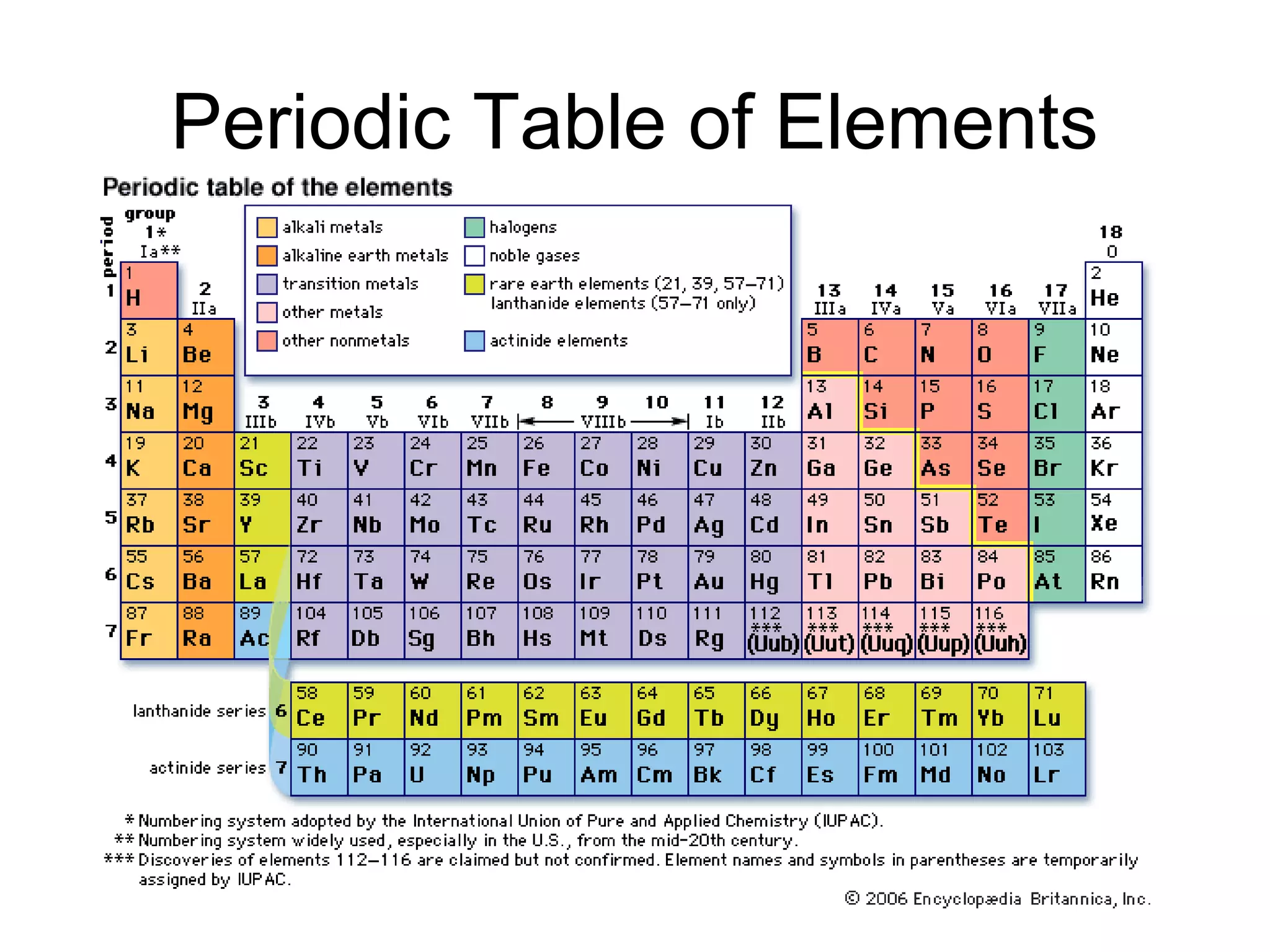
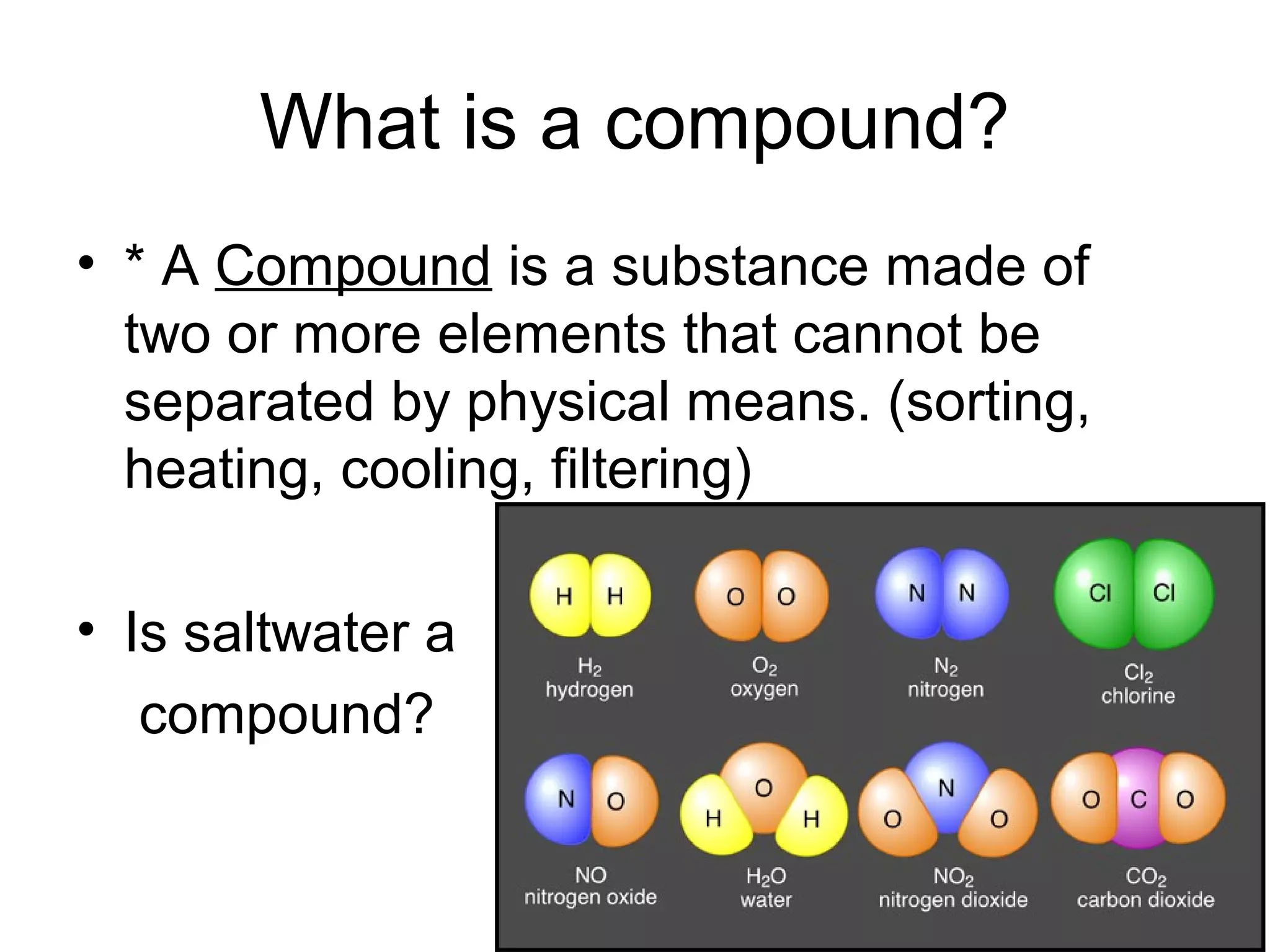
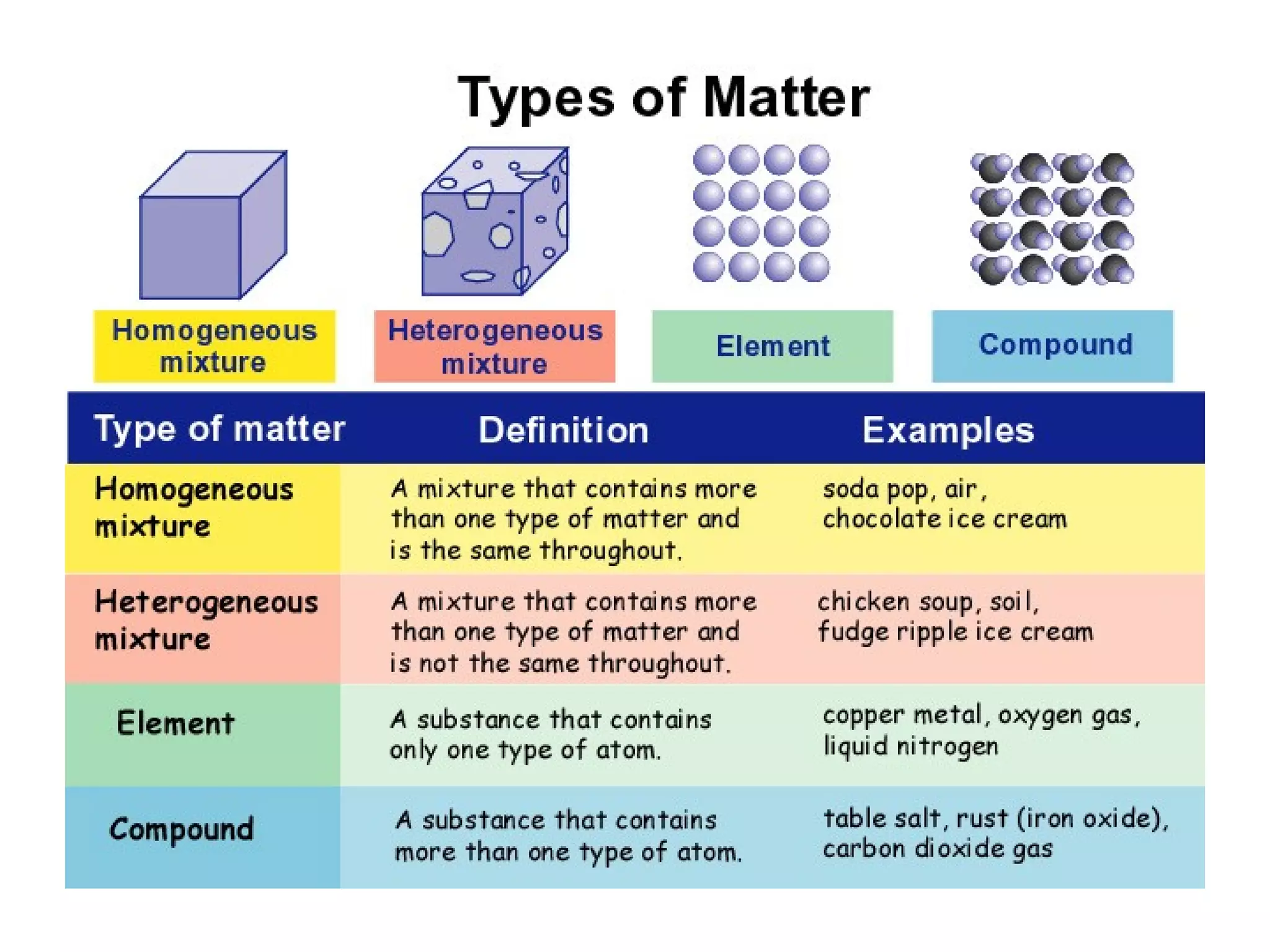
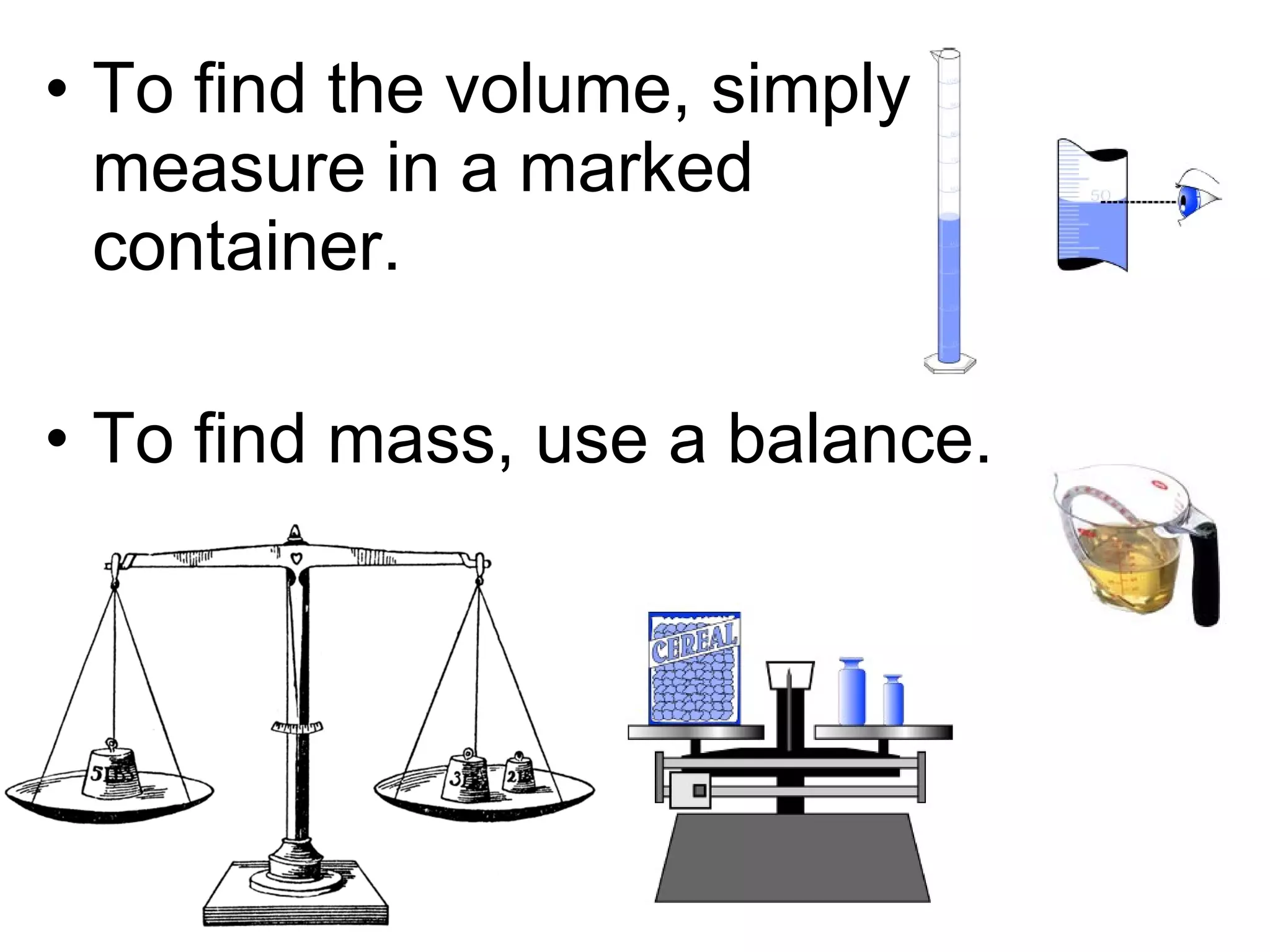
