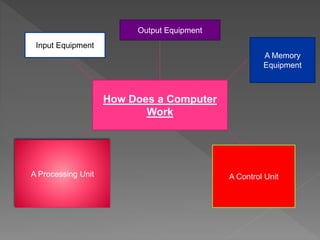
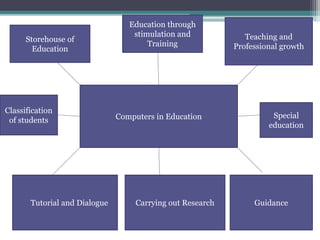
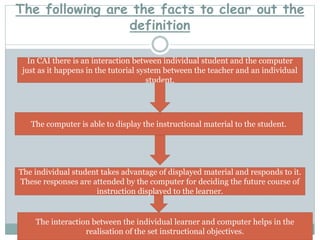
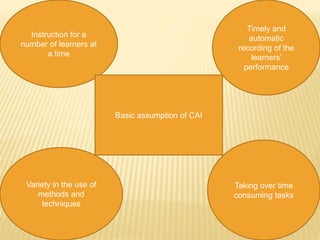
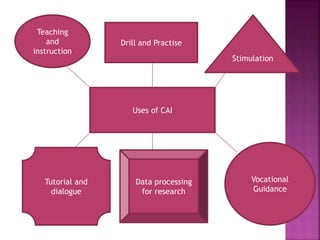
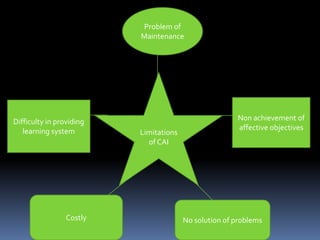
The document presents an overview of computer-assisted instruction (CAI), emphasizing its role in facilitating individualized learning through interaction between students and computers. It details the components of computers, types of CAI, and their applications in education, while also acknowledging the limitations and concerns surrounding their implementation. Ultimately, it concludes that while CAI has advantages in teaching and learning, the unique qualities of human teachers remain irreplaceable.