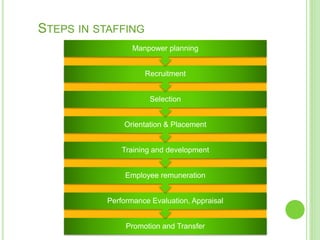
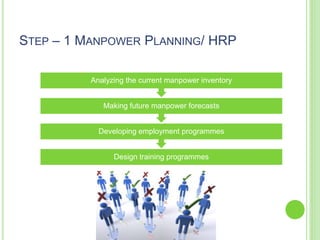
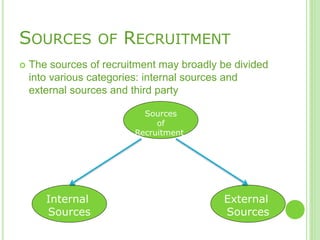
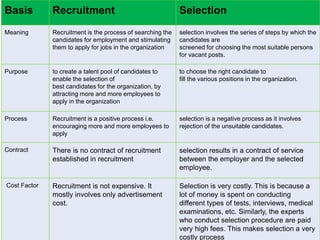
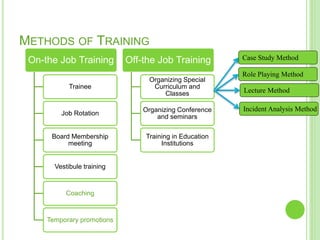
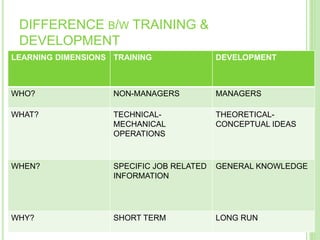
The document outlines the staffing process, emphasizing the importance of acquiring, developing, and maintaining human resources effectively. It details the steps involved in staffing, including manpower planning, recruitment, selection, orientation, training, compensation, and performance evaluation. Additionally, it highlights the significance of matching the right individuals to jobs to enhance organizational productivity and employee satisfaction.