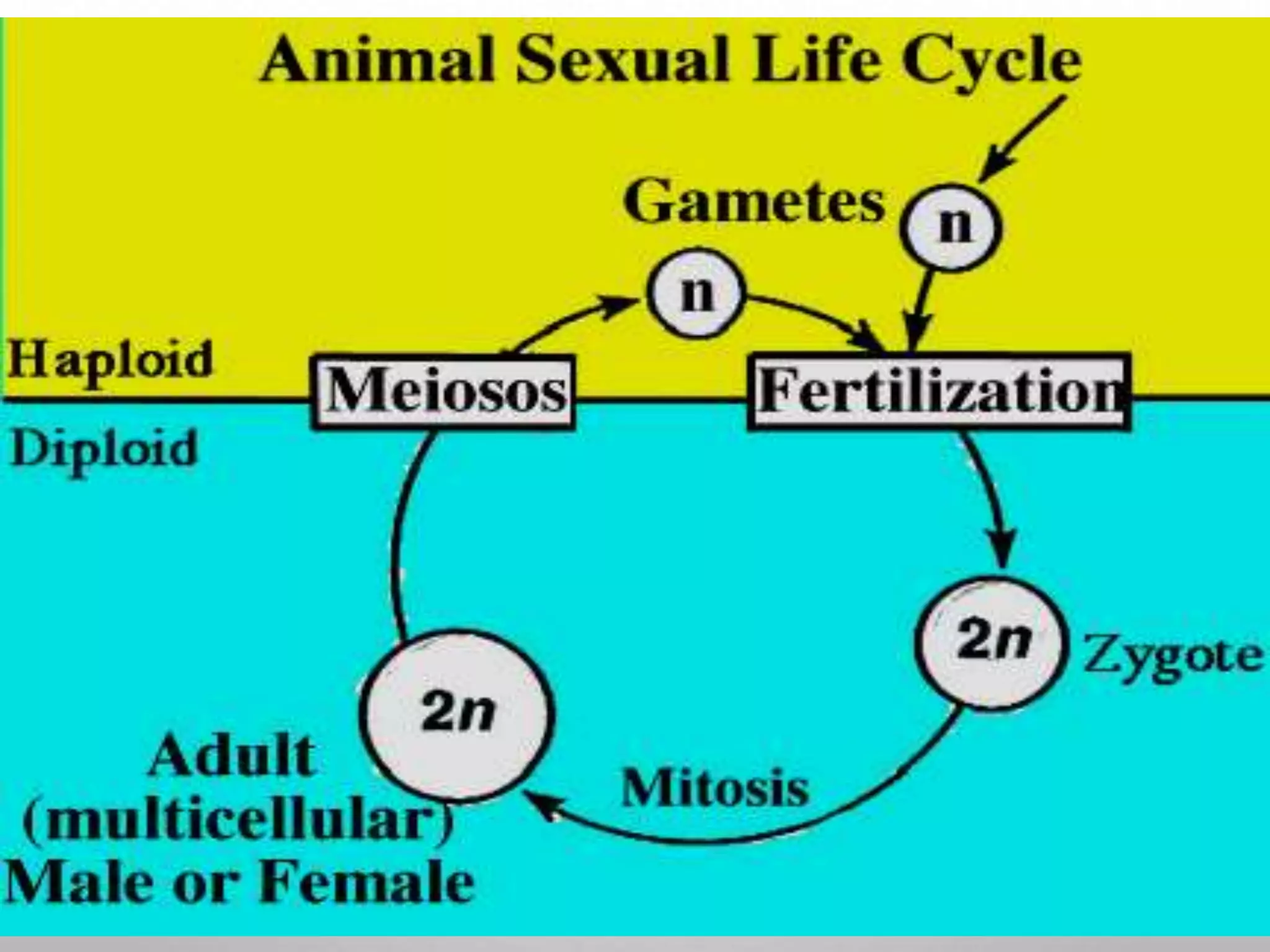
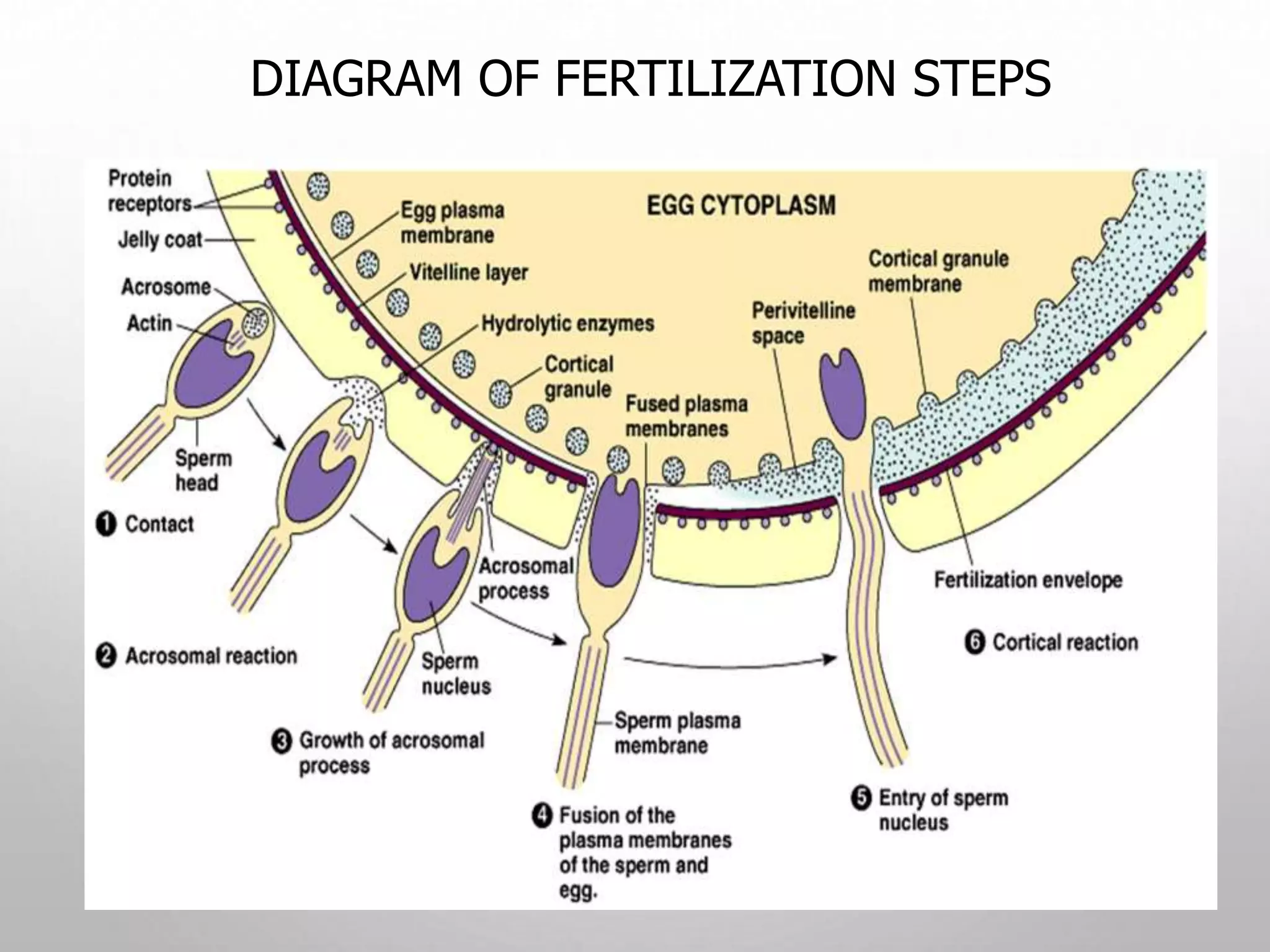
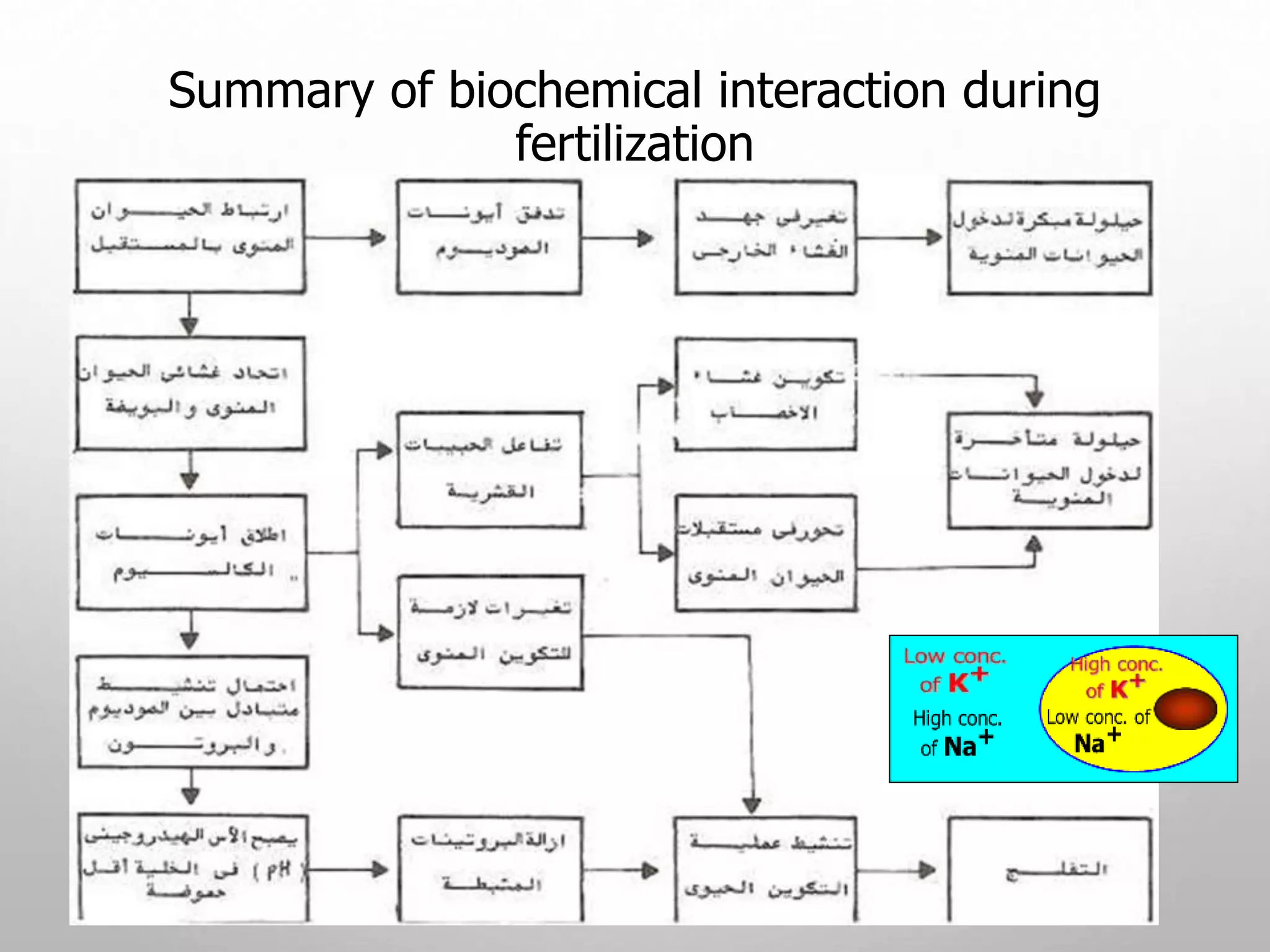
