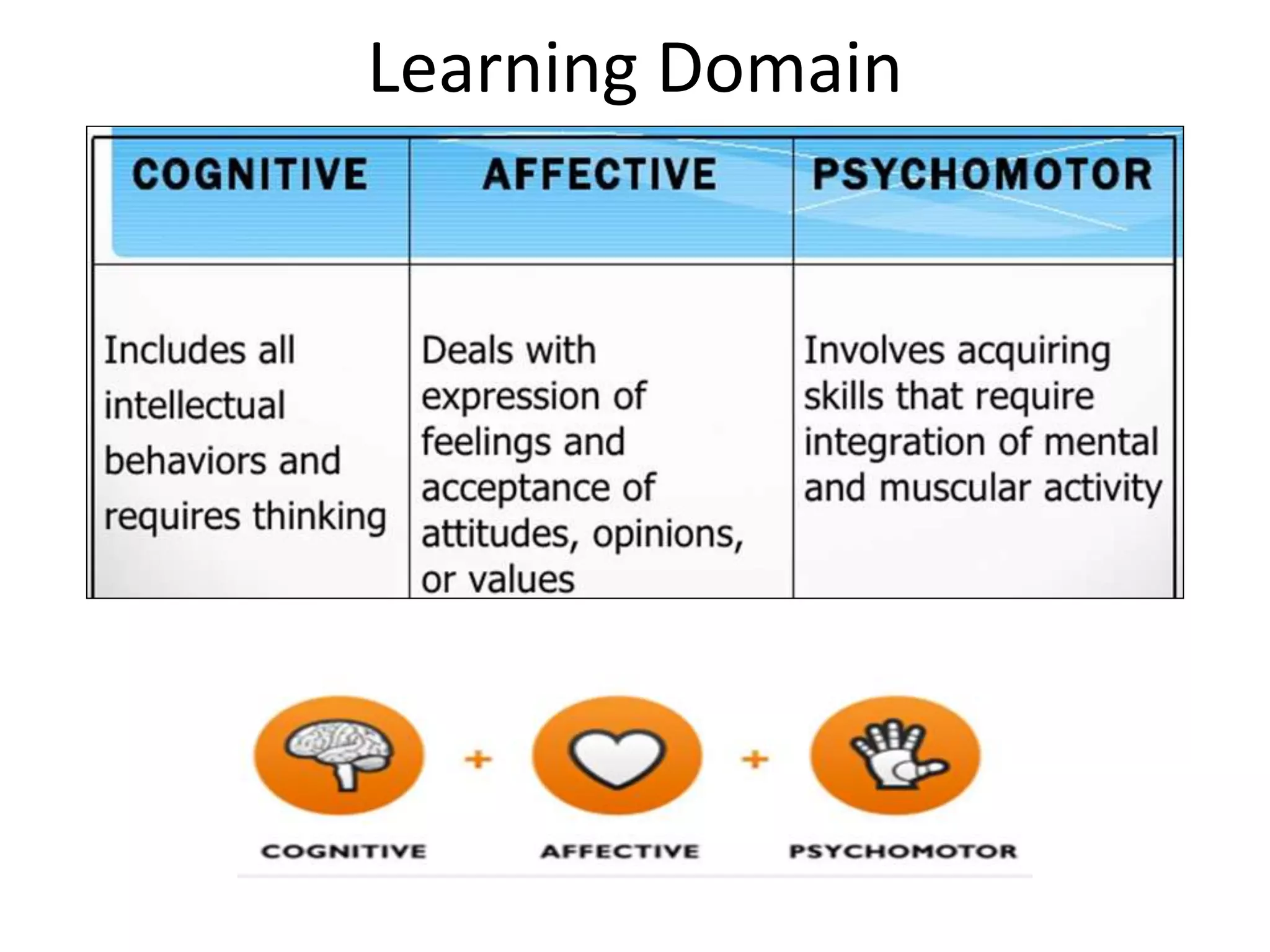
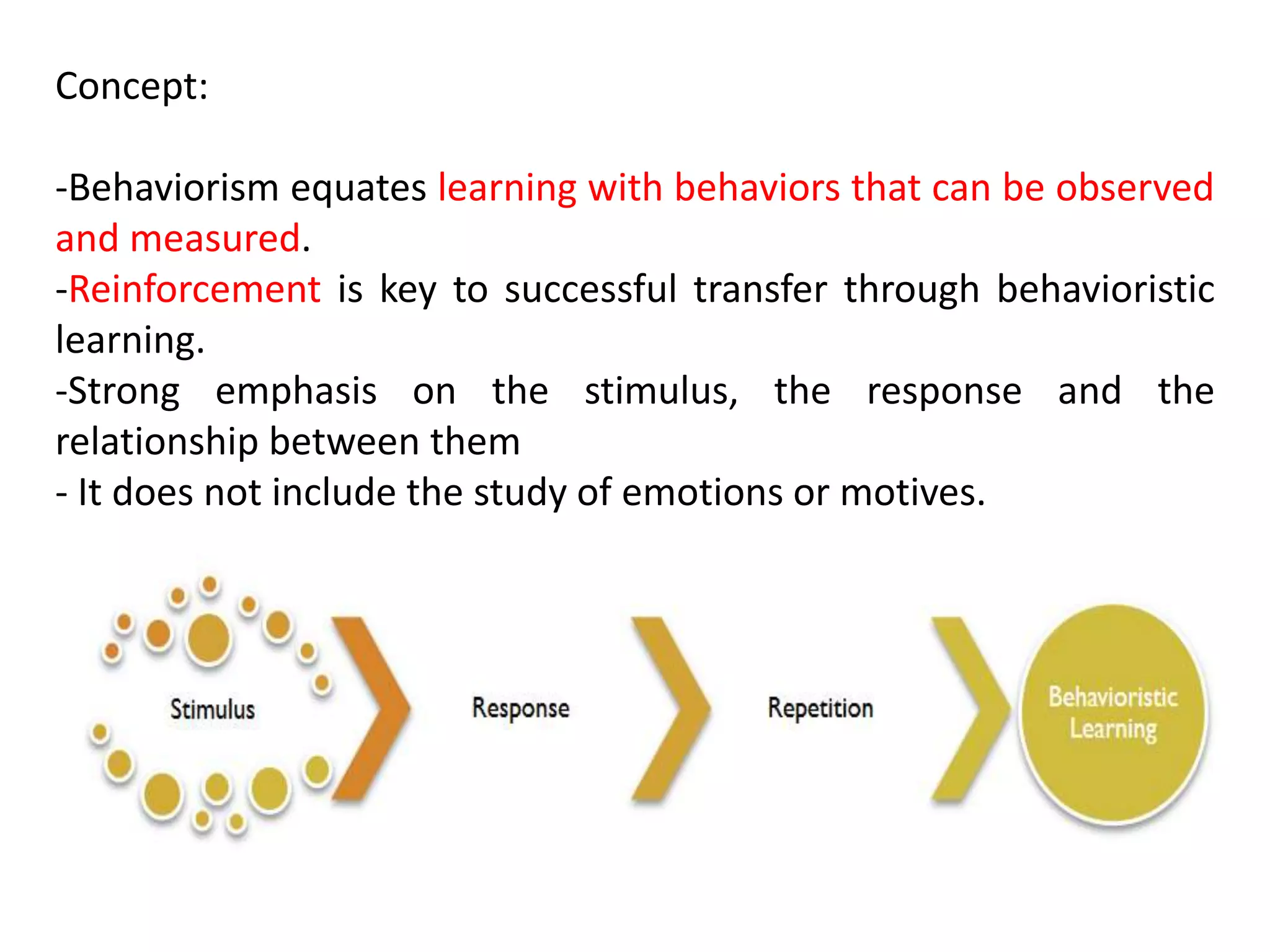
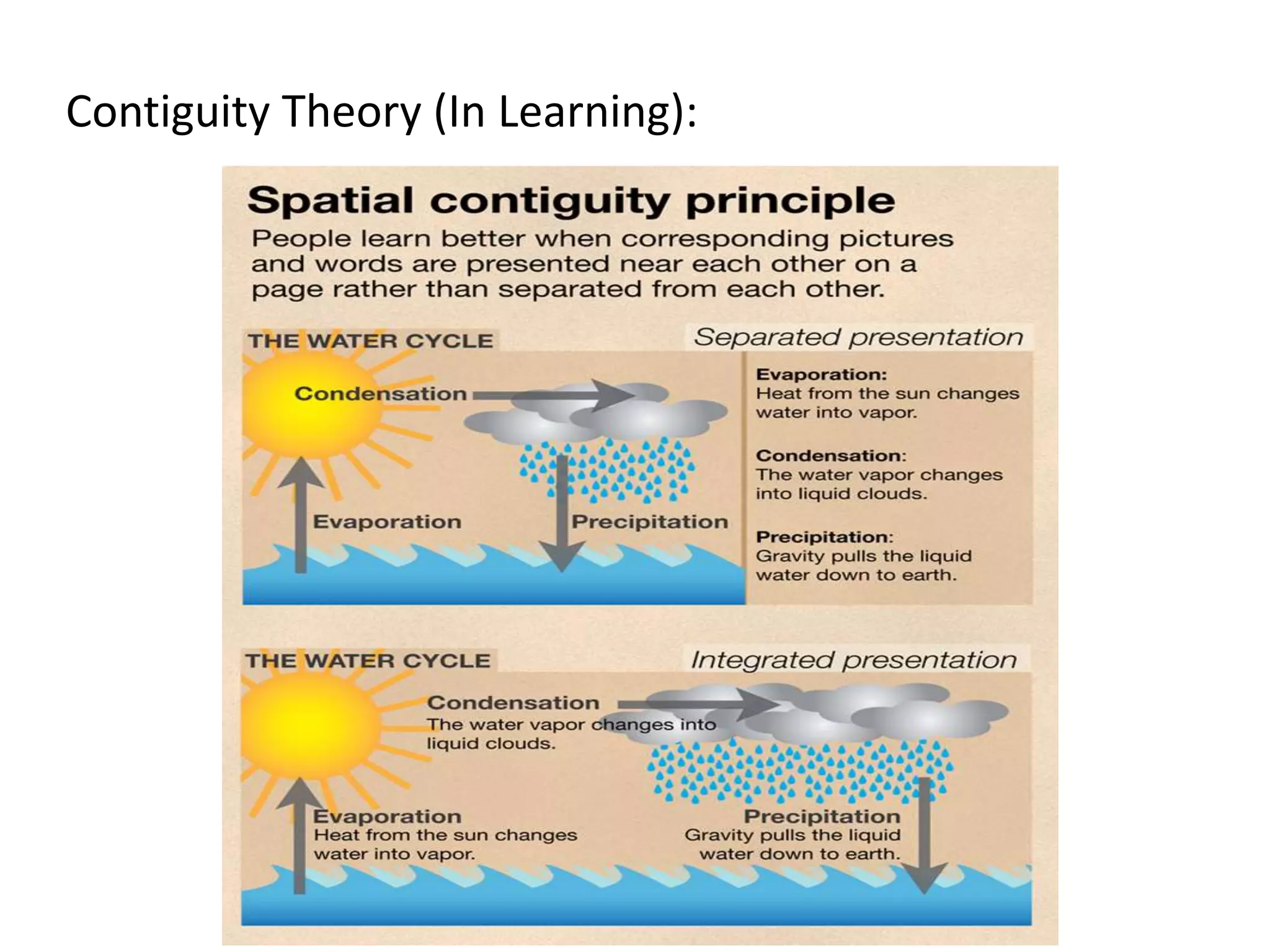
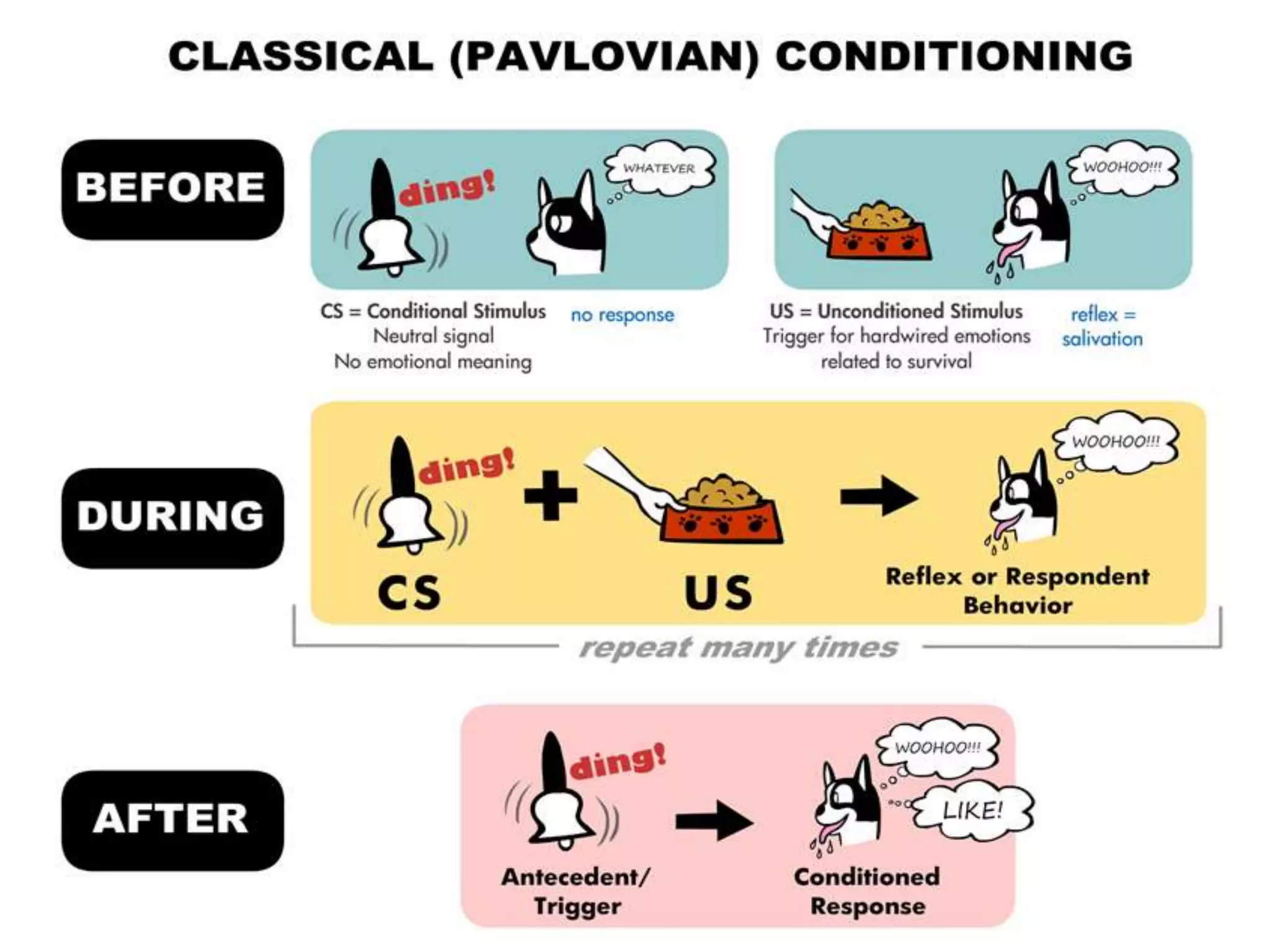
