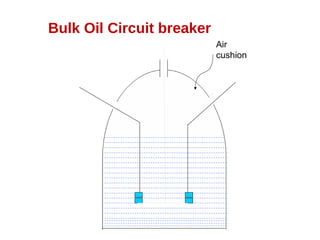
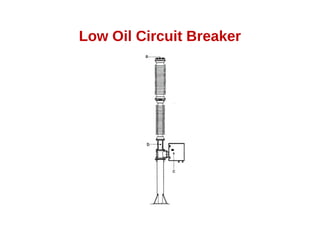
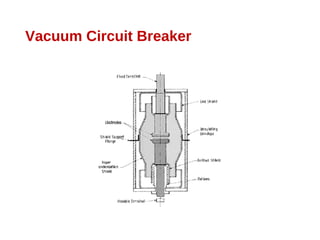
A circuit breaker is a device that breaks an electrical circuit automatically or manually under normal, full load, or short circuit conditions. It contains two contacts that remain closed during normal operation. When a fault occurs, a trip coil is energized separating the contacts. An arc is struck during contact separation, allowing current to continue briefly. Circuit breakers must extinguish the arc quickly. Different types of circuit breakers use various methods and mediums like oil, air, vacuum, or sulfur hexafluoride gas to rapidly extinguish the arc. Circuit breakers are classified and selected based on the voltage level and intended application.