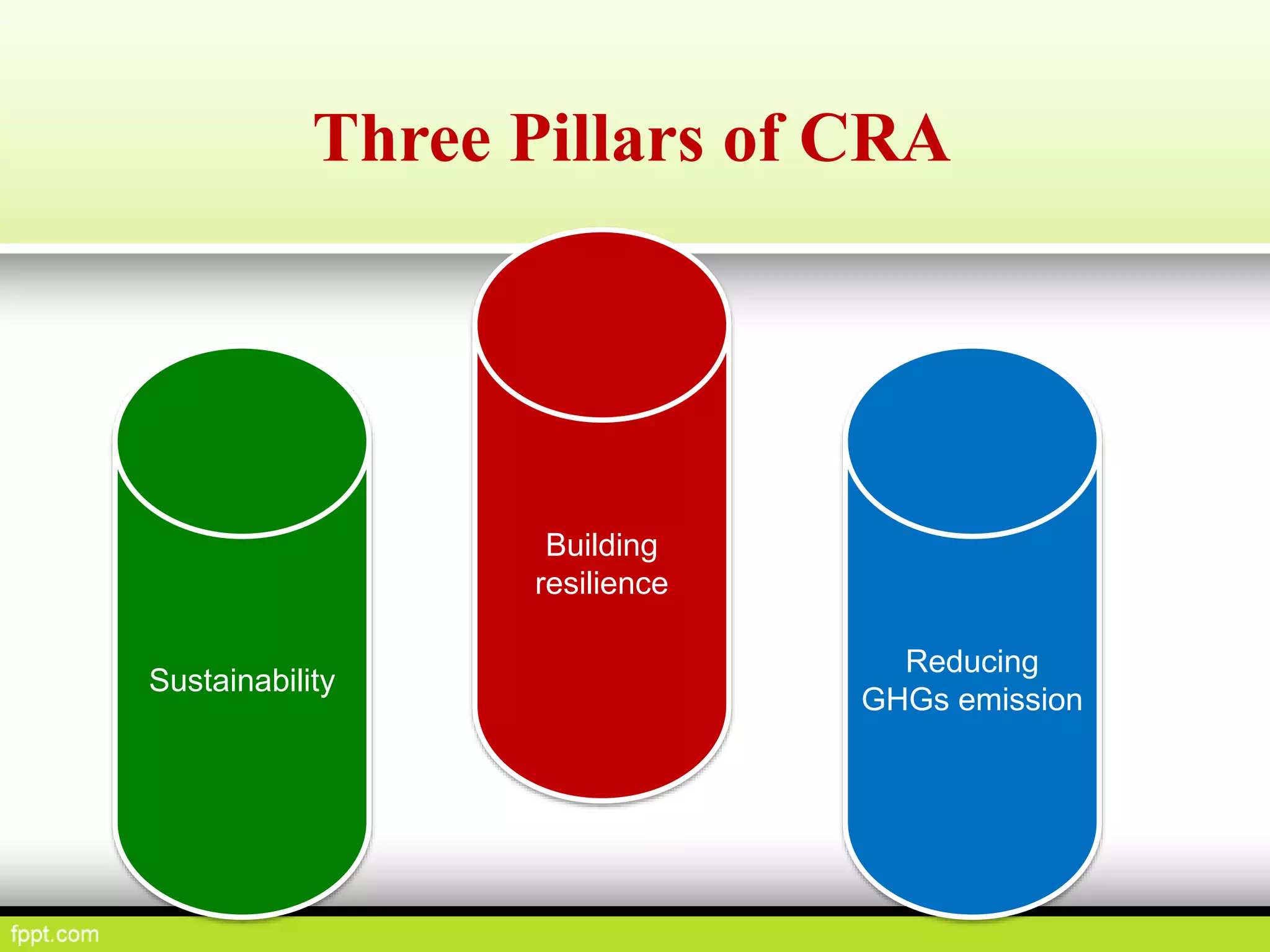
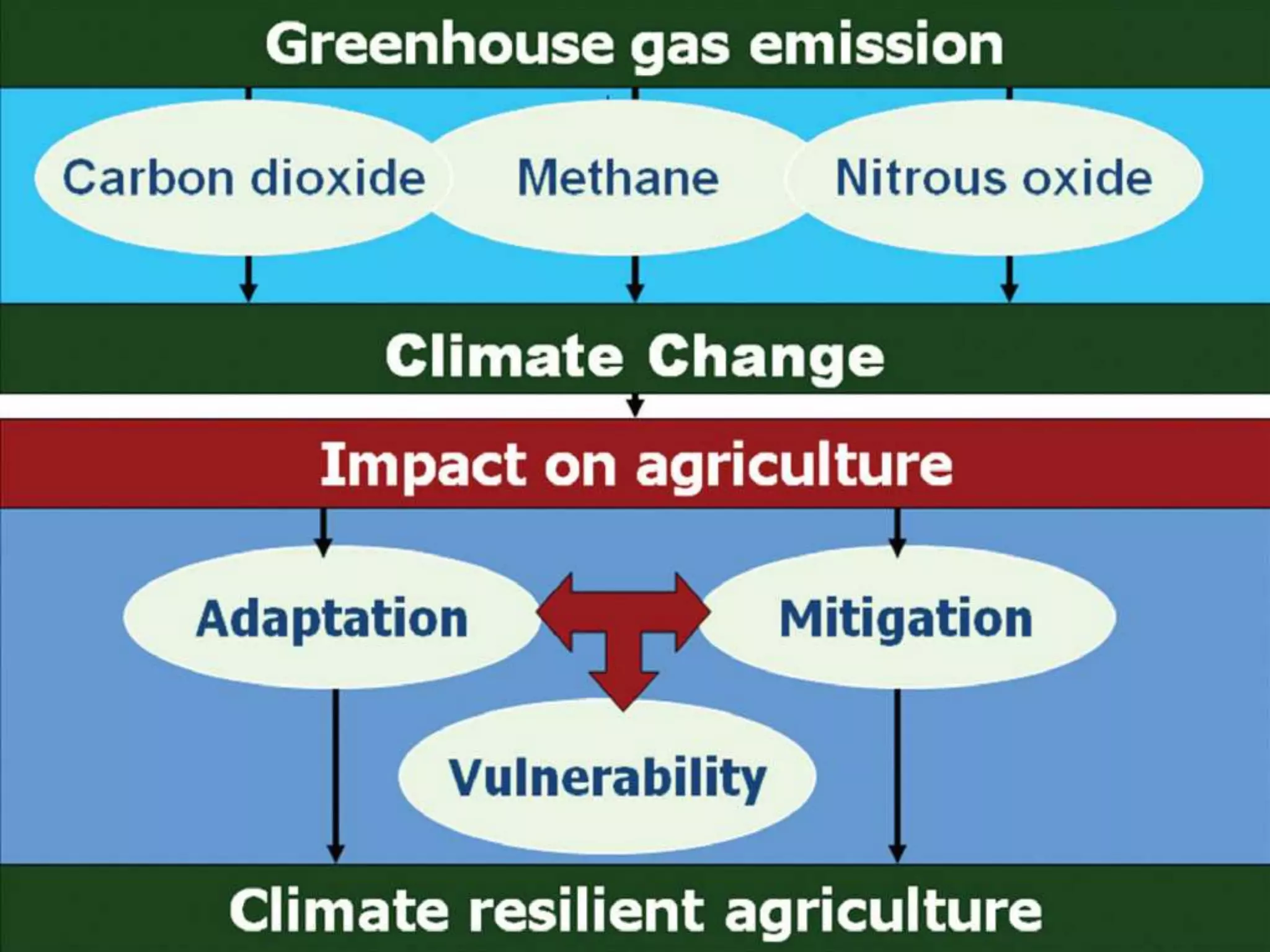
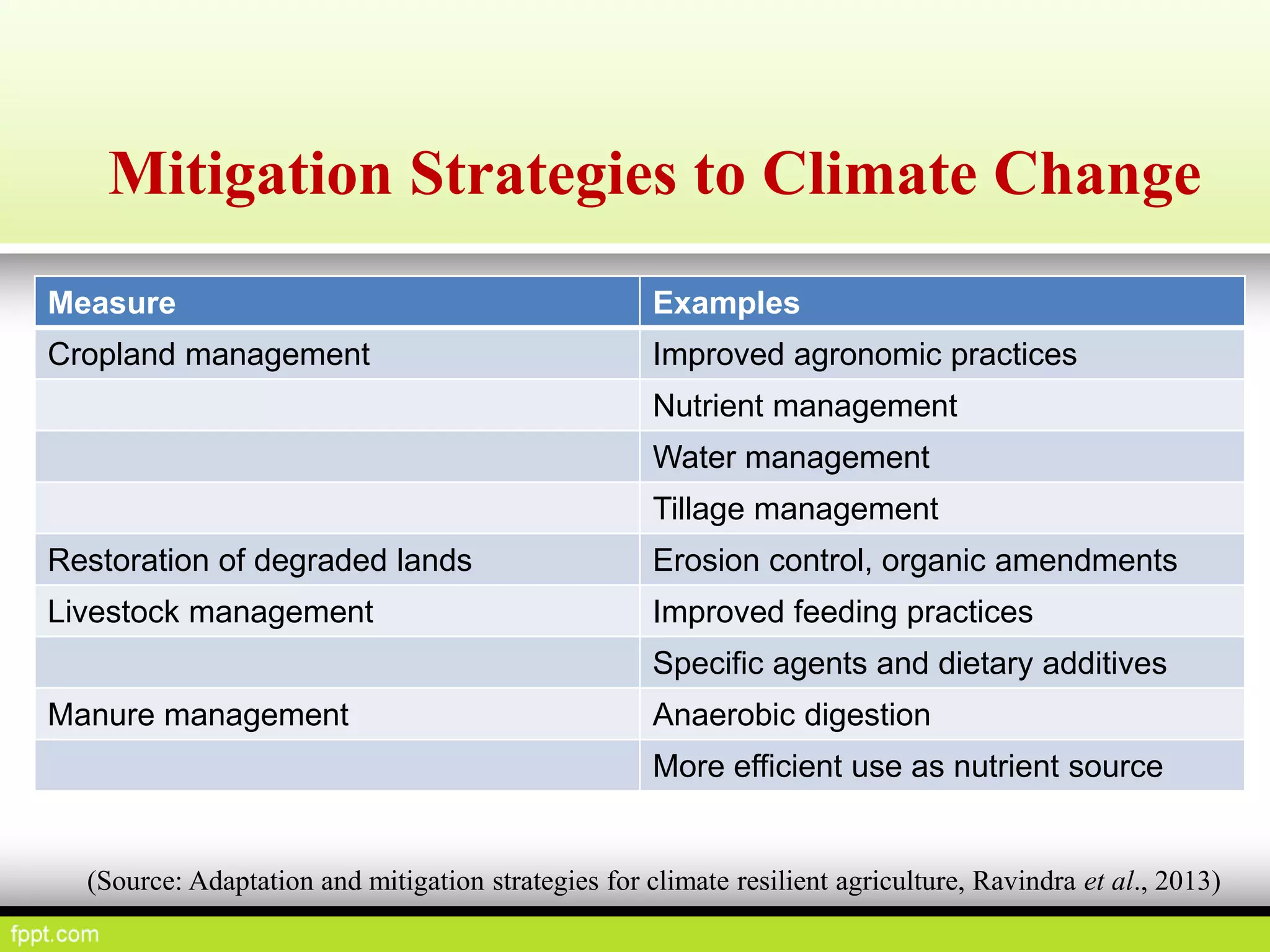
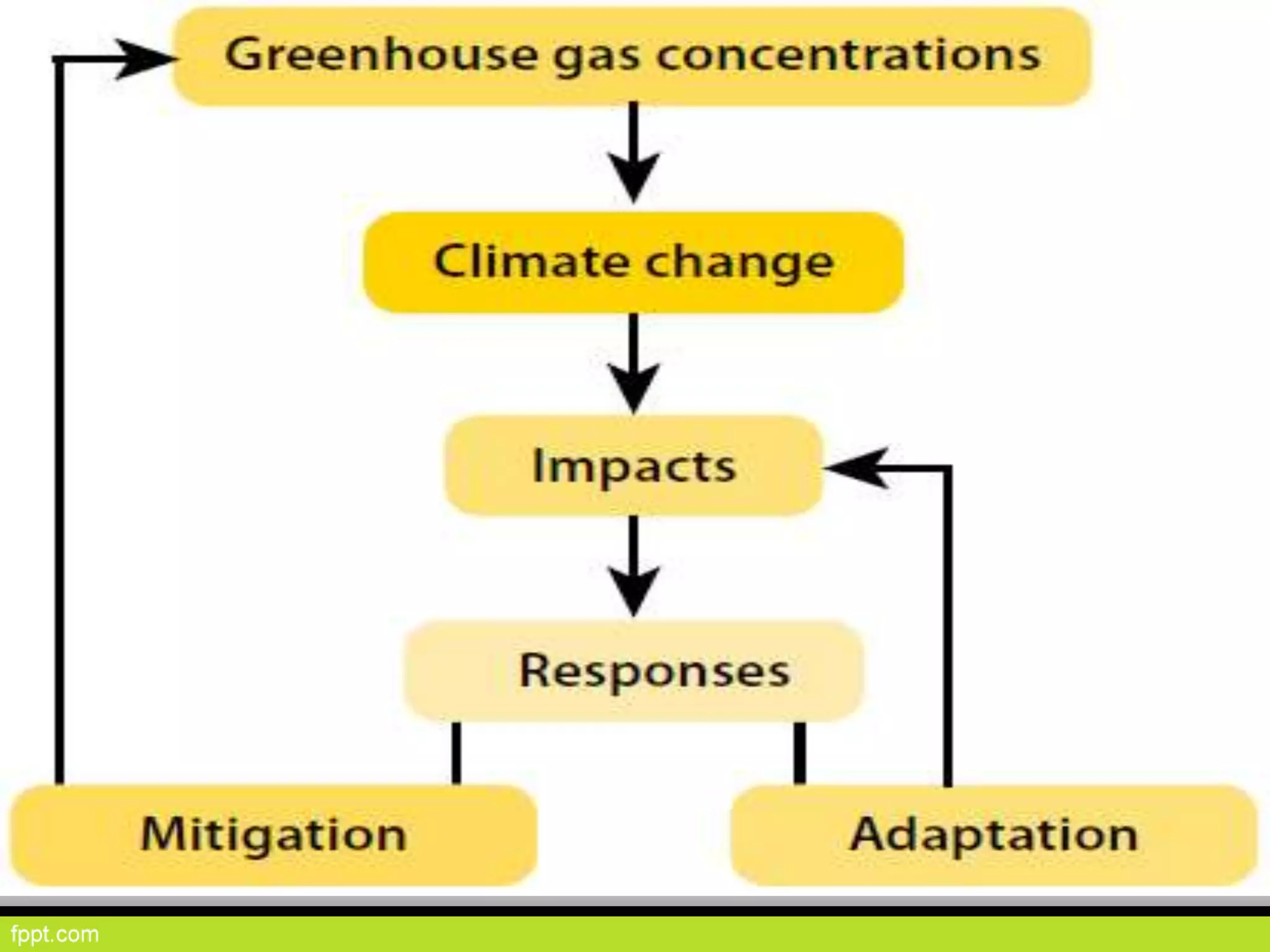
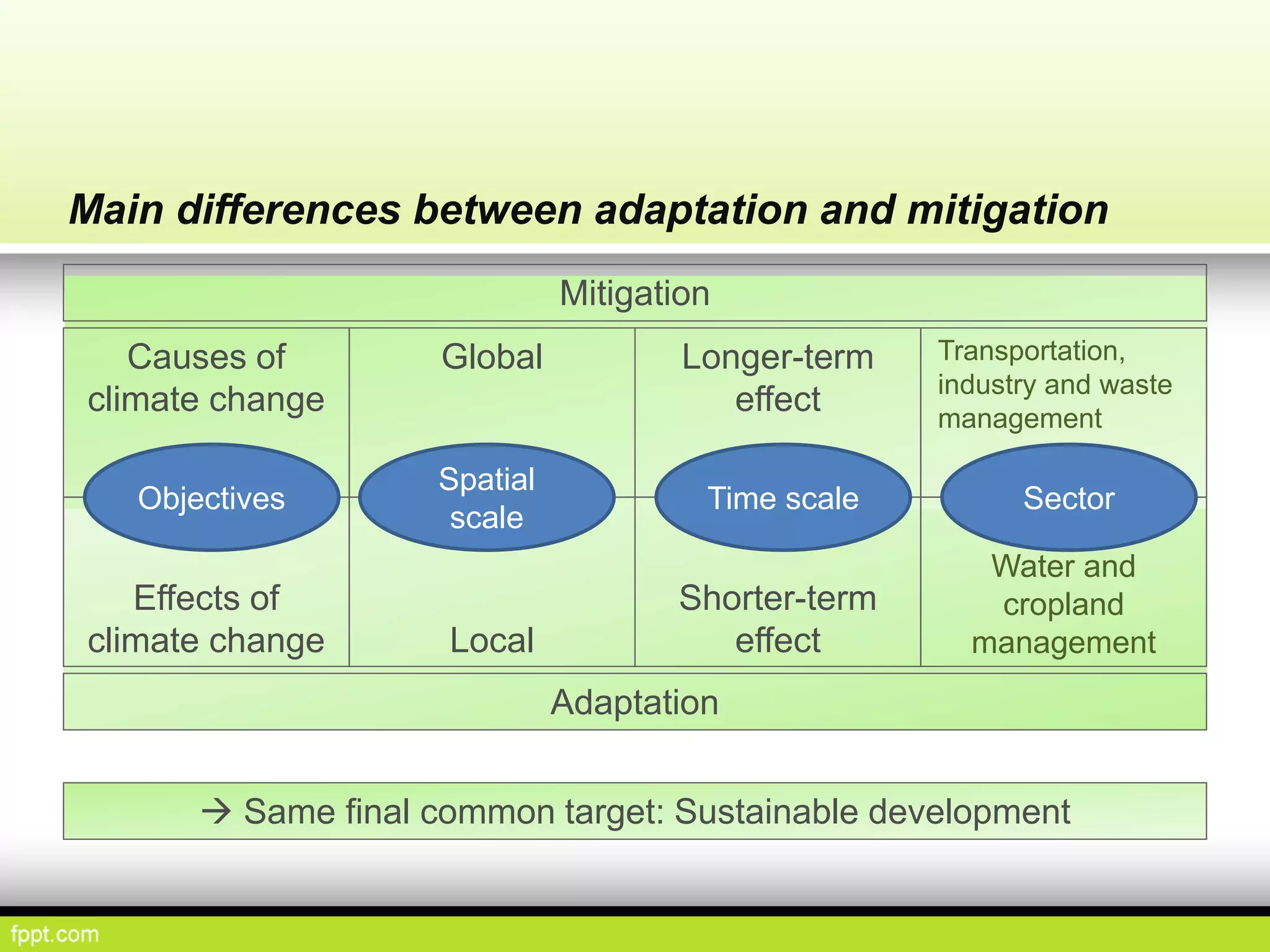
