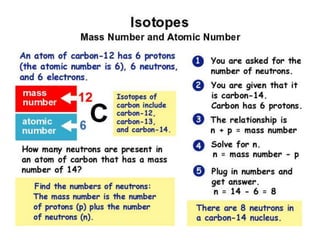
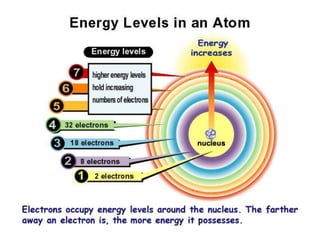
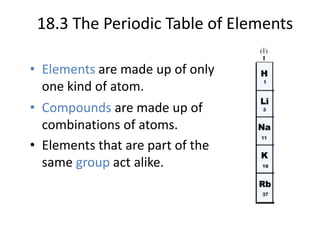
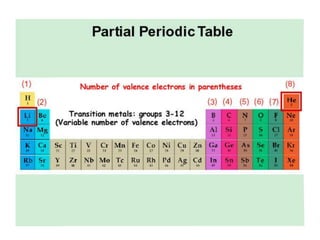
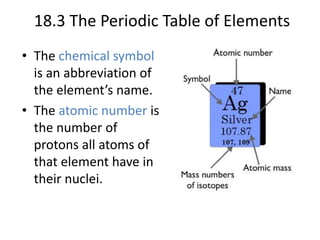
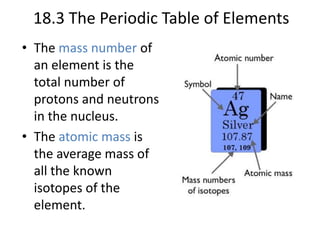
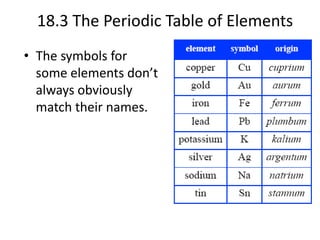
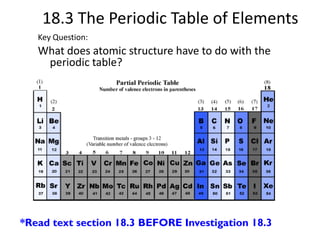
This document discusses atomic structure and the periodic table. It explains that the atomic number is the number of protons in an atom, which distinguishes one element from another. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Electrons orbit the nucleus in energy levels. The periodic table organizes elements based on their properties and places them in rows and columns according to atomic number.