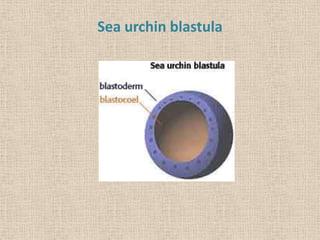
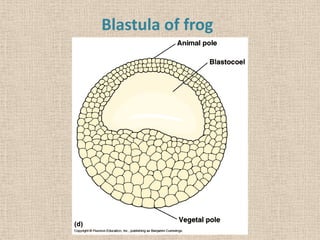
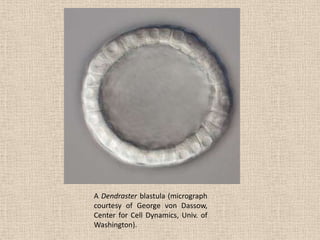
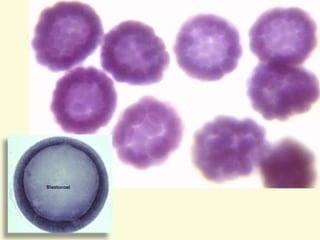
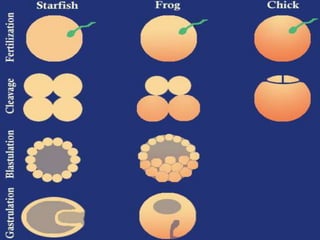
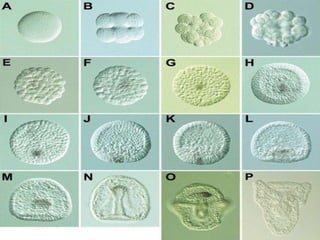
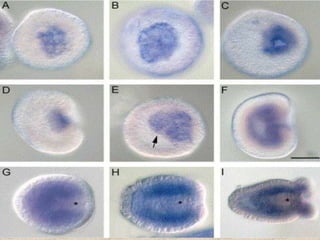
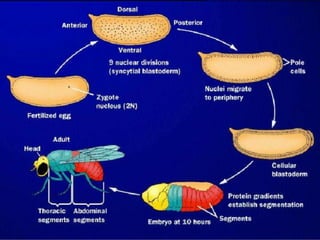
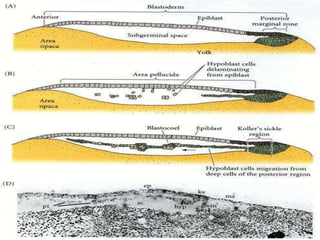
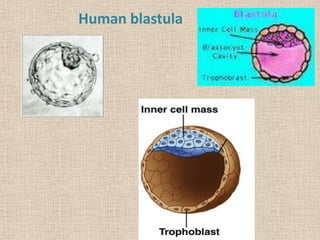
The document summarizes the process of blastulation in embryonic development. It describes how the zygote undergoes cleavage, forming blastomeres that arrange into a structure called a morula. The morula then develops into the blastula stage, where the cells form a blastoderm layer surrounding an interior cavity called the blastocoel. There are different types of blastulae depending on features like whether the blastocoel is present, the number of cell layers in the blastoderm, and how yolk is distributed. Key blastula types include coeloblastula, stereoblastula, periblastula, discoblastula, and blastocyst.