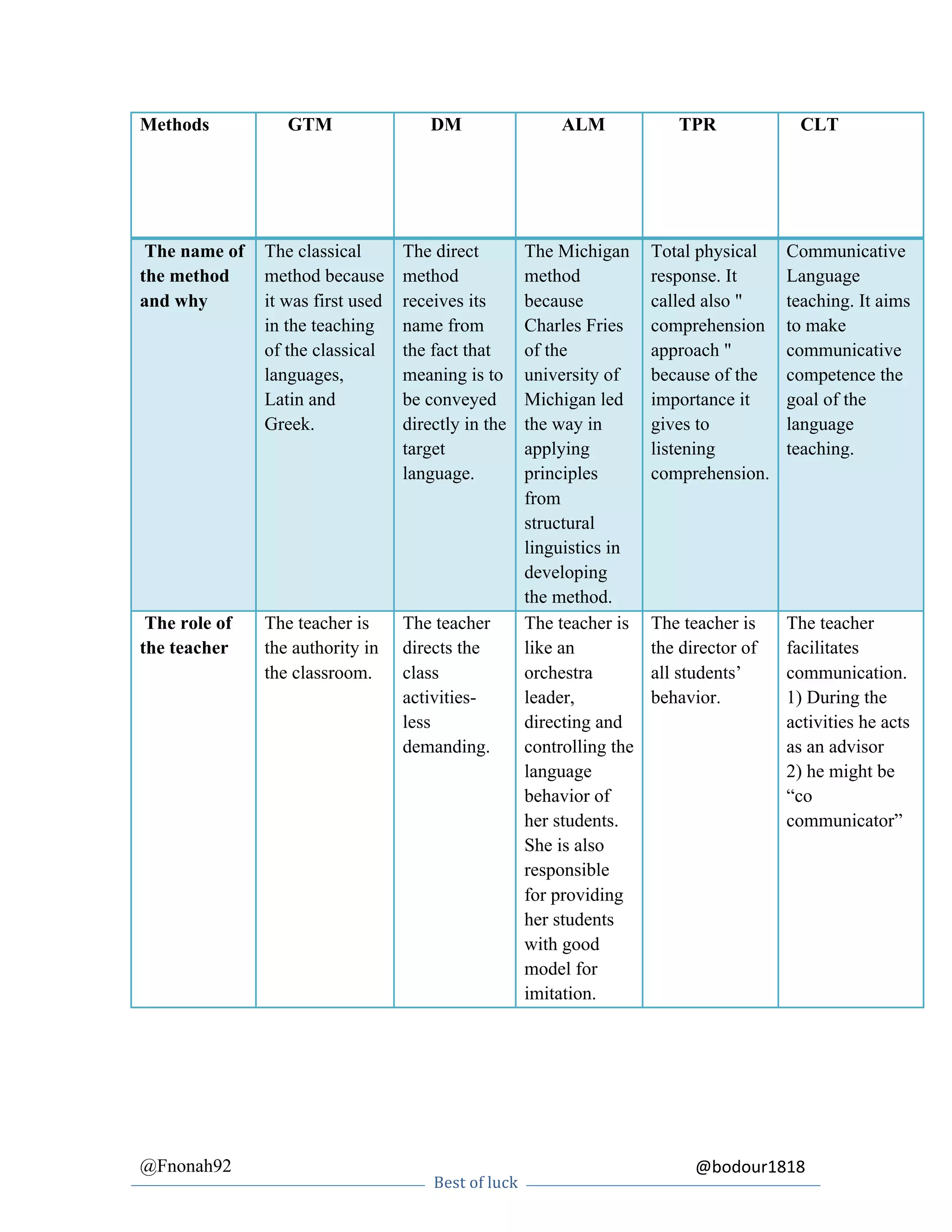
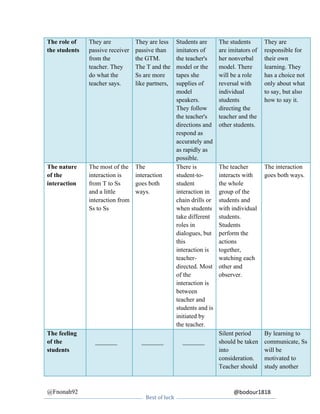
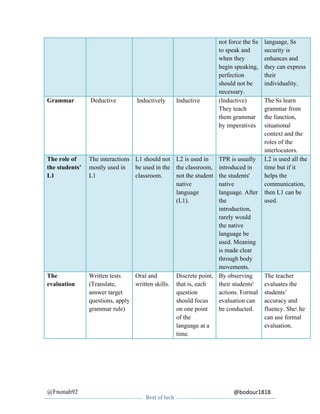
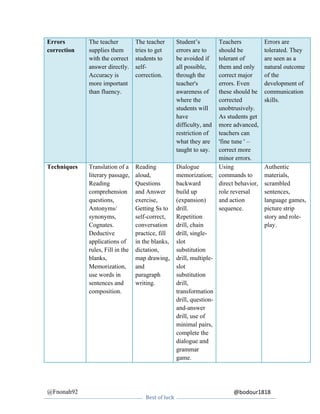
This document summarizes and compares several language teaching methods: the Grammar Translation Method, Direct Method, Michigan Method, Total Physical Response, and Communicative Language Teaching. For each method it provides details on the name and origins, the role of the teacher and students, the nature of interaction, how grammar is taught, the use of students' native language, error correction approach, evaluation techniques, and classroom techniques/activities.