1. Fertilization involves the fusion of a sperm and egg nuclei to form a zygote.
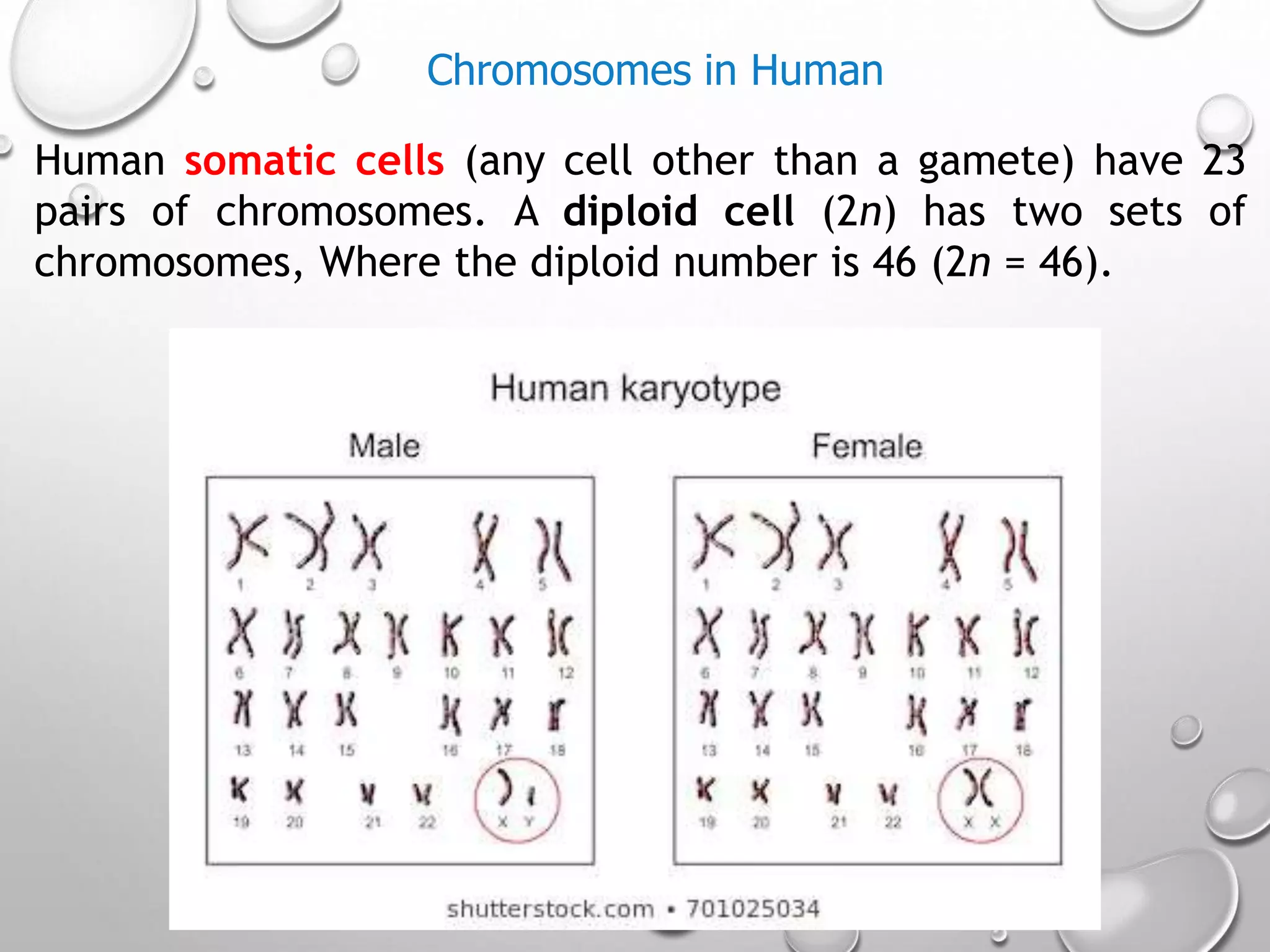
