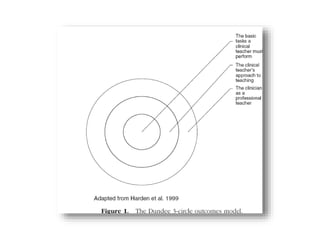
This document discusses clinical physiotherapy education and teaching. It outlines the goal of clinical physiotherapy education as producing physiotherapists that teachers would want if they were sick patients. It describes the clinical environment, focus on patients, problem diagnosis and management. It also discusses challenges of clinical teaching like time constraints and engaging multiple levels of learners. Skills of excellent clinical teachers are outlined as well as challenges of inpatient and outpatient teaching. Different learning styles, clinical teaching models, problems and dos/don'ts of clinical teaching are also summarized.