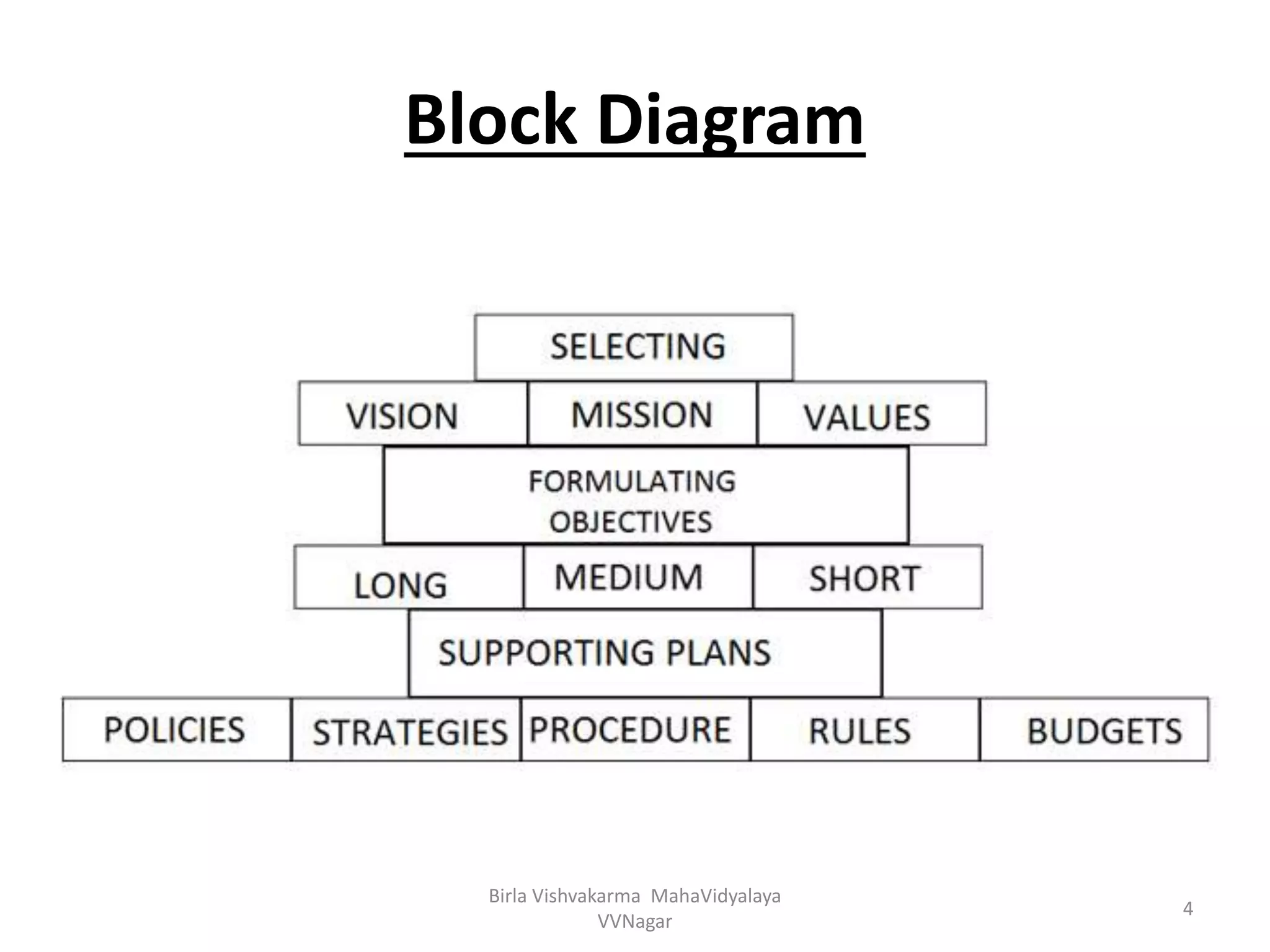
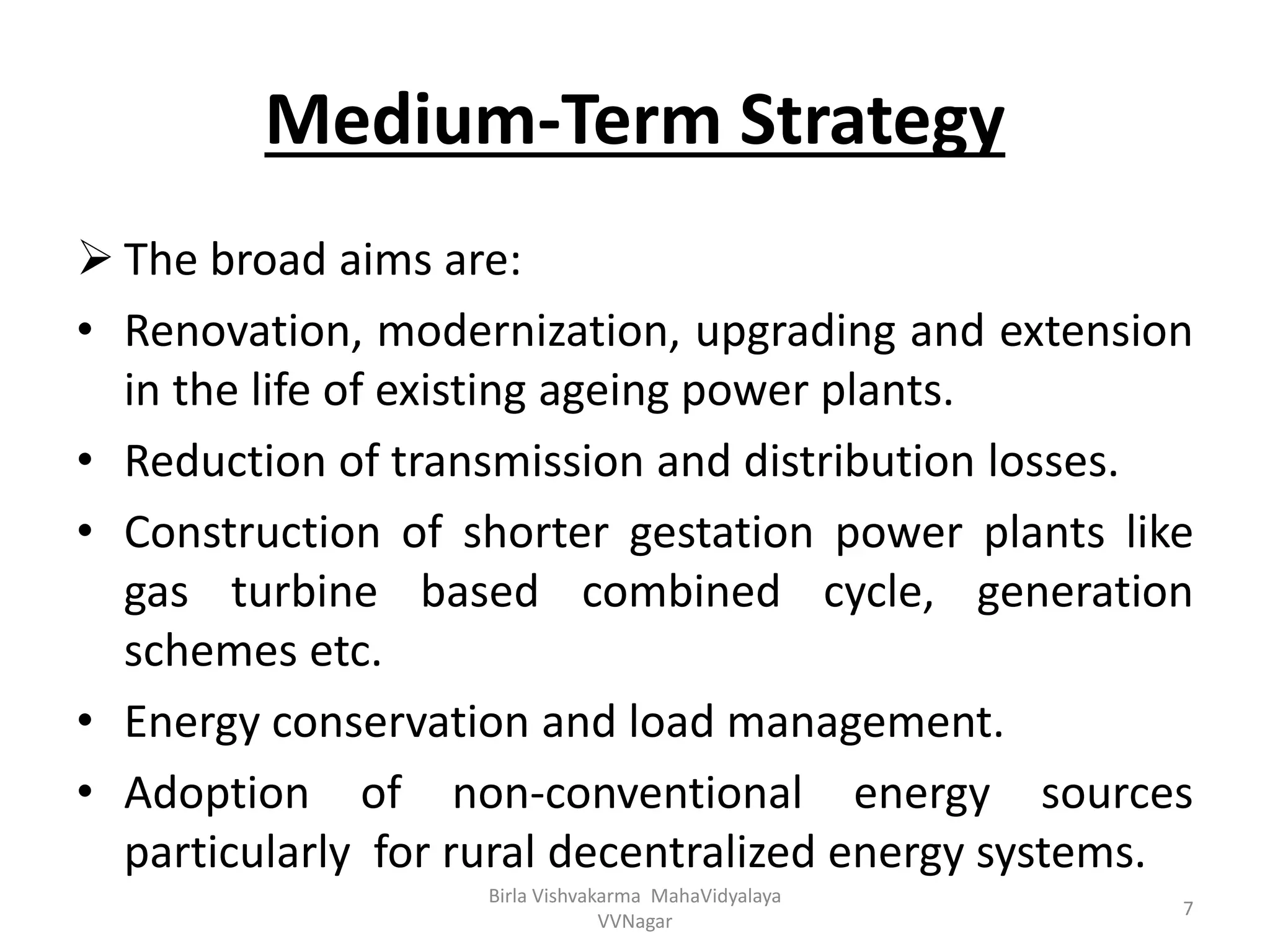
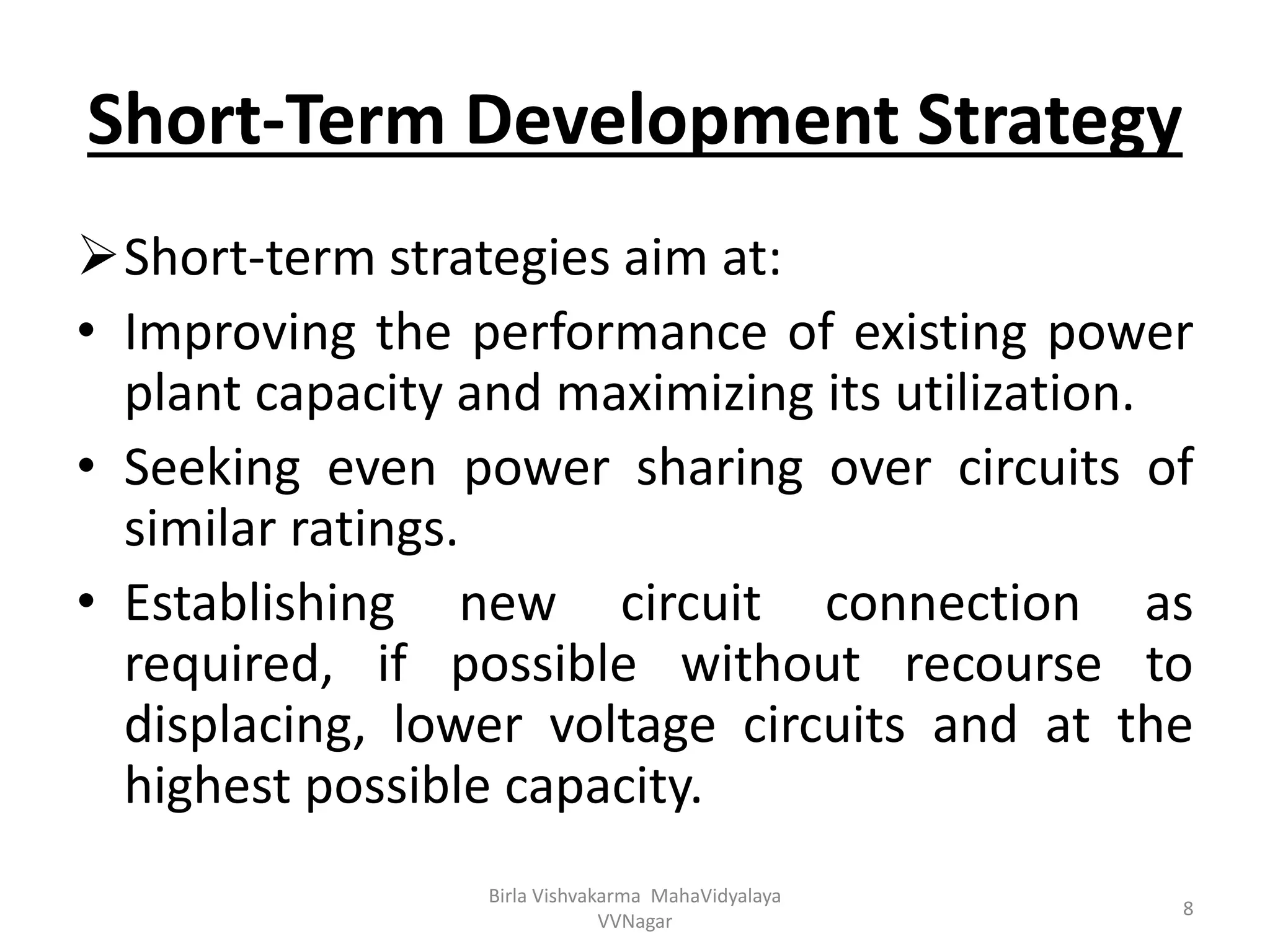
The document outlines the components and steps of power system planning using a block diagram approach. It discusses identifying problems and opportunities, setting goals and objectives, developing possible solutions, selecting the best solution, and reviewing performance. It also describes the long-term, medium-term, and short-term strategies involved, including capacity augmentation, reducing losses, construction of quicker projects, adoption of renewable energy, improving existing plant performance, and computerizing work management.