2. It restores the diploid number of chromosomes and determines the sex of the embryo.
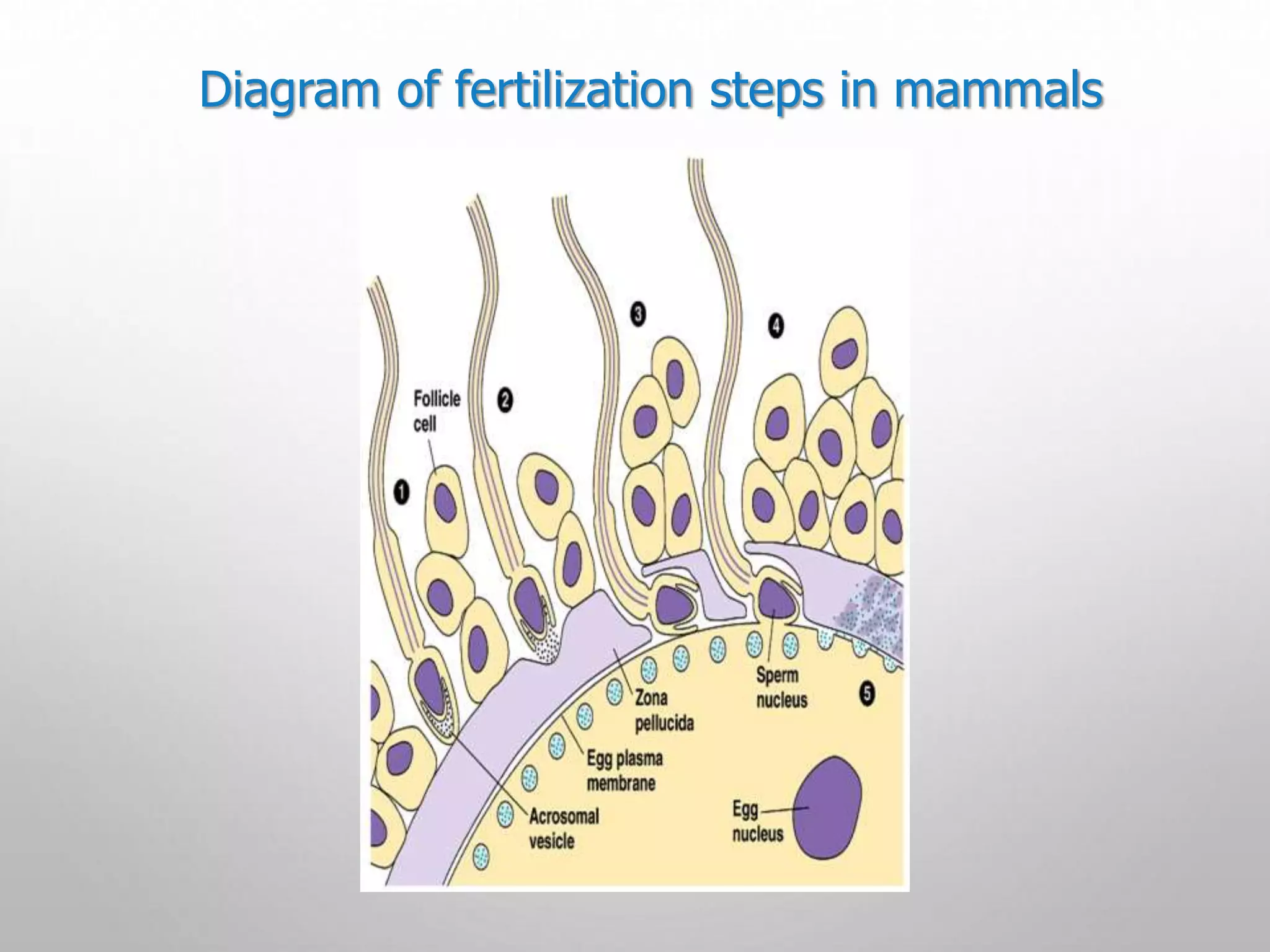
3. A series of events must occur for fertilization to be successful, including capacitation of sperm, penetration of the zona pellucida, fusion of membranes, and formation of male and female pronuclei.