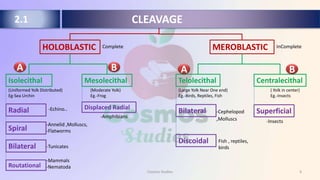
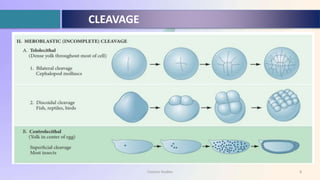
Cleavage is a series of mitotic divisions that divides the egg cytoplasm into smaller cells called blastomeres, starting after fertilization and ending when the embryo balances nucleus and cytoplasm. The type of cleavage (holoblastic or meroblastic) depends on the yolk content, affecting cell division patterns. Additionally, cleavages can be indeterminate, allowing for flexibility in blastomere fate, or determinate, where blastomeres are predetermined to develop into specific embryo parts.