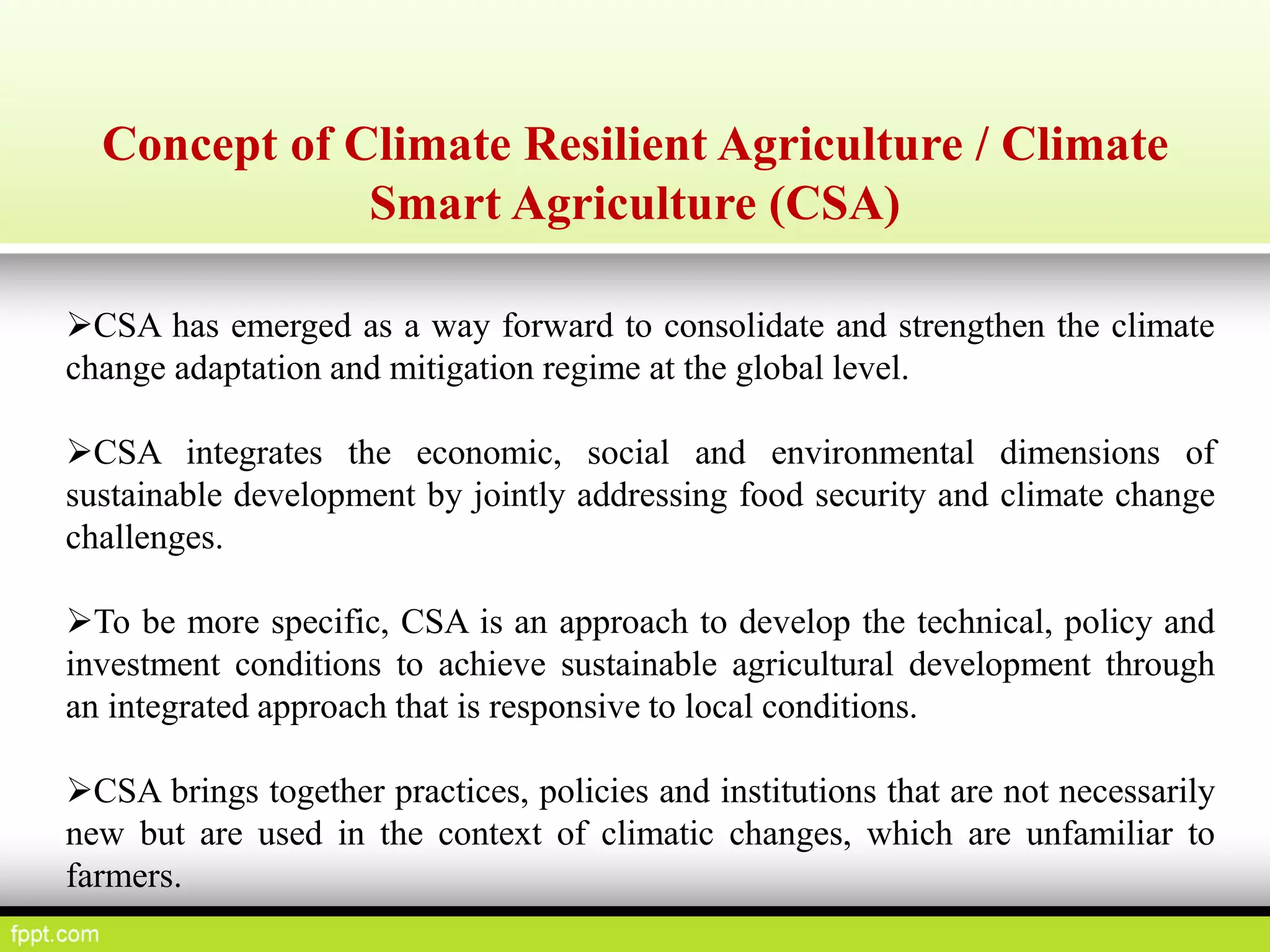
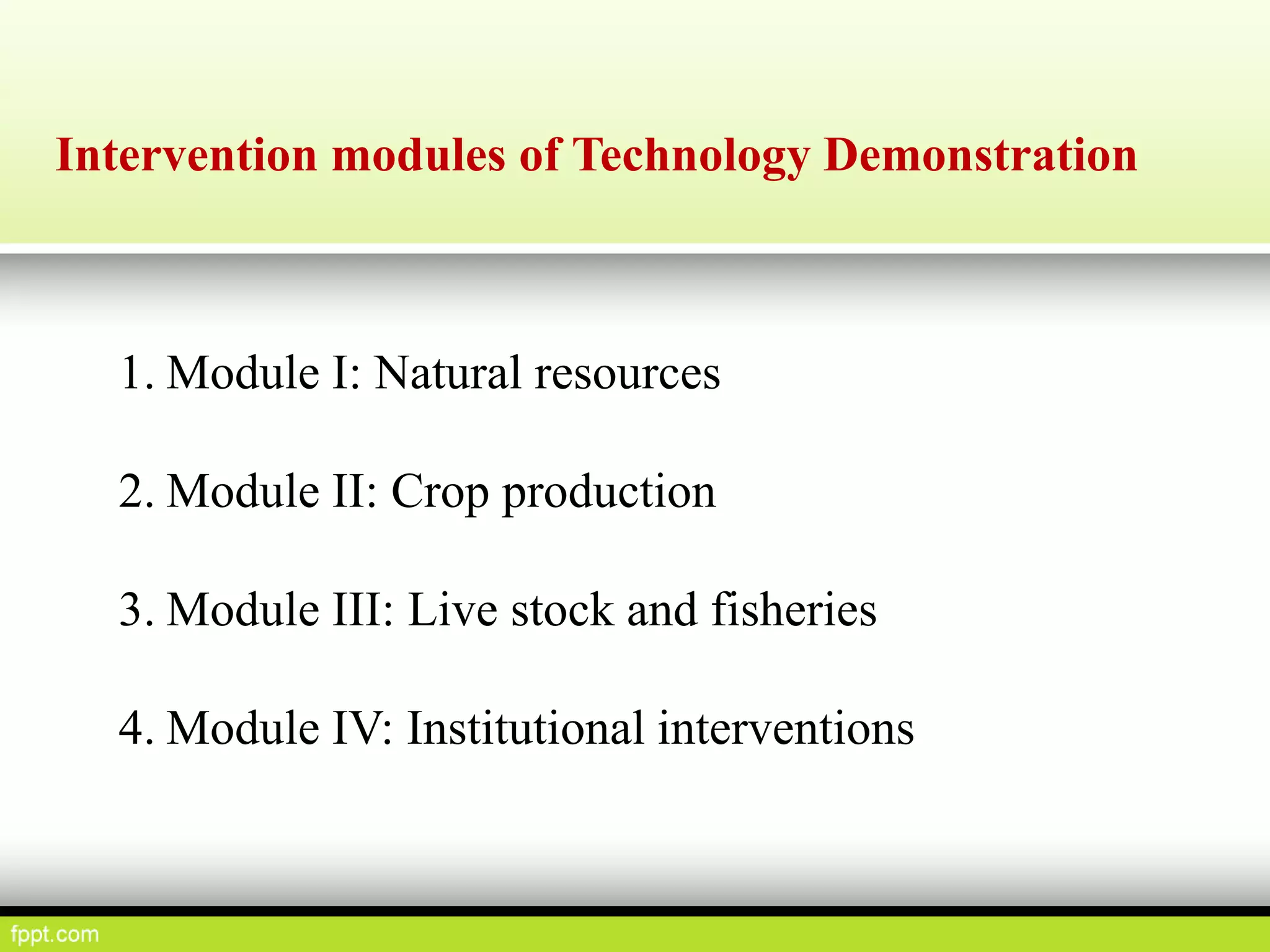
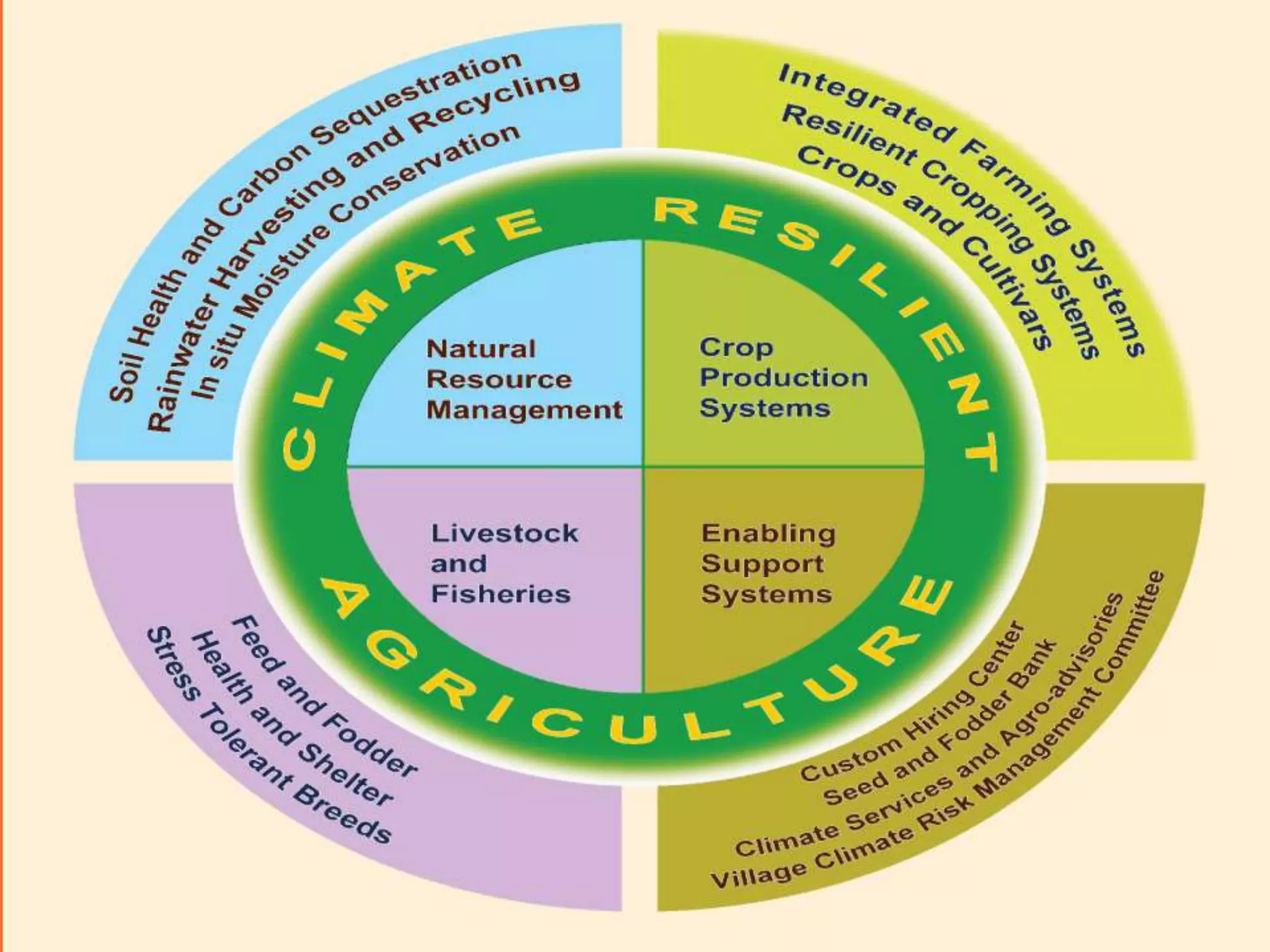
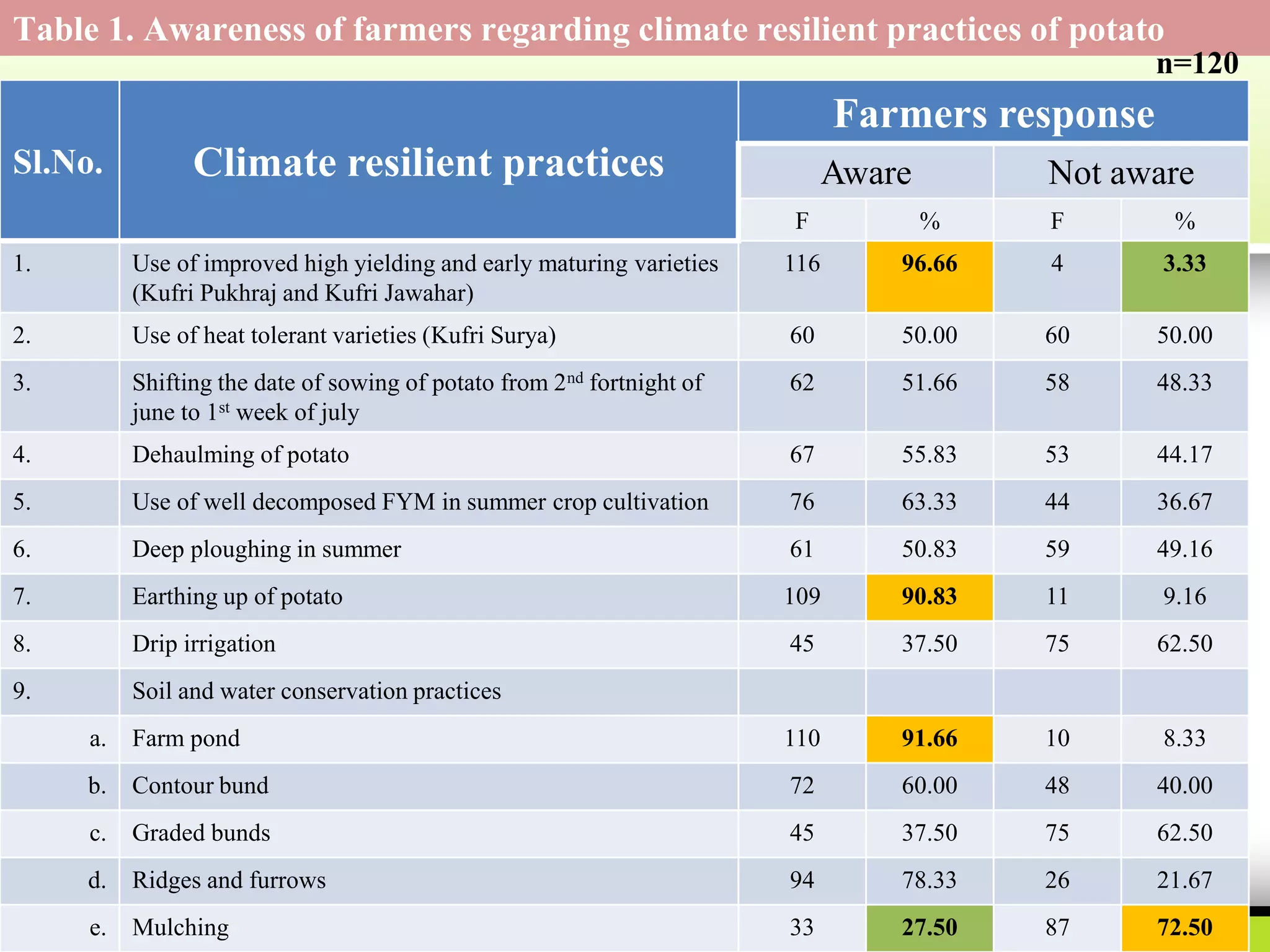
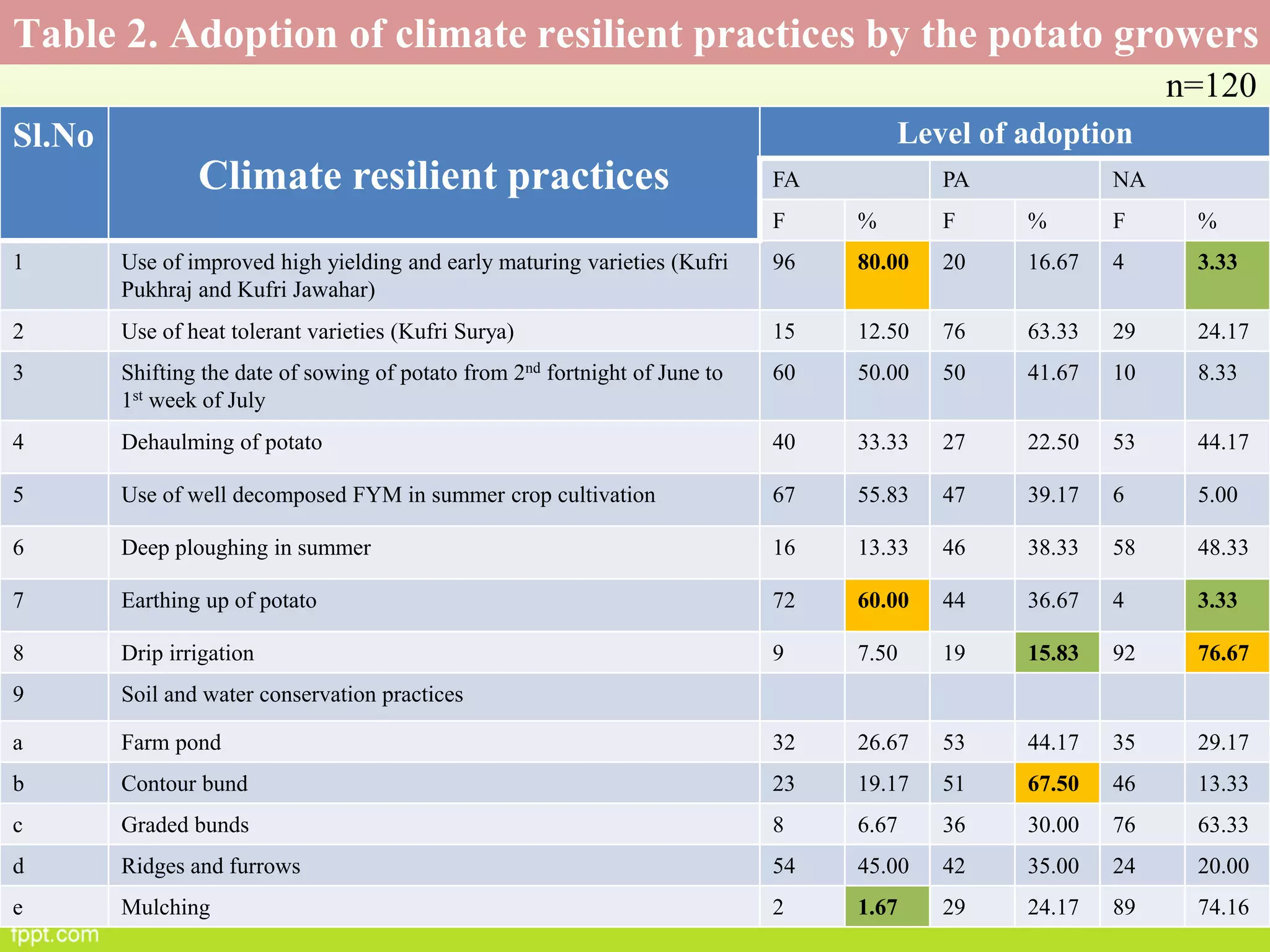
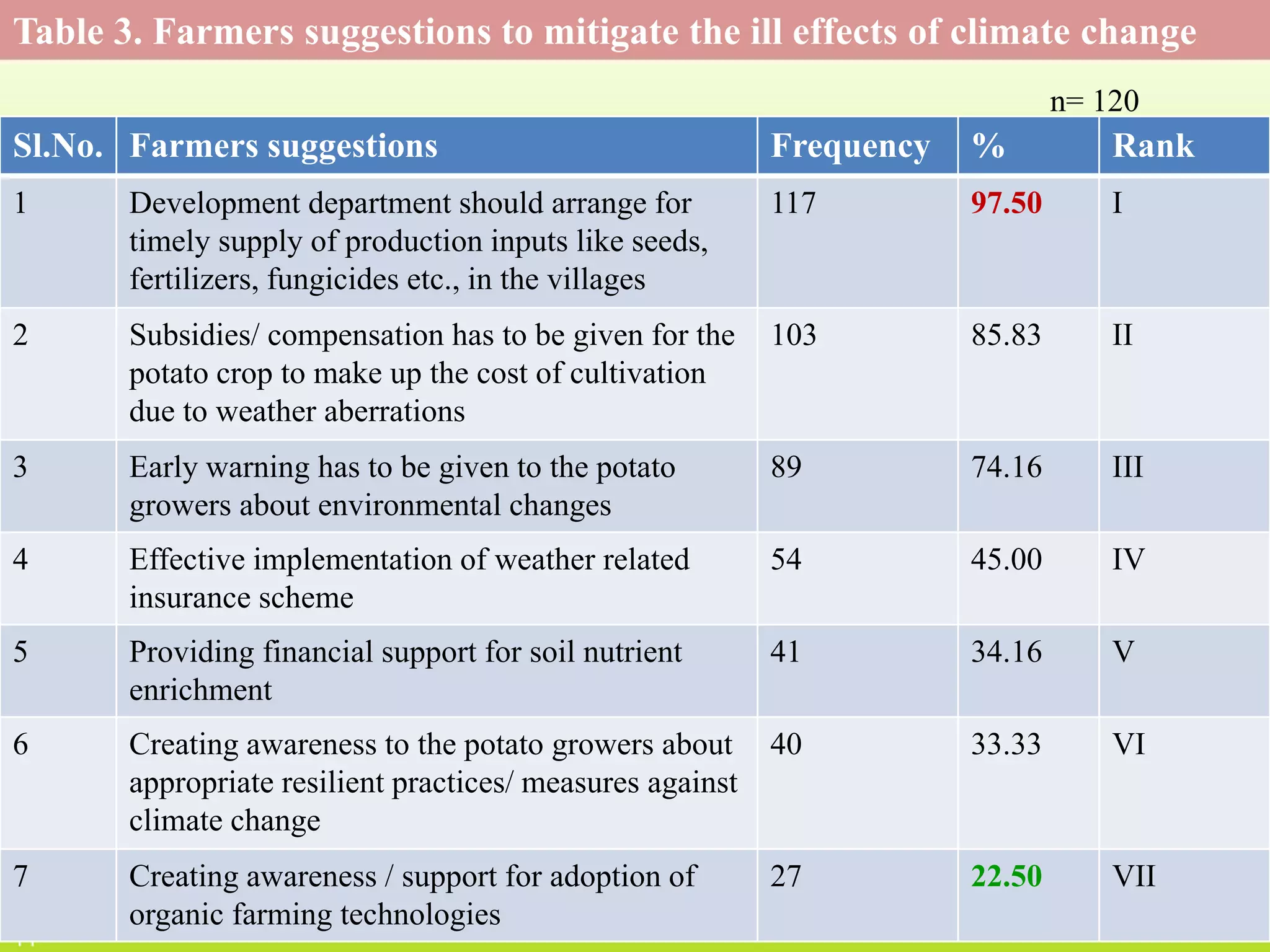
