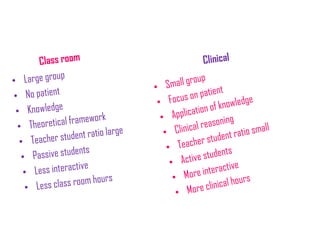
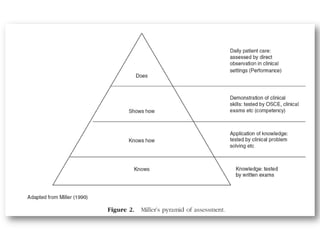
This document discusses clinical physiotherapy education and teaching. It outlines several key challenges of clinical teaching including time constraints, unpredictable situations, engaging multiple levels of learners, and patient-related barriers. Excellent clinical teachers demonstrate clinical competence, clear organization, rapport building, and self-evaluation. Teaching in outpatient and inpatient settings each have their own difficulties such as brief interactions, priority of patient care, and unpredictable events. The document also reviews different learning styles, clinical teaching models, and tips for effective clinical teaching.