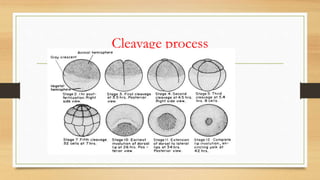
1. The development of frog consists of copulation, spawning, fertilization, cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation, and post-embryonic development.
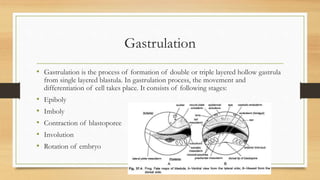
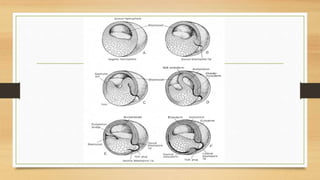
2. During gastrulation, epiboly, imboly, contraction of the blastopore, and involution occur, forming the three germ layers - ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
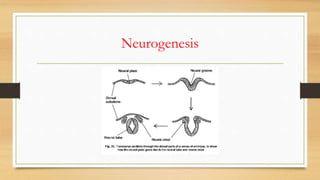
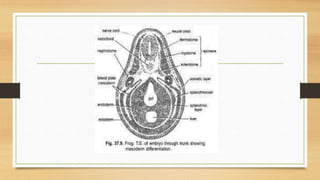
3. Post-embryonic development includes neurogenesis forming the neural tube, notogenesis forming the notochord, and coelom formation separating the mesoderm into three layers.