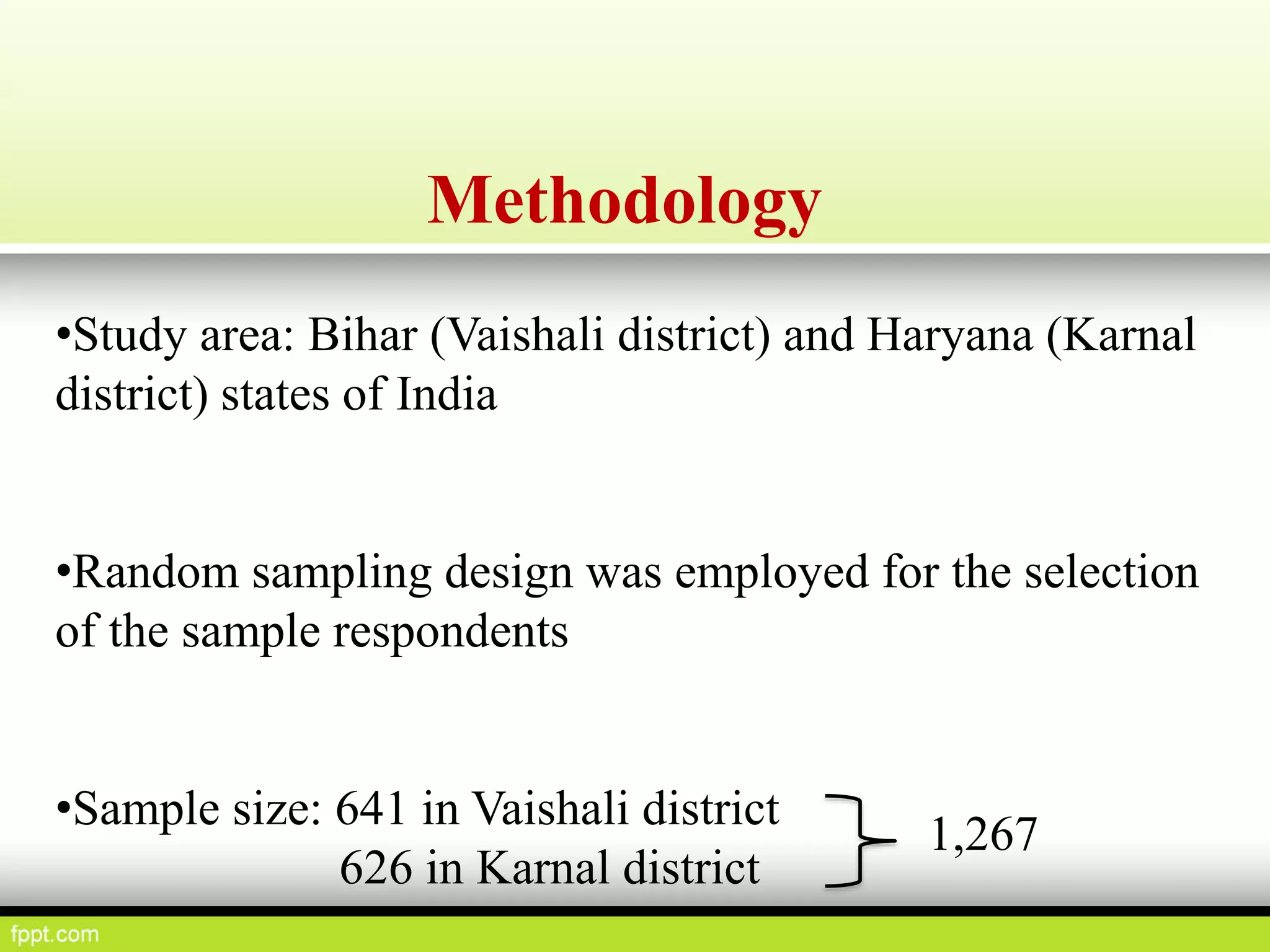
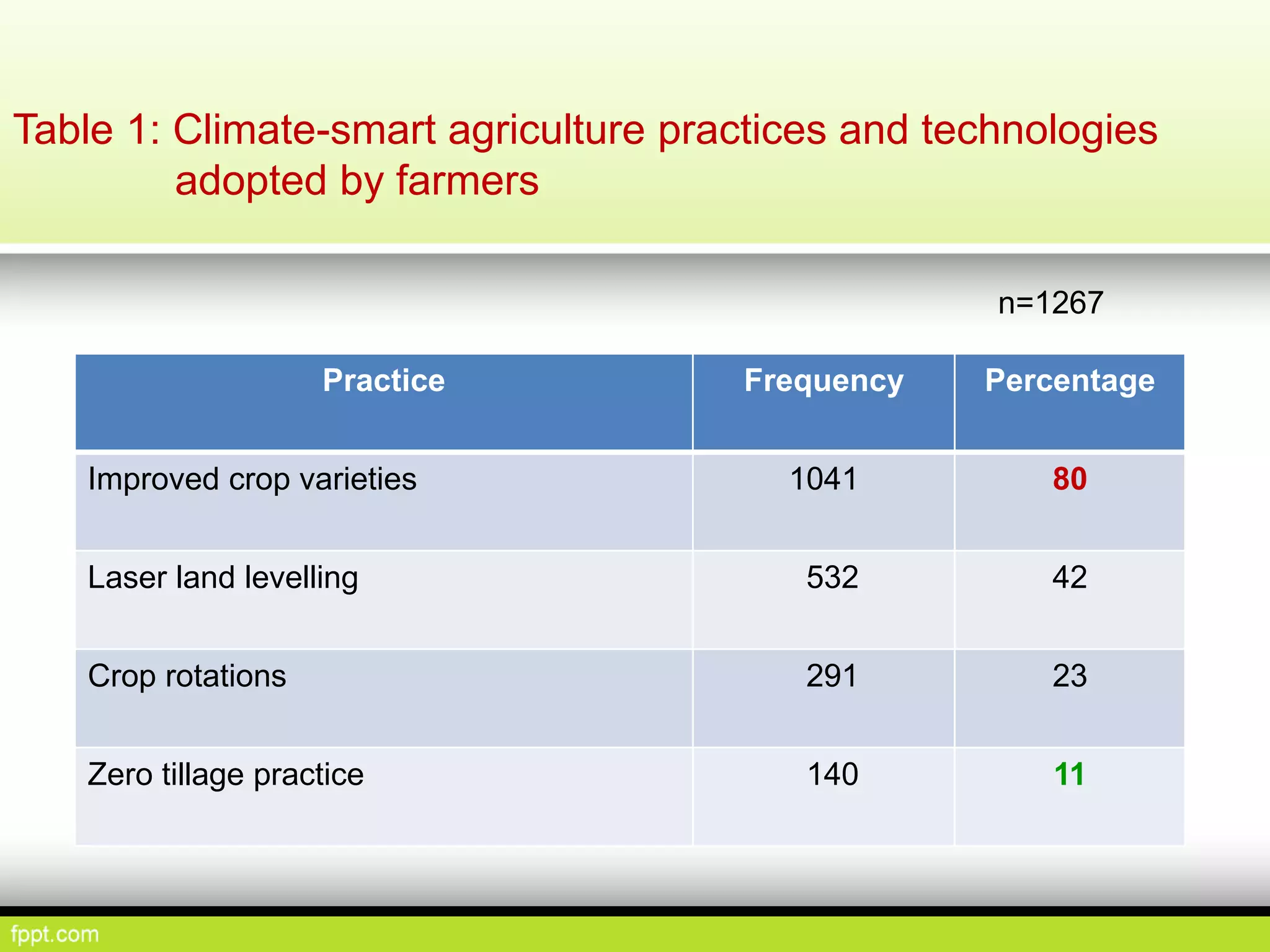
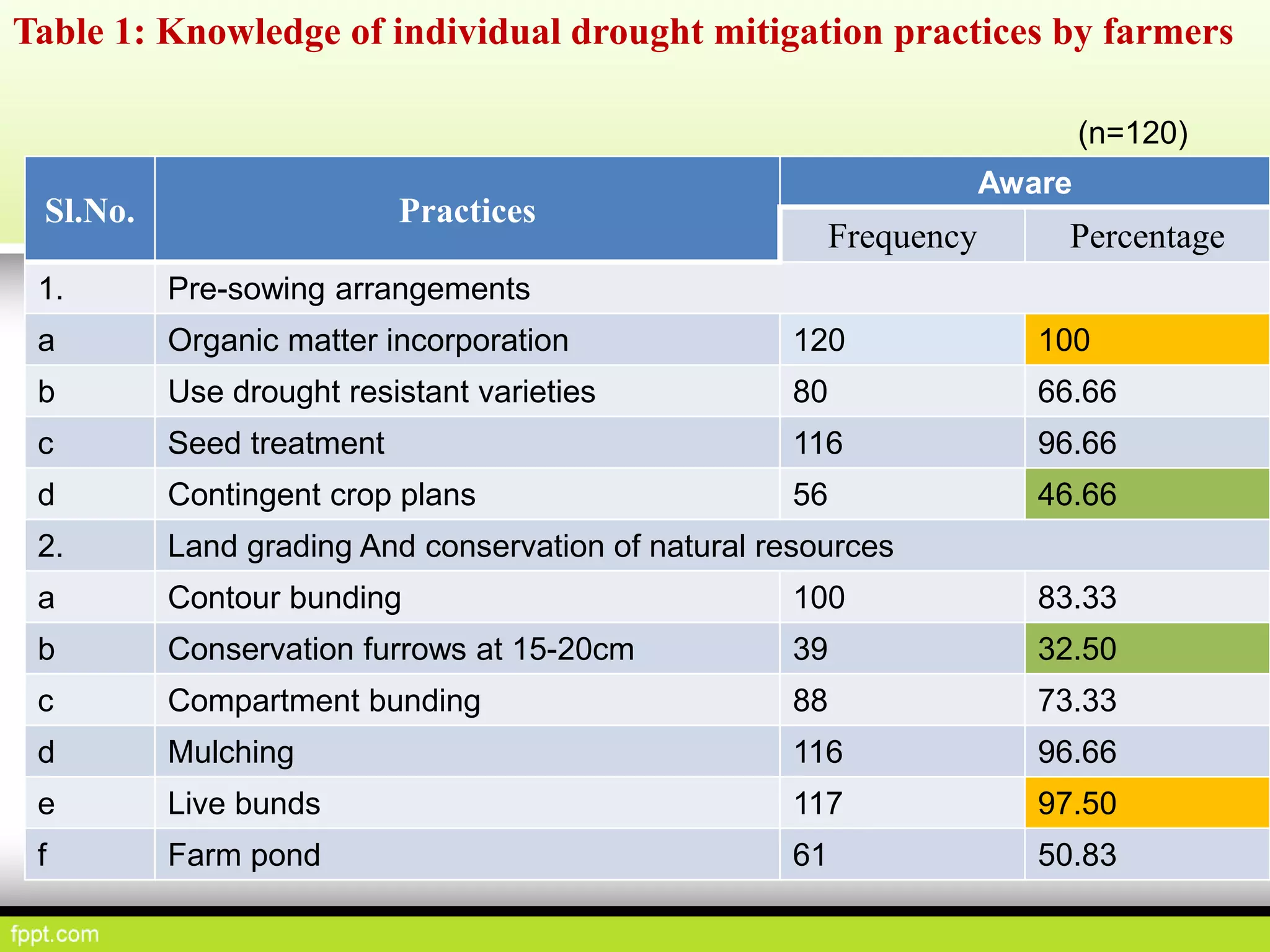
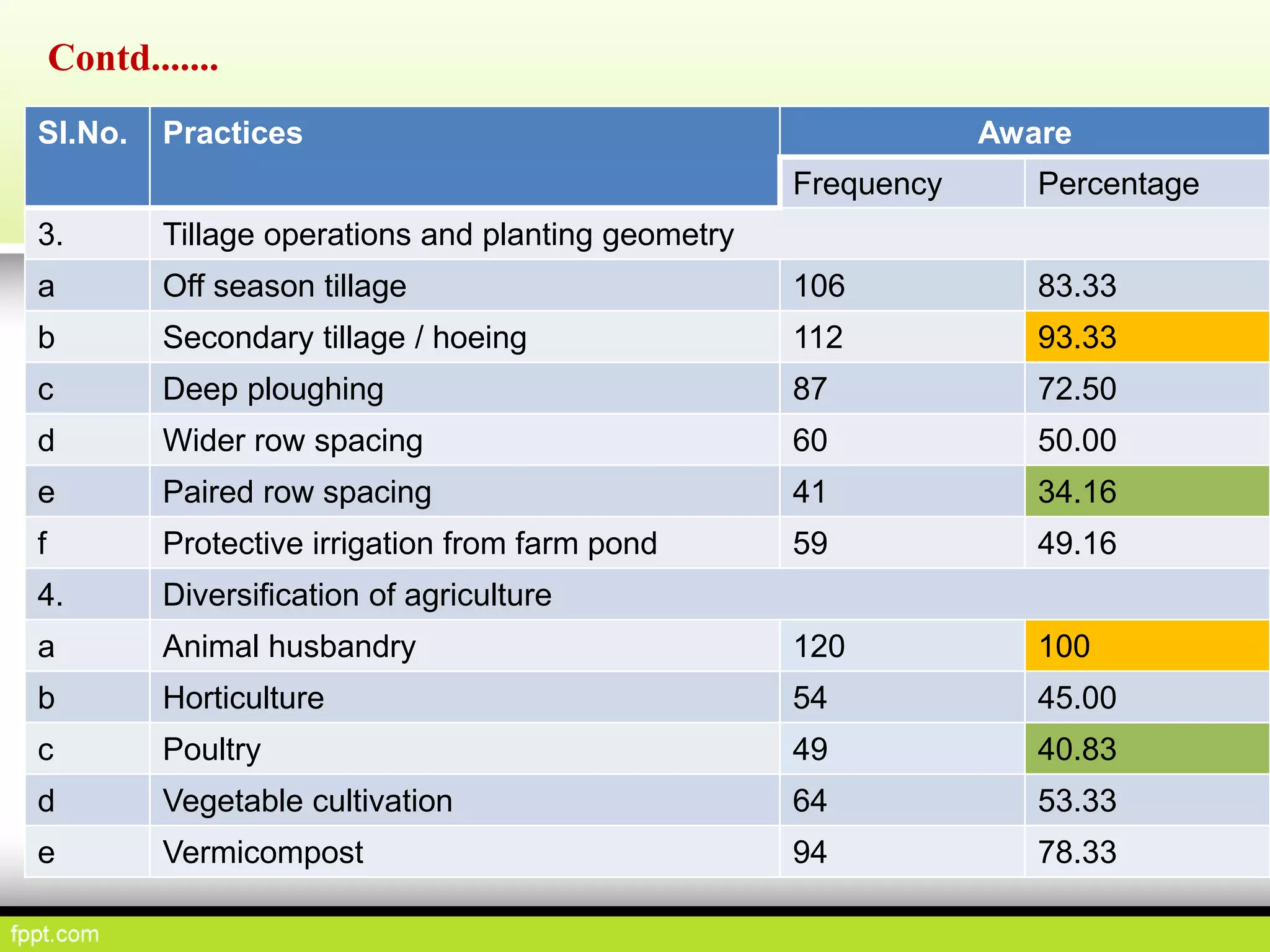
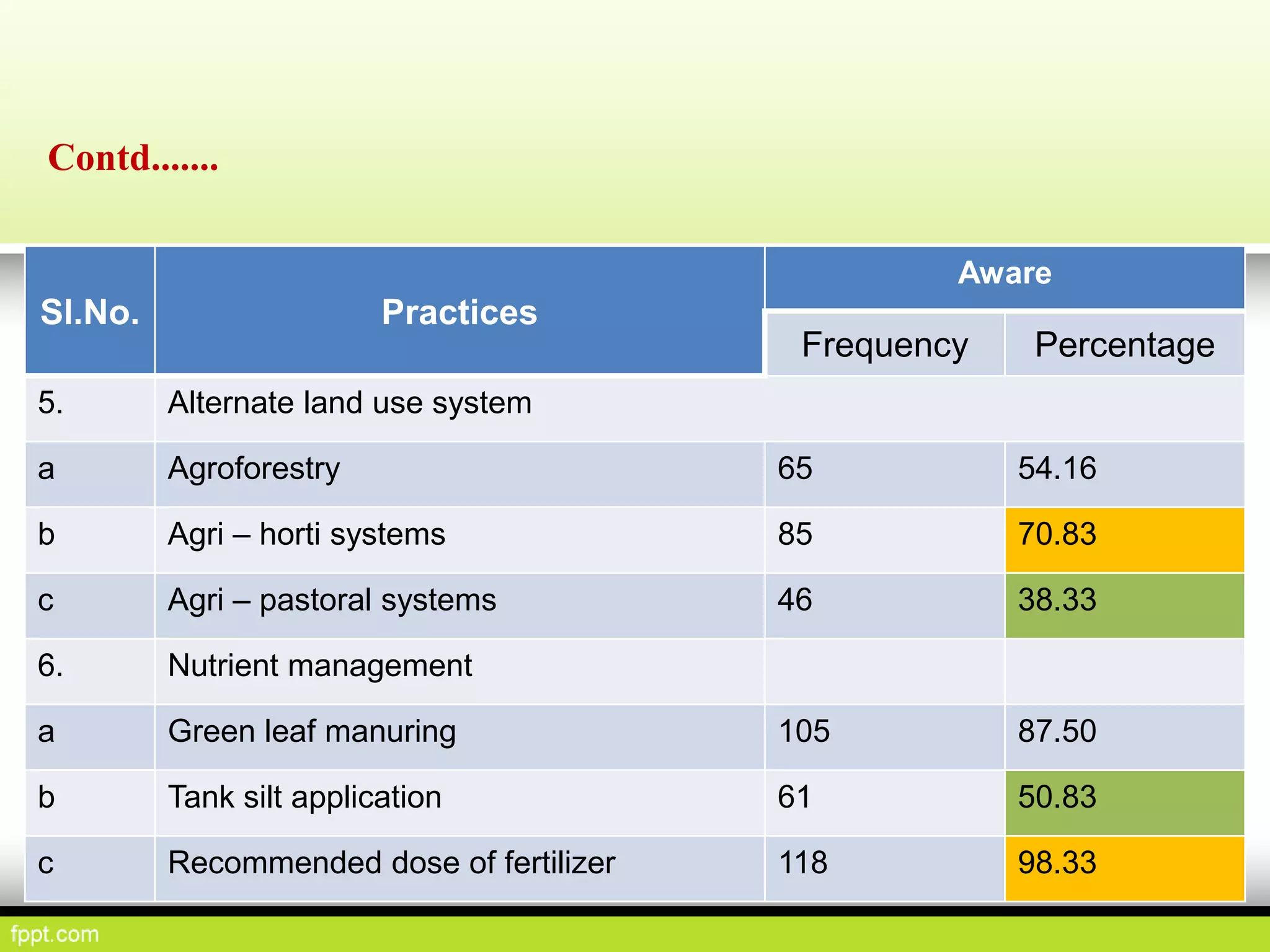