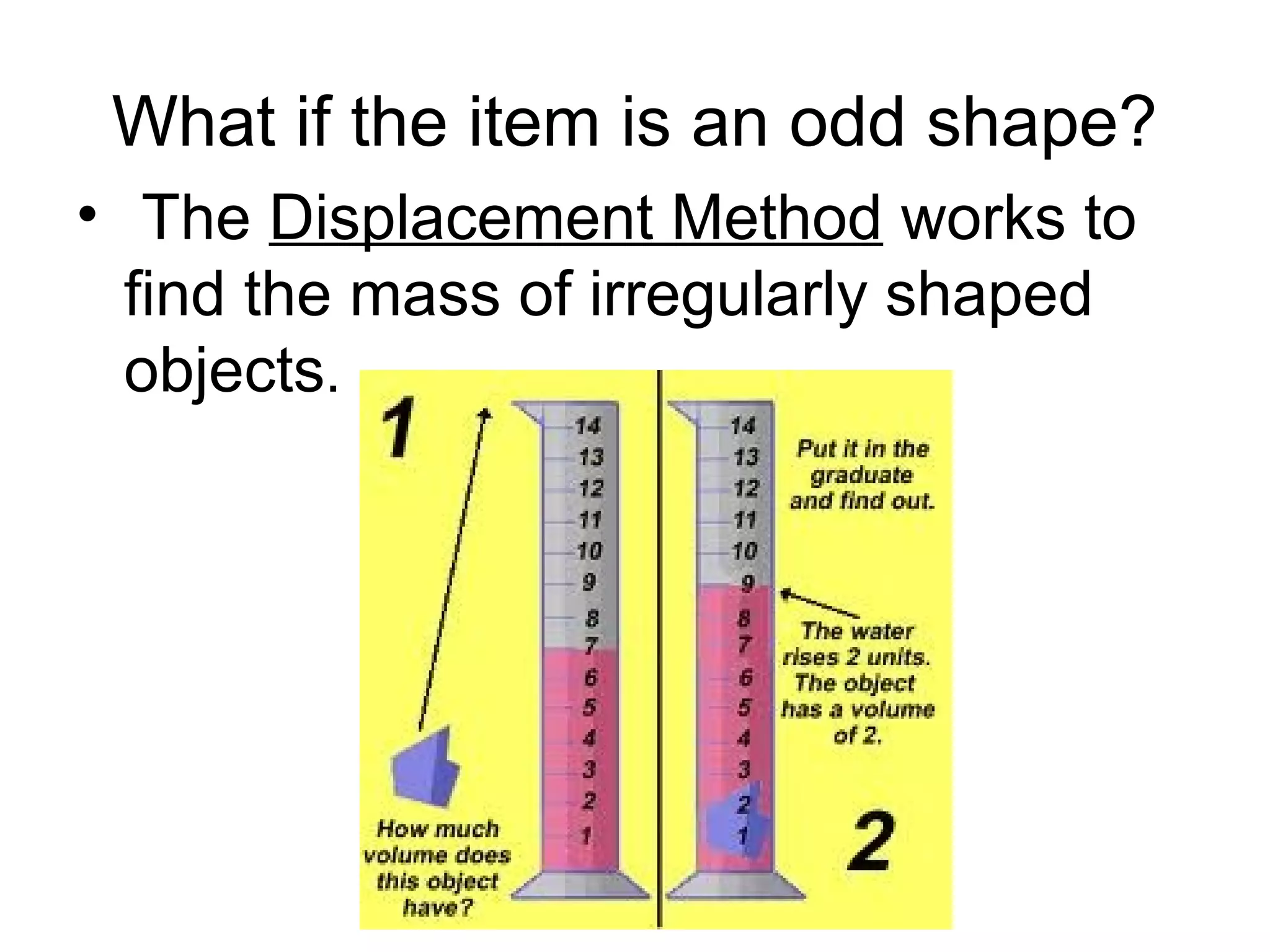
The document discusses the classification and properties of matter, explaining that matter can be classified as either mixtures which contain more than one type of matter, or as substances which cannot be separated into different types of matter. It also describes the four states of matter - solid, liquid, gas, and plasma - and how temperature influences the movement and arrangement of molecules in each state. Measurement techniques for determining the volume, mass, and amount of different types of matter are also outlined.