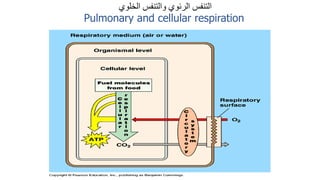
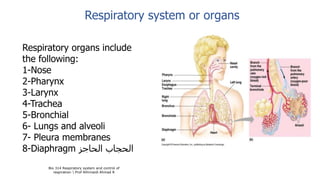
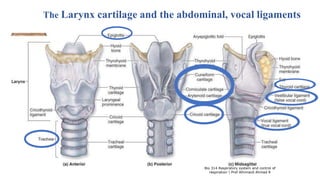
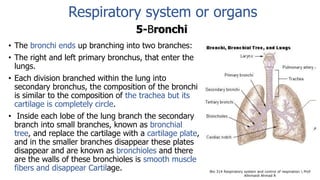
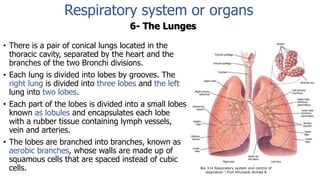
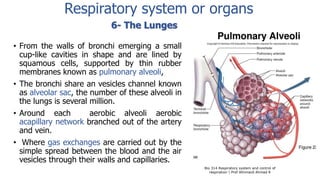
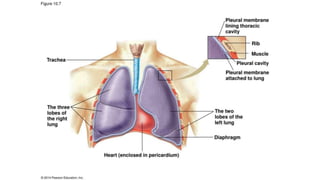
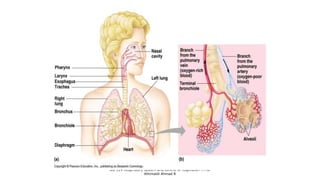
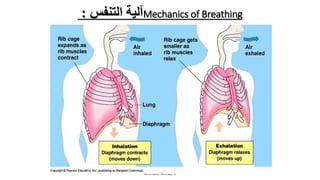
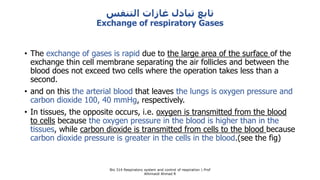
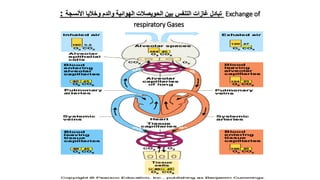
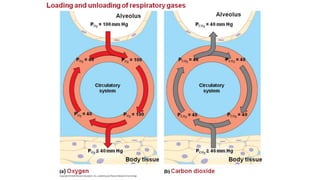
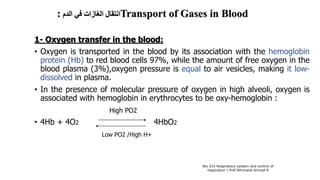
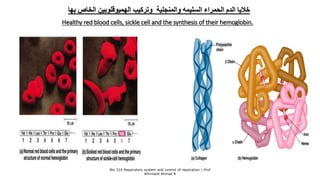
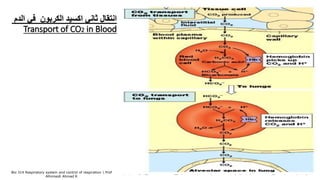
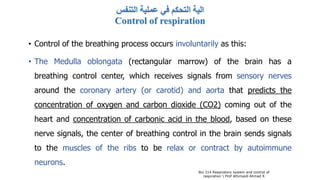
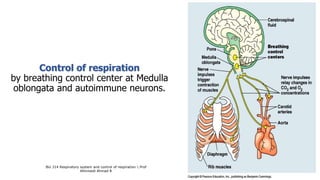
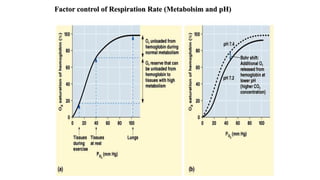
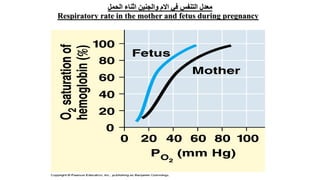
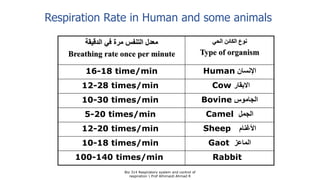
The document provides an overview of the respiratory system and control of respiration. It describes the key organs involved, including the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs and alveoli. It explains the mechanics of breathing through inspiration and expiration. Gas exchange occurs as oxygen passes from the alveoli into the blood and carbon dioxide passes from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled. The lungs, diaphragm, ribs and autonomic nervous system work together to regulate breathing and ventilation.