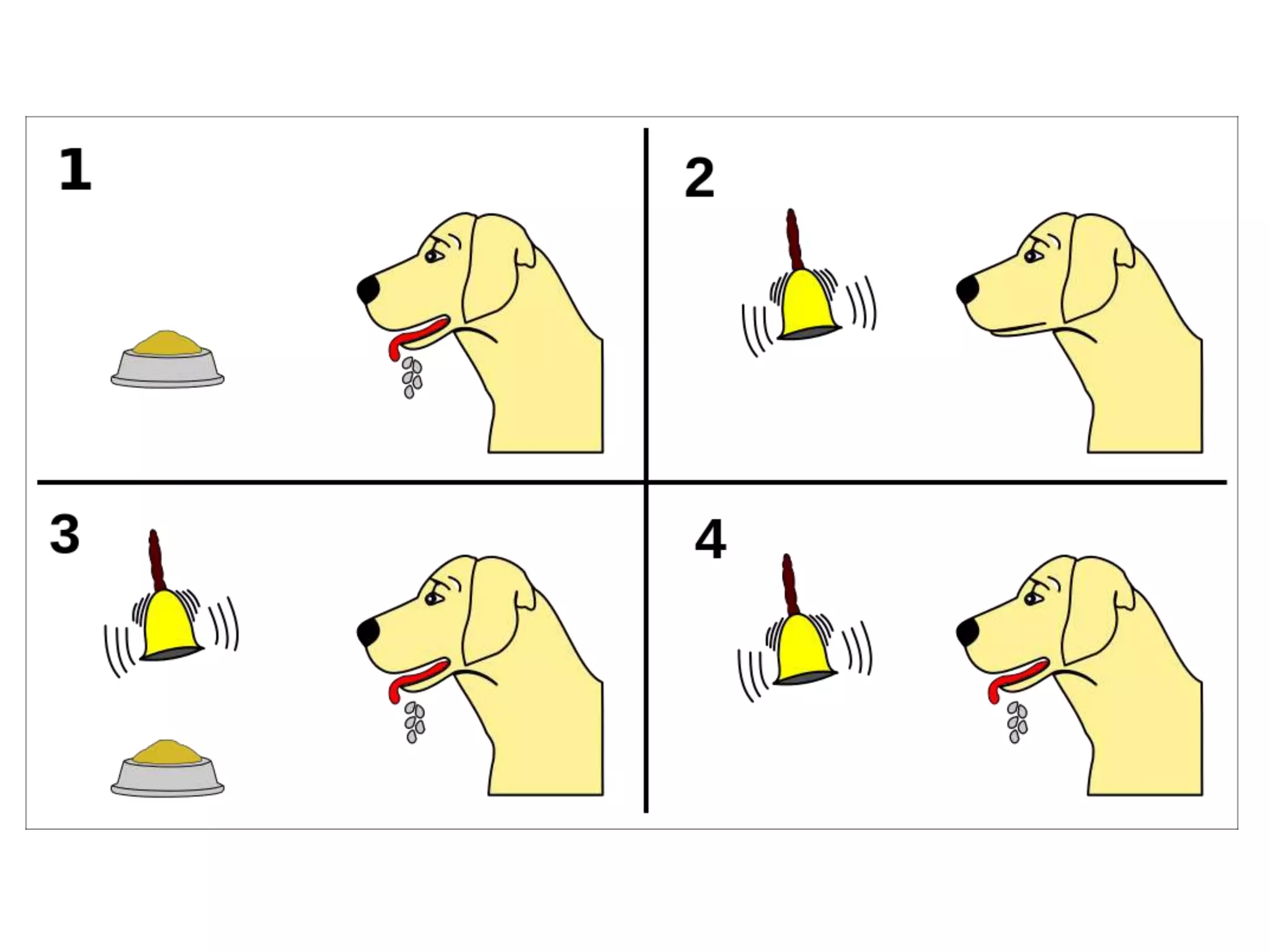
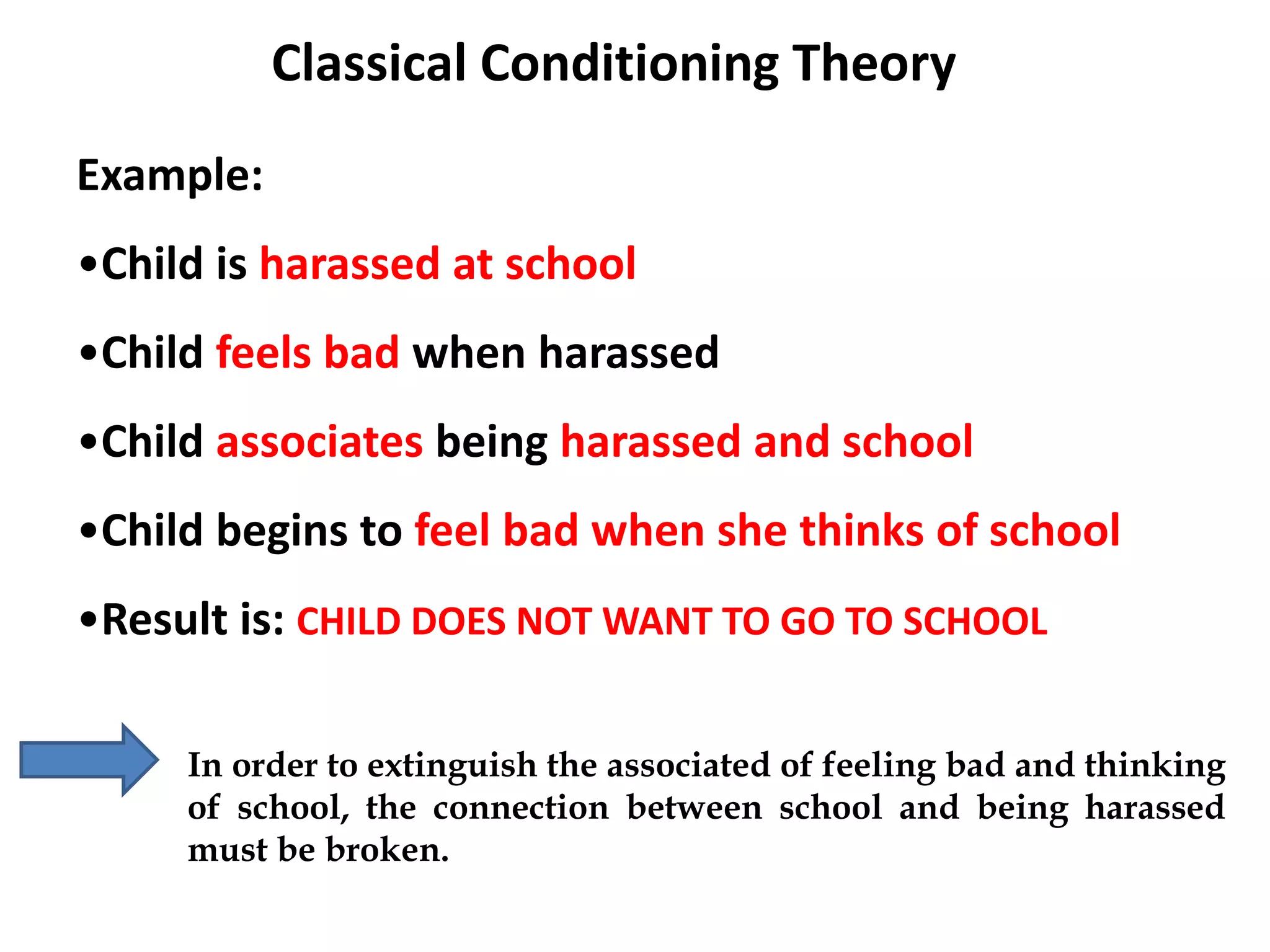
Behaviorism is a learning theory based on the idea that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning. It focuses on observable behaviors and interactions between stimuli and responses. The three major behaviorist learning theories are:
1. Contiguity theory - any stimulus and response connected in time and space will form an association.
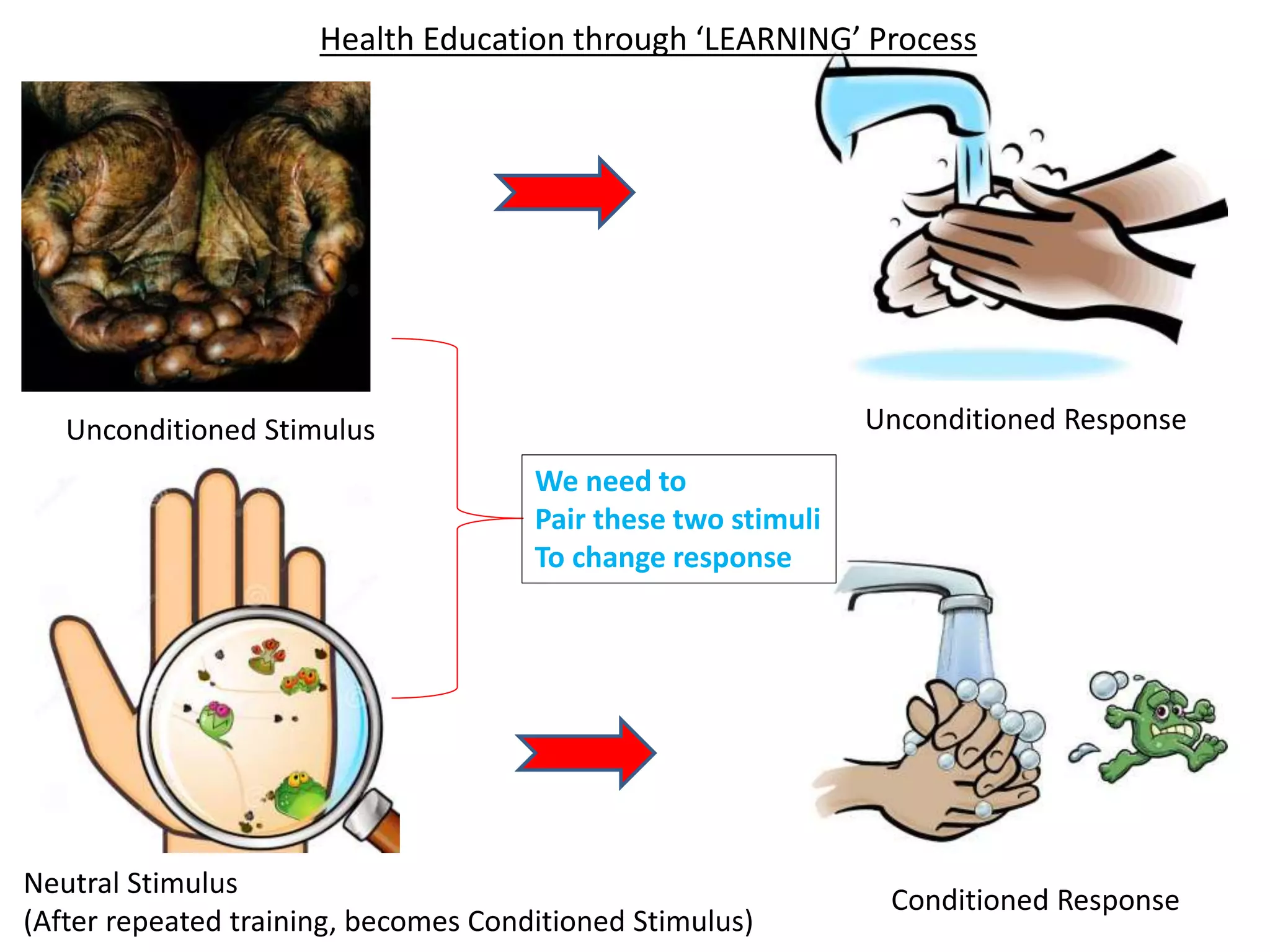
