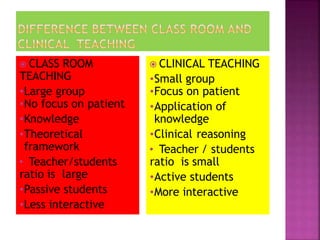
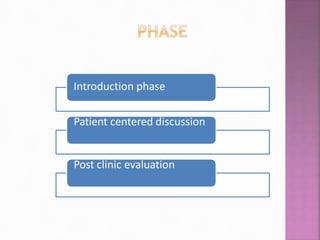
This document discusses clinical teaching in nursing education. It defines clinical teaching as individualized or group teaching of nursing students in clinical settings by nurse educators, staff, and managers. The goals of clinical teaching are to help students develop skills like critical thinking, communication, and technical proficiency so they can provide holistic, patient-centered care. Clinical teaching provides opportunities for students to apply theoretical knowledge at the bedside through methods like bedside clinics, nursing rounds, and demonstrations. This allows students to bridge the gap between theory and real-world nursing practice.