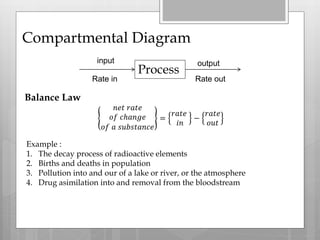
1. Compartmental models divide a system into compartments and model the flow of substances between compartments. Examples include radioactive decay, population growth, pollution in lakes, and drug assimilation.
2. The rate of change of a substance in a compartment equals the inflow rate minus the outflow rate. This is modeled using differential equations. Exponential decay models radioactive elements and is used for radiometric dating.
3. Drug assimilation can be modeled with compartments for the GI tract and bloodstream. The rate of change in each depends on the inflow and outflow between compartments. This models how drugs enter the bloodstream and are removed.