2. Classical conditioning - involuntary learned responses, exemplified by Pavlov's dog experiment.
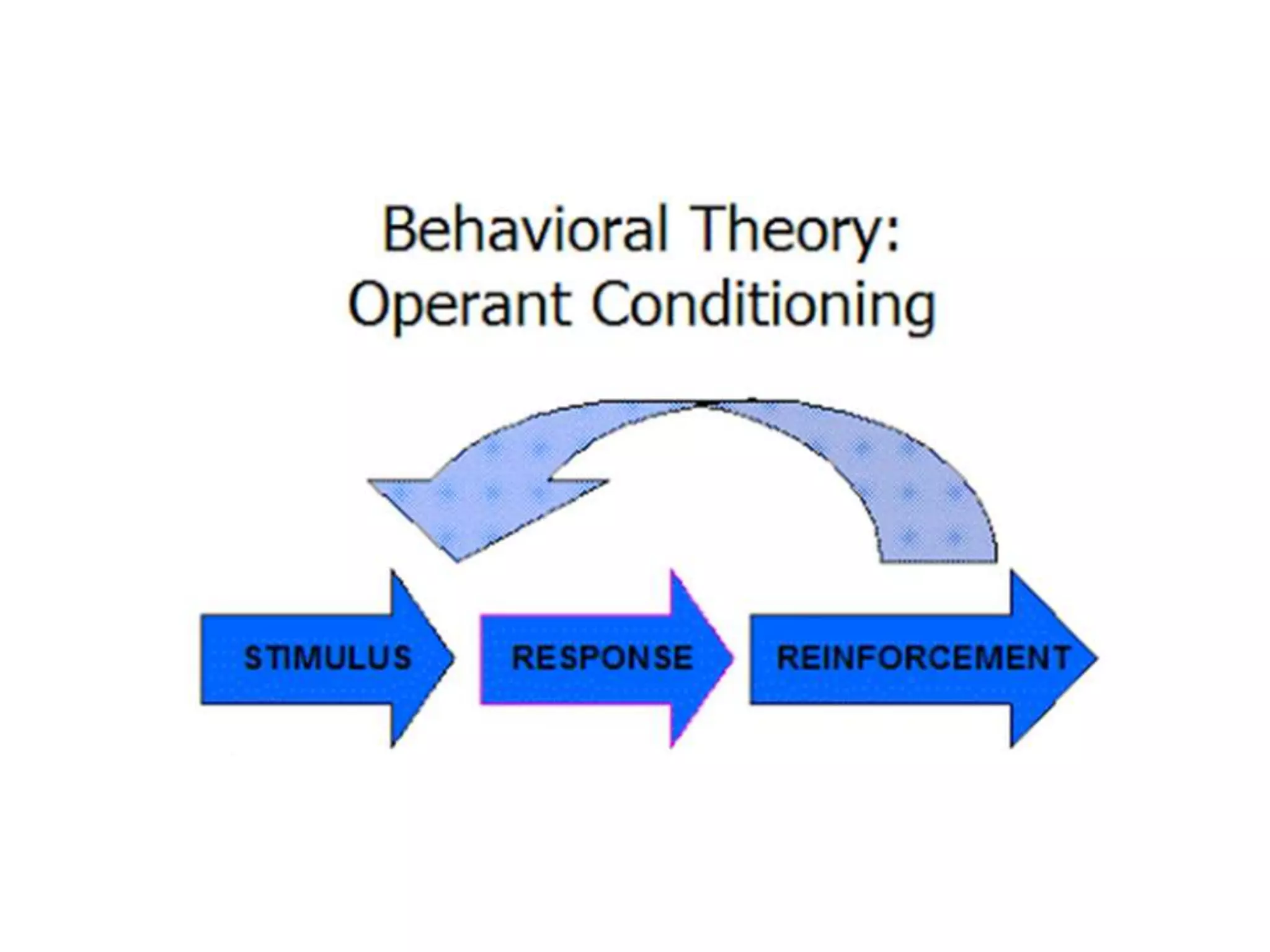
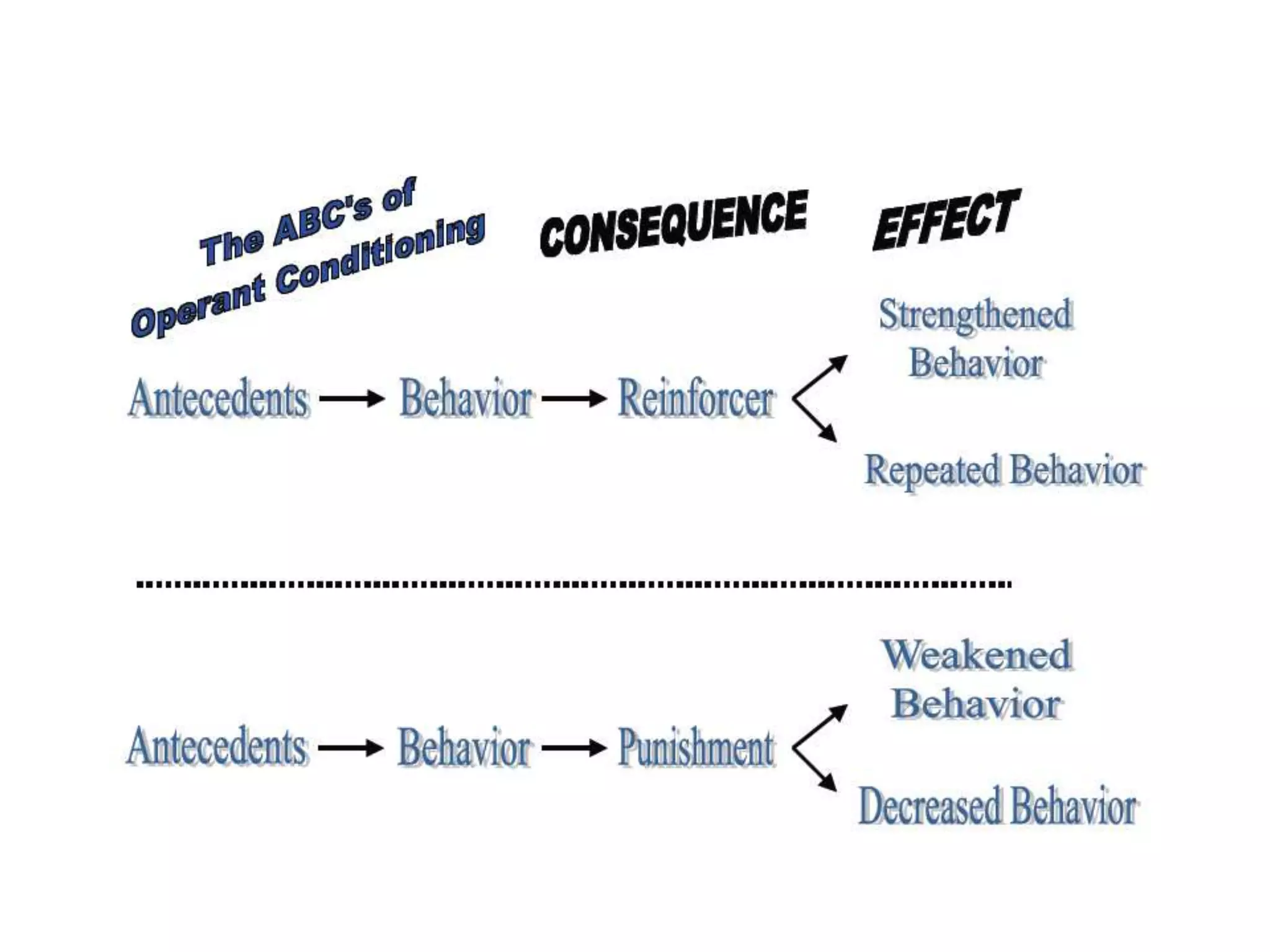
