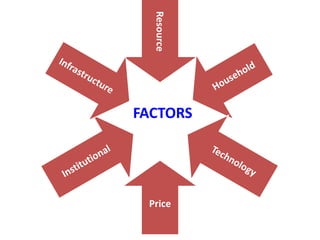
The document discusses crop diversification as a strategy to enhance sustainable agriculture by producing a variety of crops to improve income, ecological balance, and risk management. It outlines types of diversification, strategies for implementation, and examples specific to various Indian states, highlighting the advantages and constraints faced in this approach. Additionally, it mentions government policies to support agricultural practices and improve market conditions.