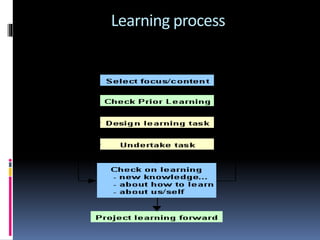
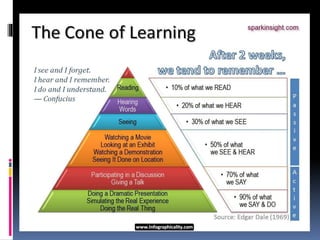
The document discusses meaningful learning and how it can be facilitated through various approaches. Meaningful learning refers to fully understanding knowledge and how it relates to other information. It requires active engagement and constructing or reconstructing meanings by integrating new knowledge with prior knowledge. Characteristics of meaningful learning include it being synergetic, interrelated, interactive, and interdependent. Approaches that can foster meaningful learning discussed in the document include active, constructive, intentional, authentic, and cooperative learning. Technology can also facilitate meaningful learning by allowing students to represent their own knowledge and providing rich flexible media for learning.