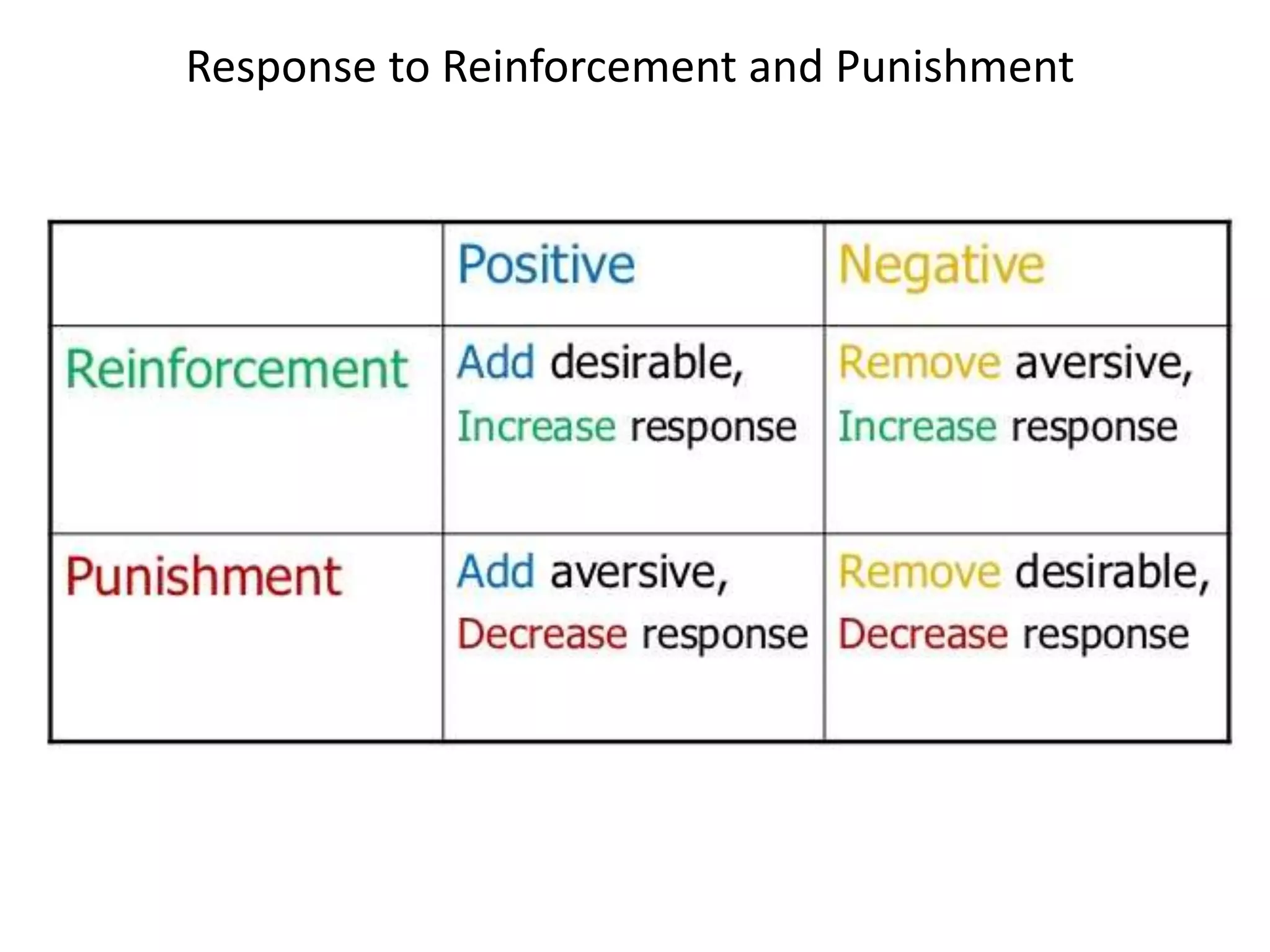
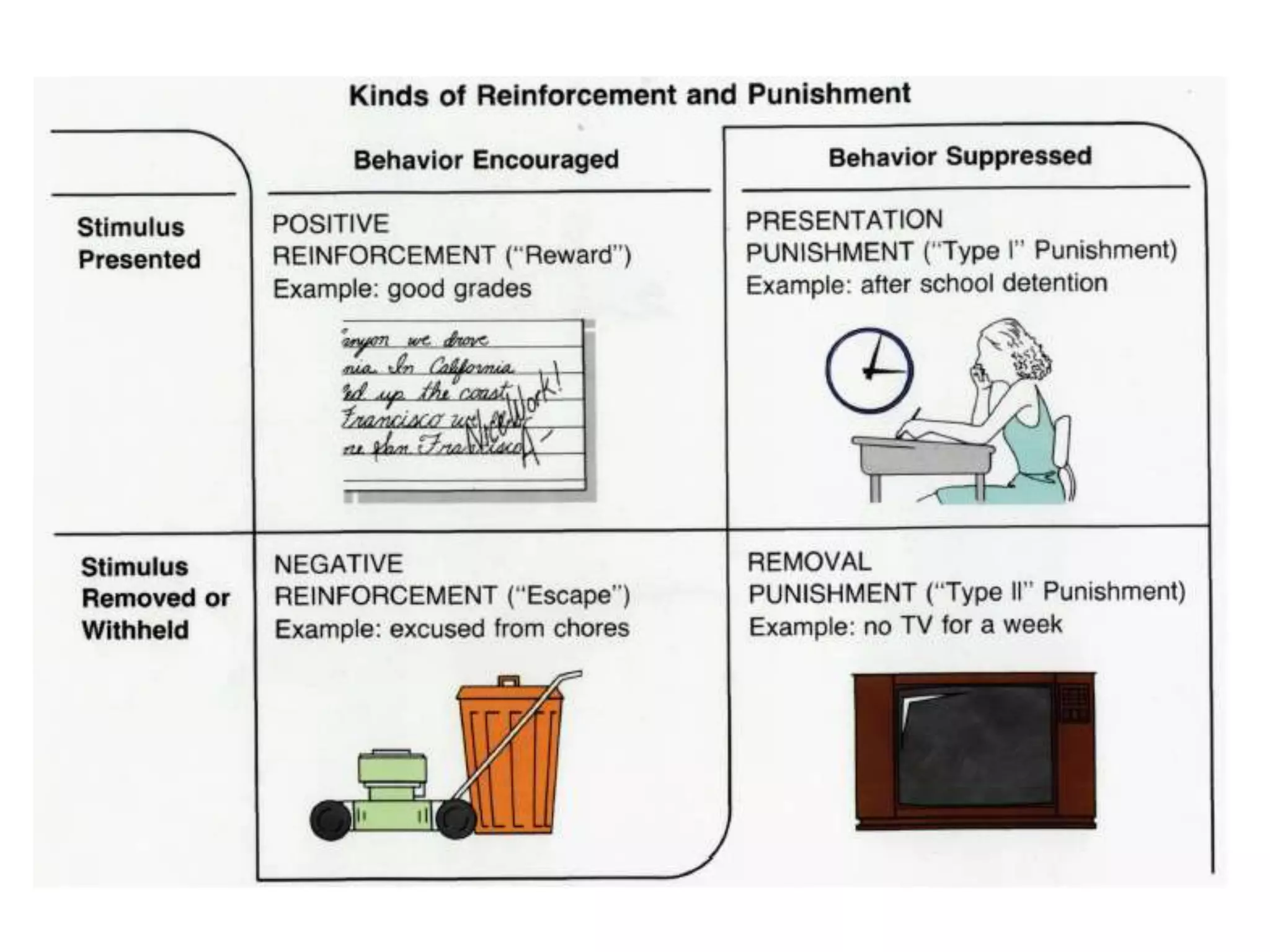
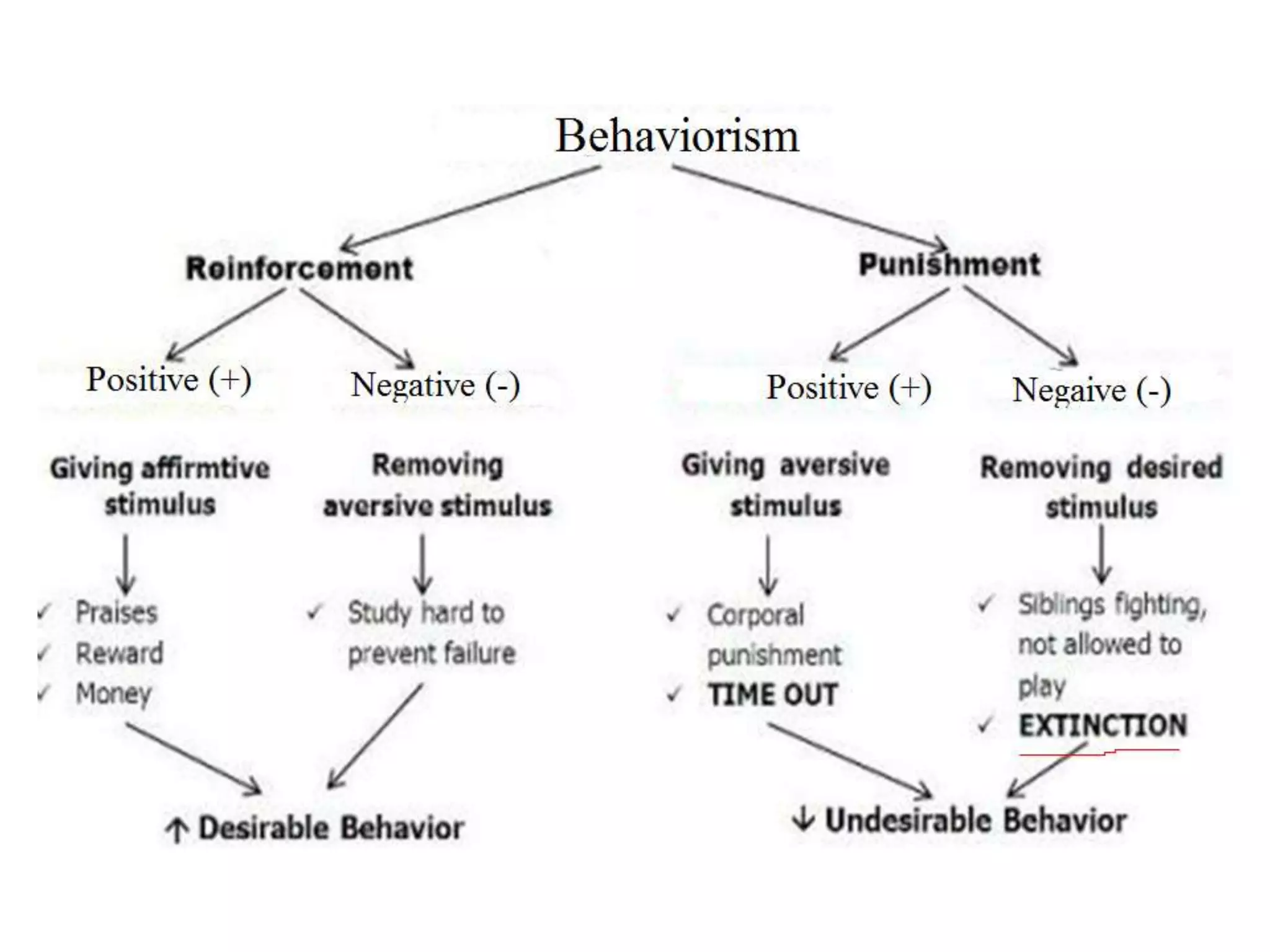
3. Operant conditioning - voluntary behaviors