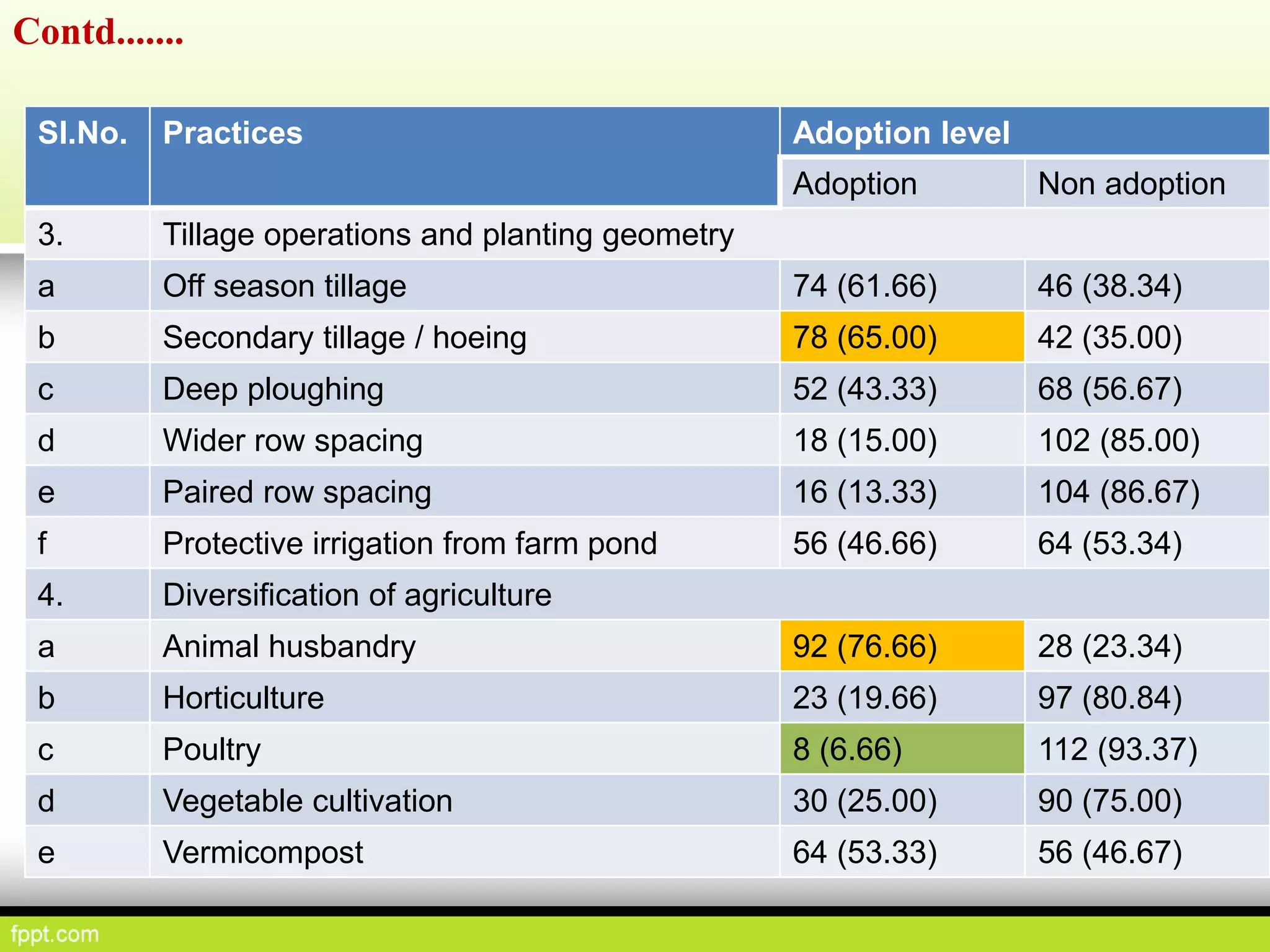
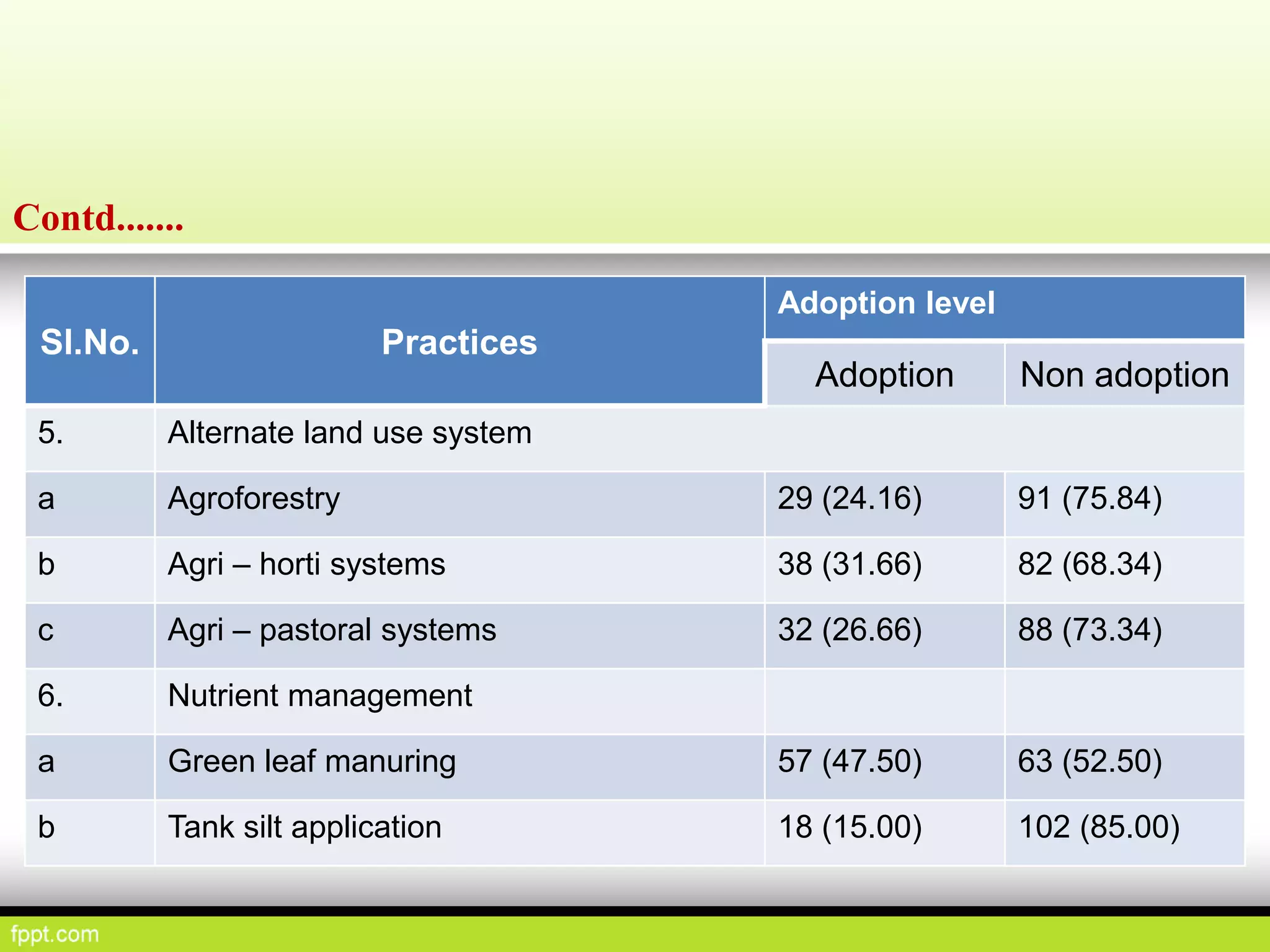
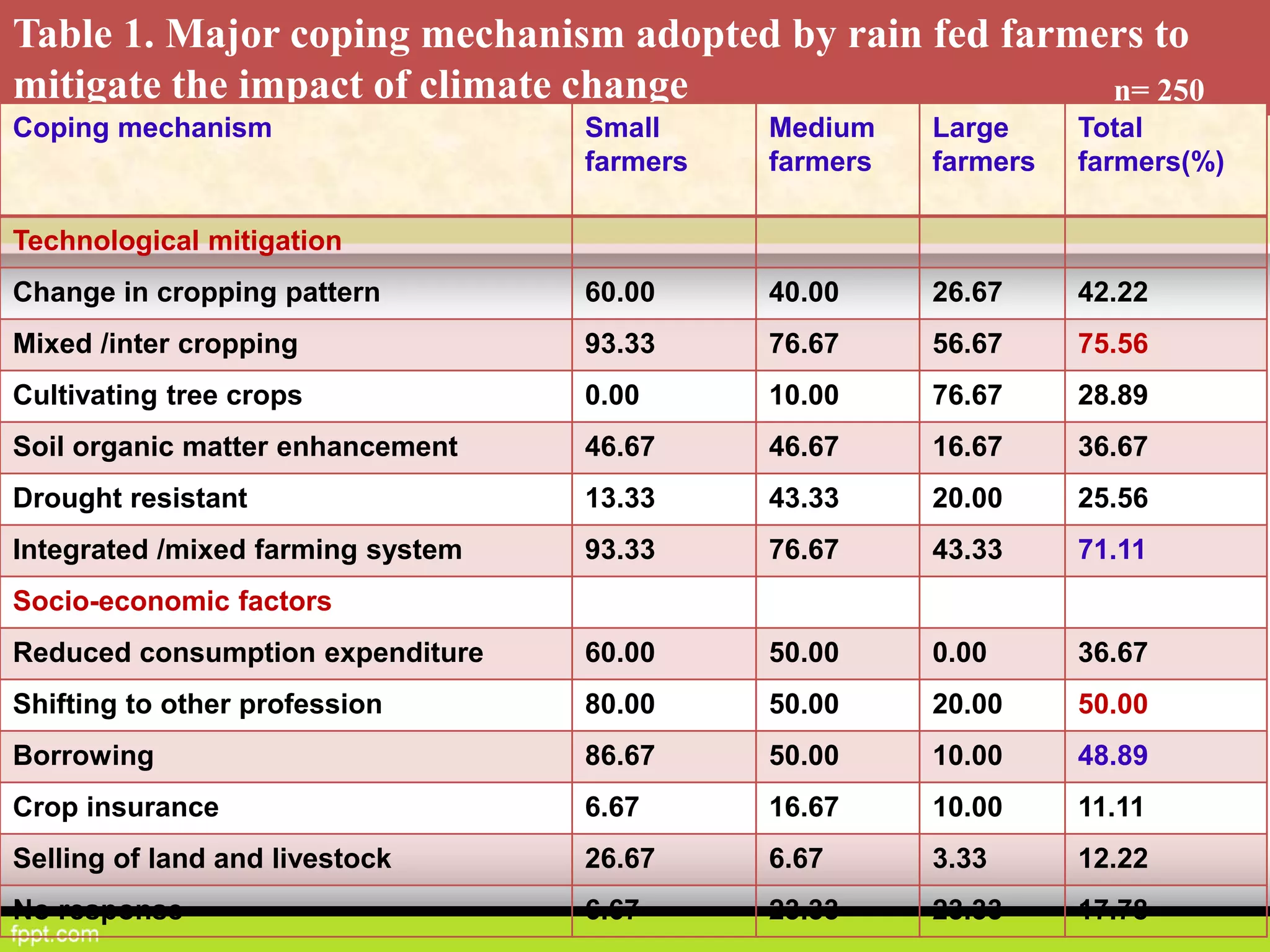
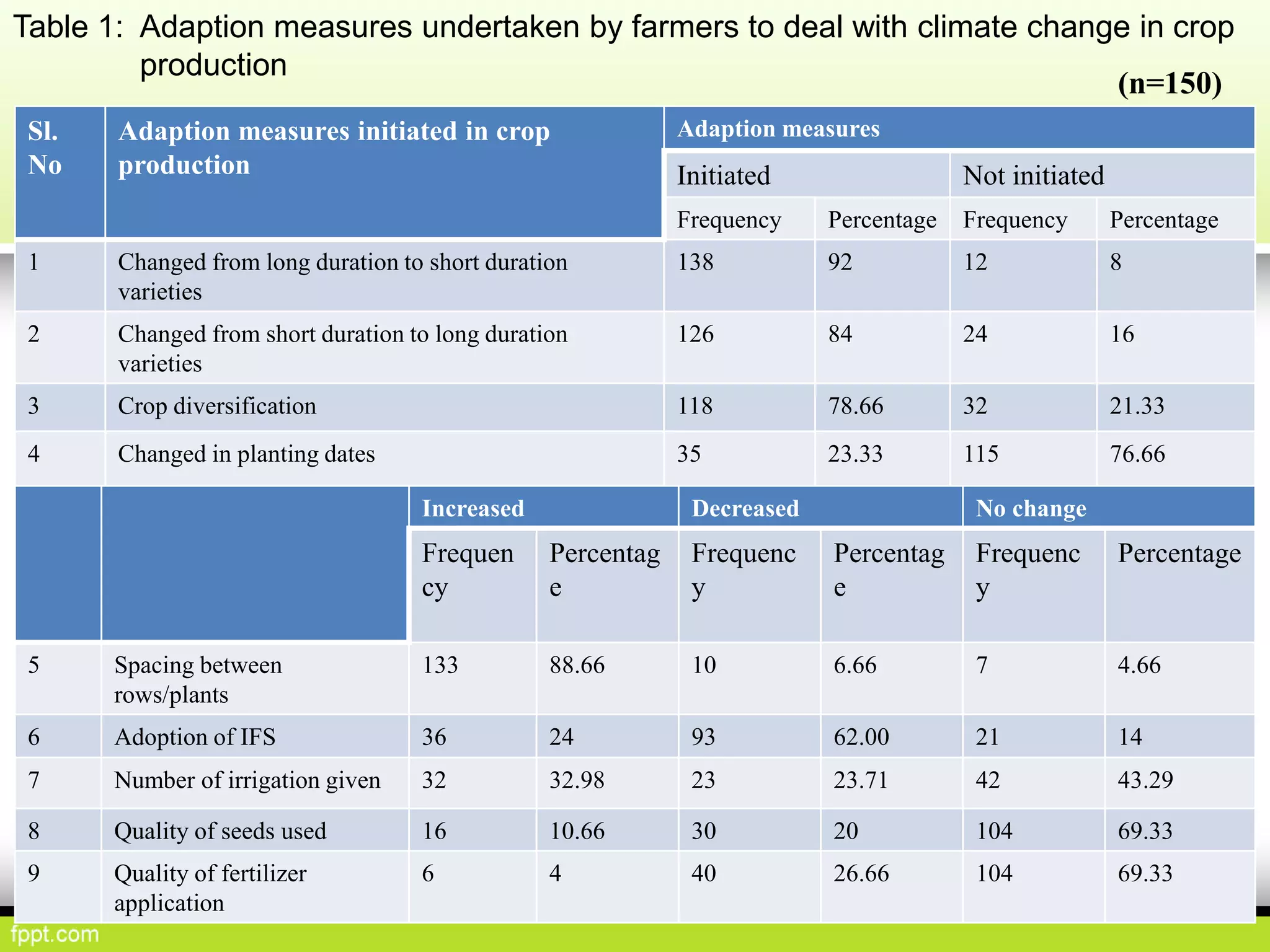
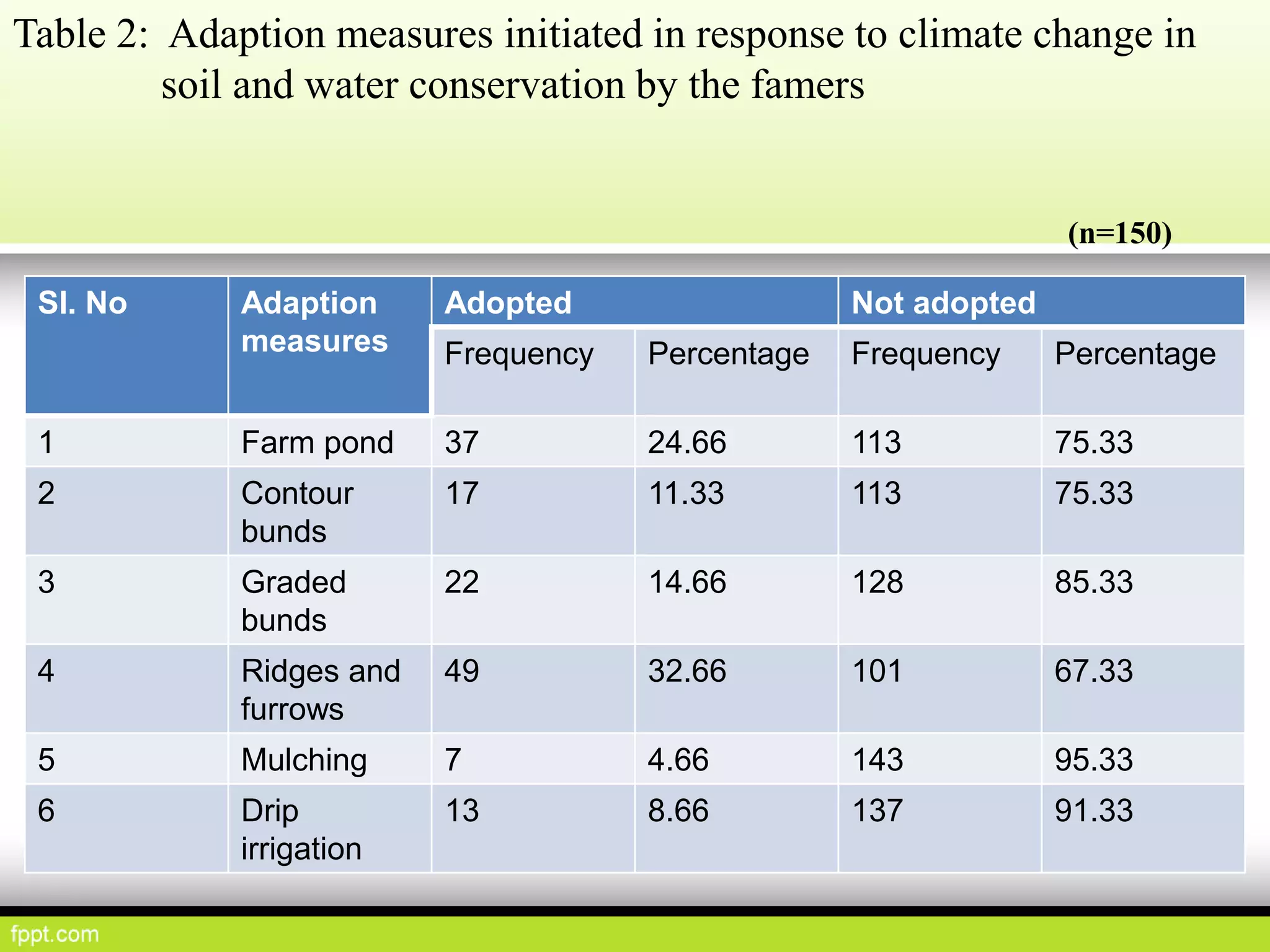
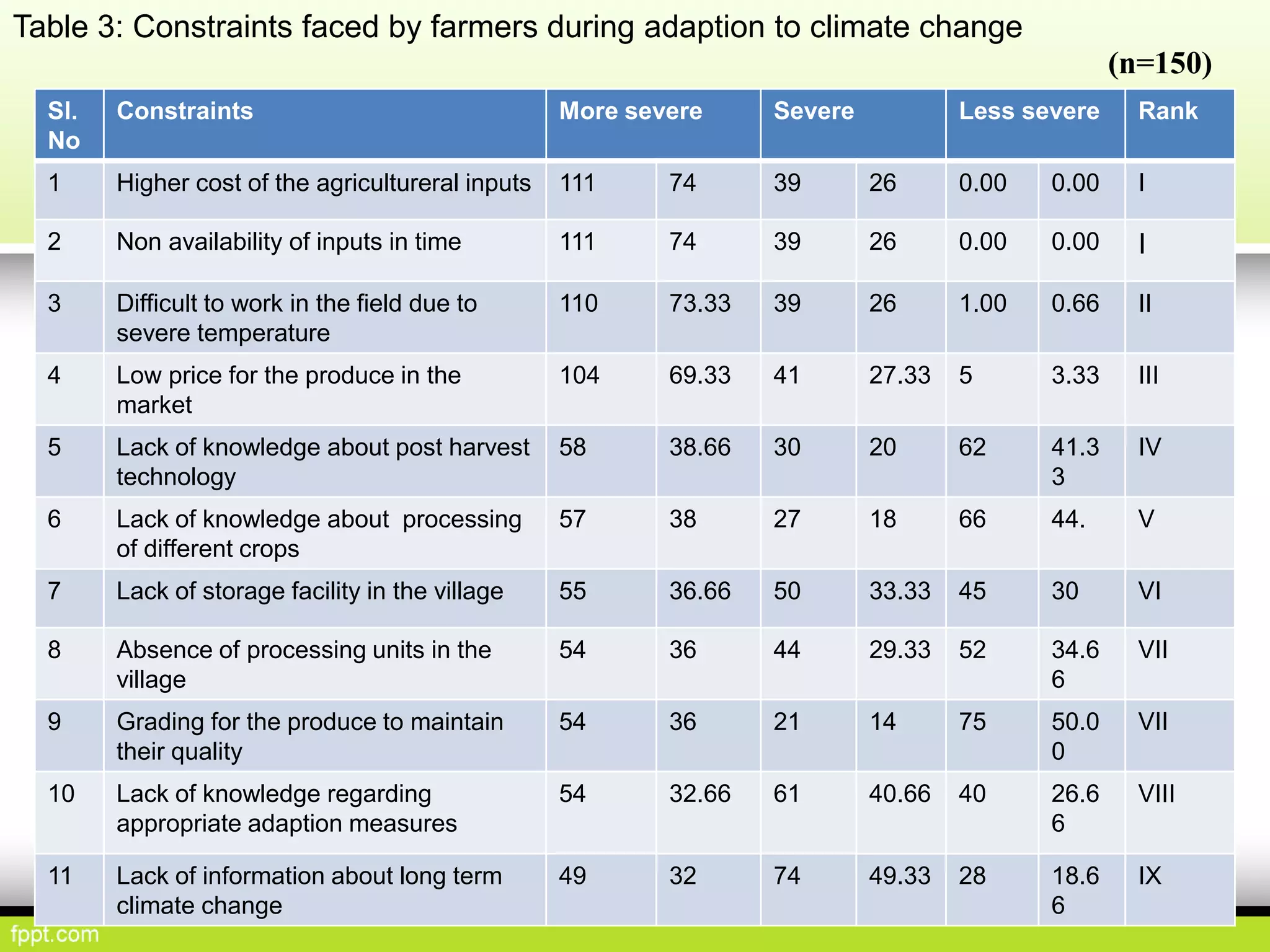
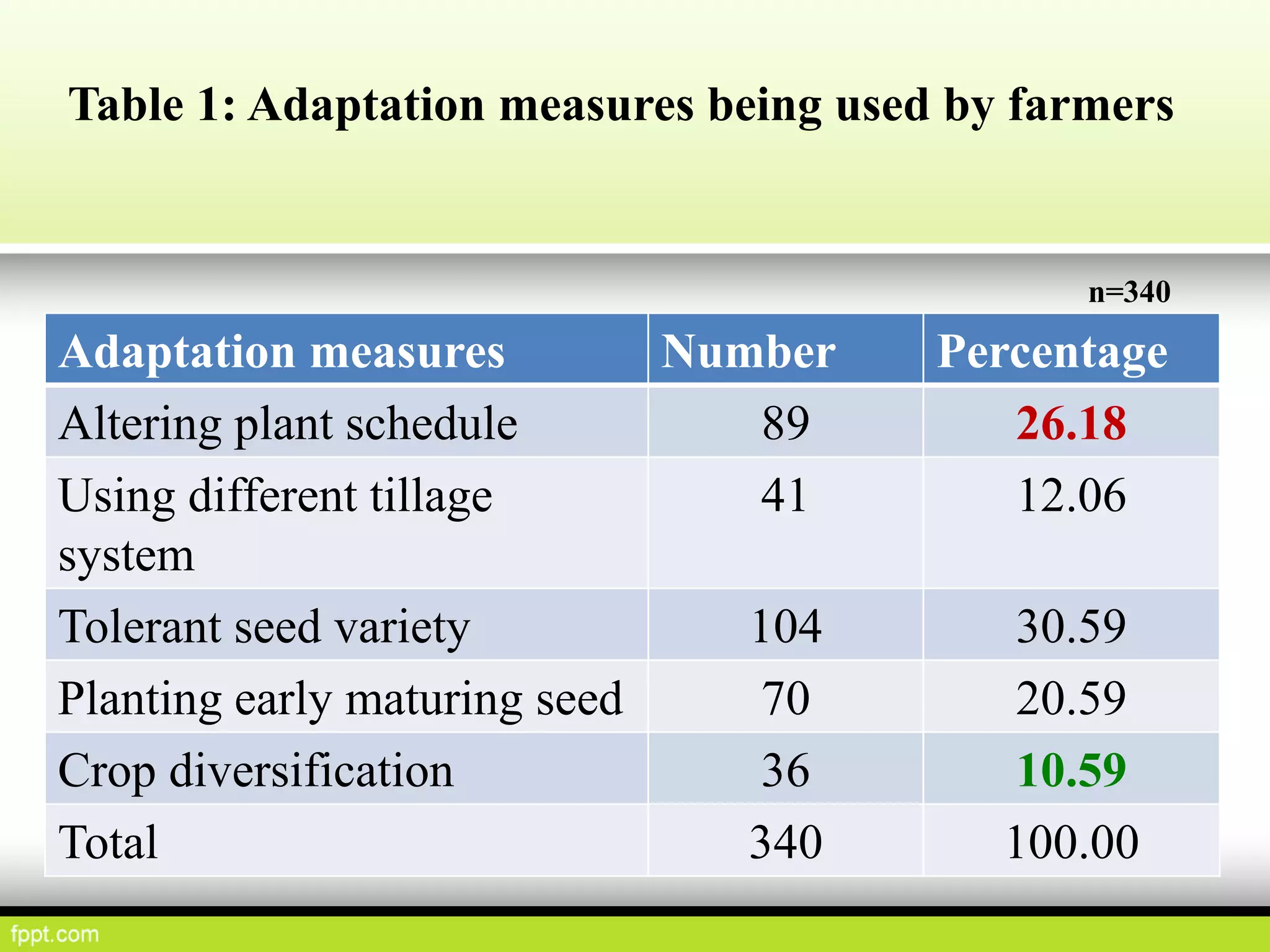
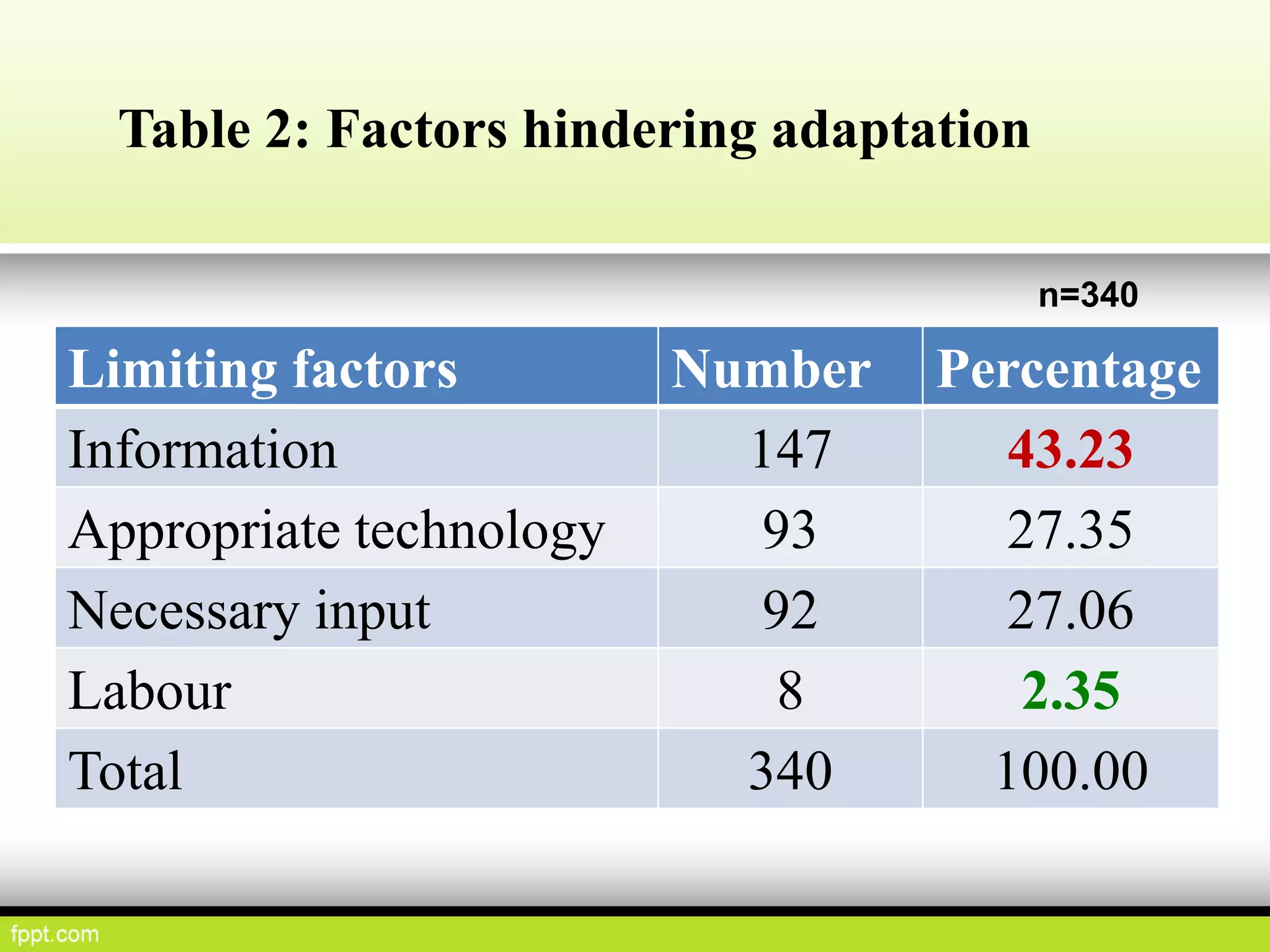
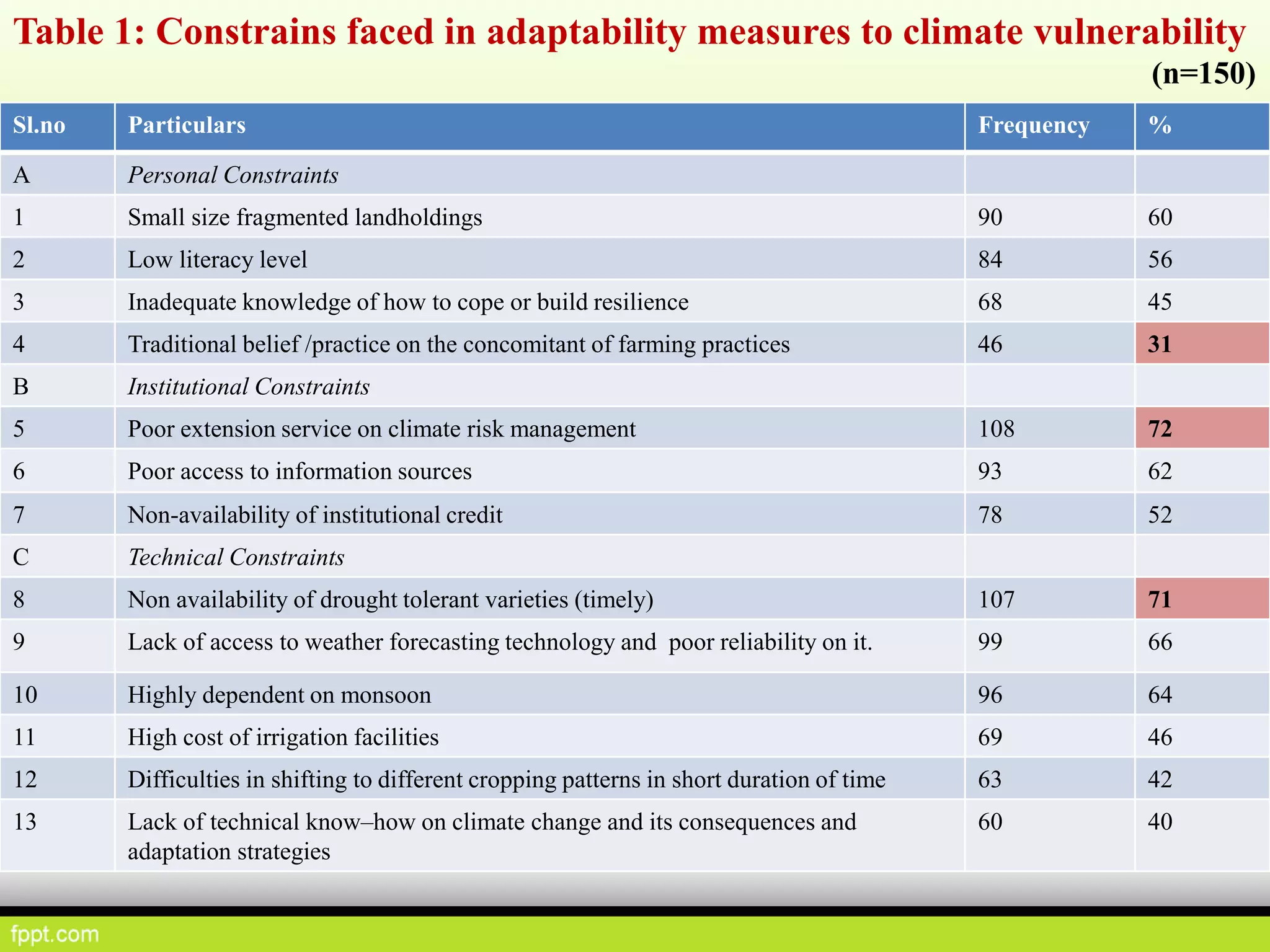
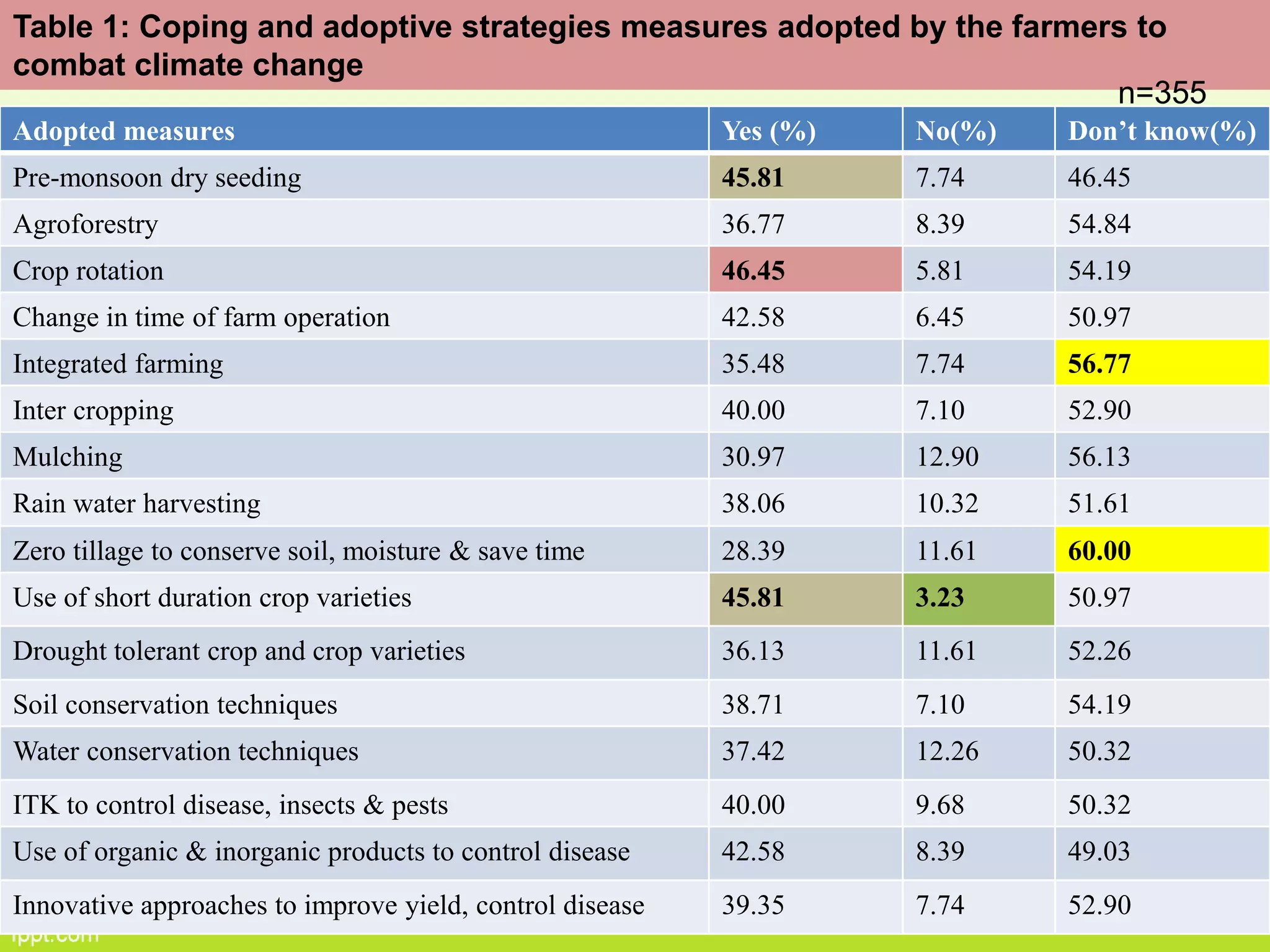
This document discusses climate resilient agriculture and its importance in India. It provides definitions of key terms like climate resilience, adaptation, and mitigation. It outlines various strategies for climate resilient practices in agriculture, including developing drought/heat tolerant crop varieties, improved water management, and diversifying crops and farm practices. The National Initiative on Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) is described as the major government project focused on building resilience through strategic research, technology demonstrations, and capacity building. Several case studies on awareness, adoption and impact of climate resilient practices by farmers in India are summarized.