are shaped by consequences like reinforcement and punishment.
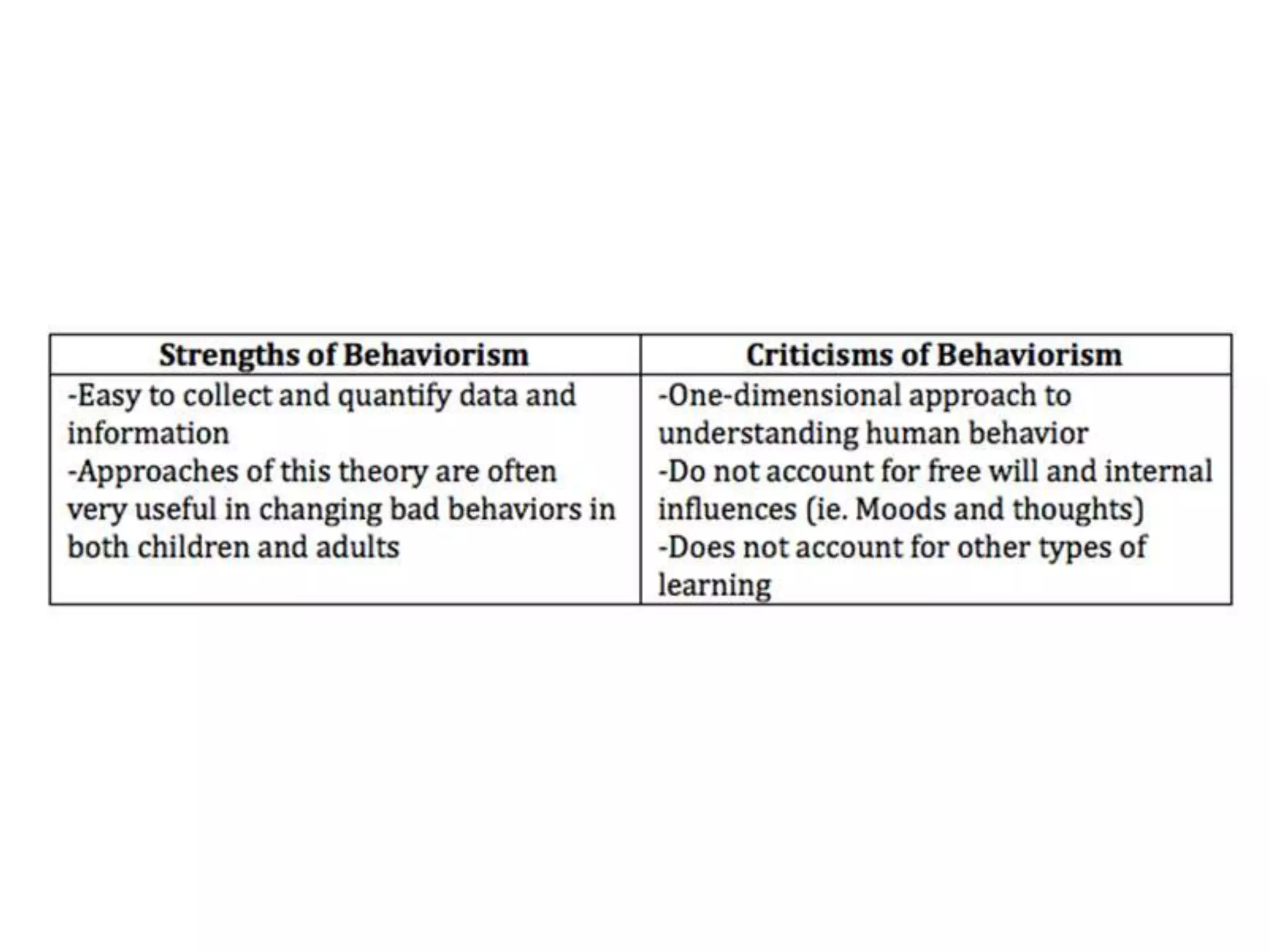
Behaviorism was influential in education, emphasizing reinforcement, punishment, and a structured teacher-centered approach, but it was criticized for being too reductionist and not accounting for internal cognitive processes.