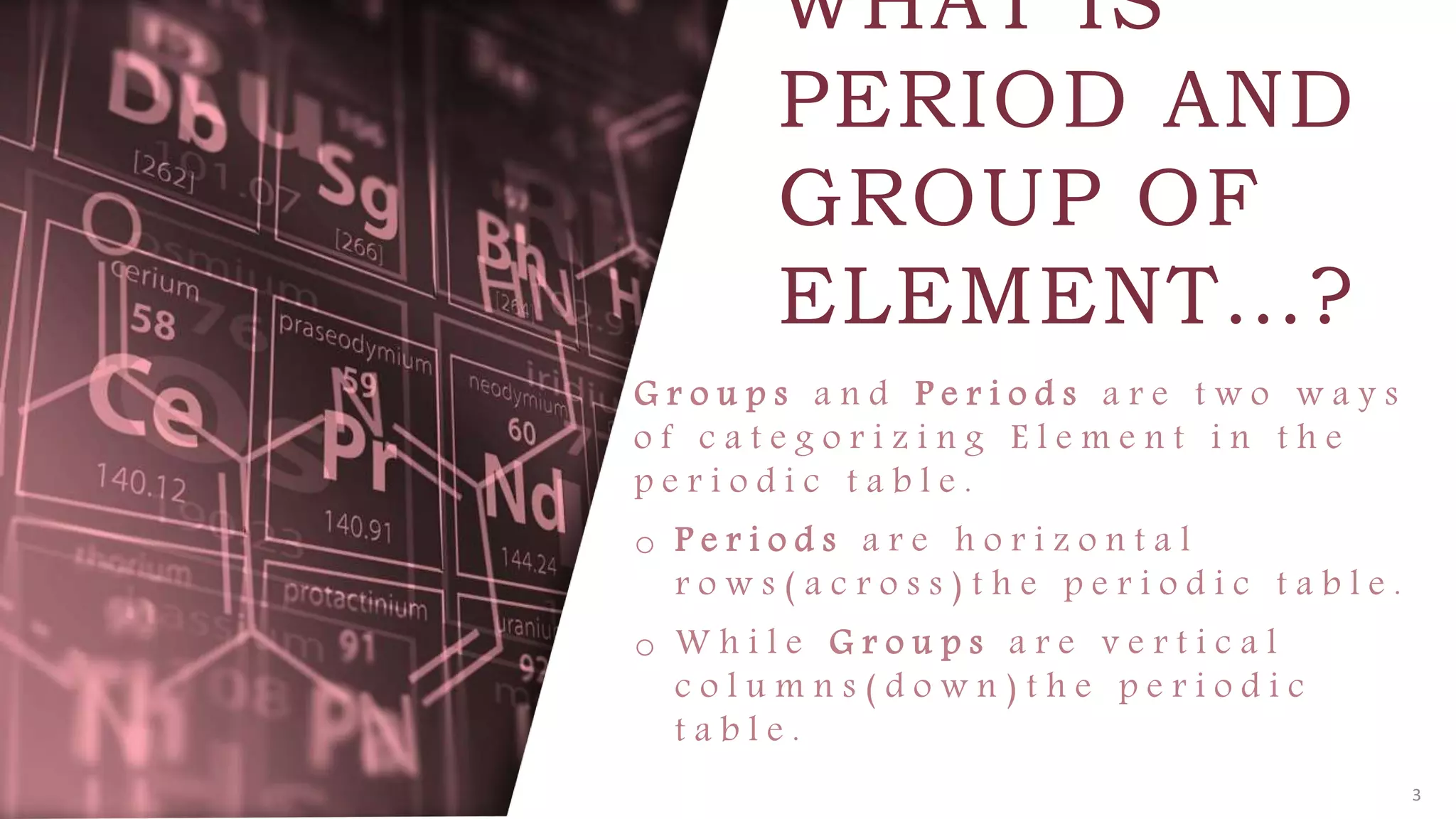
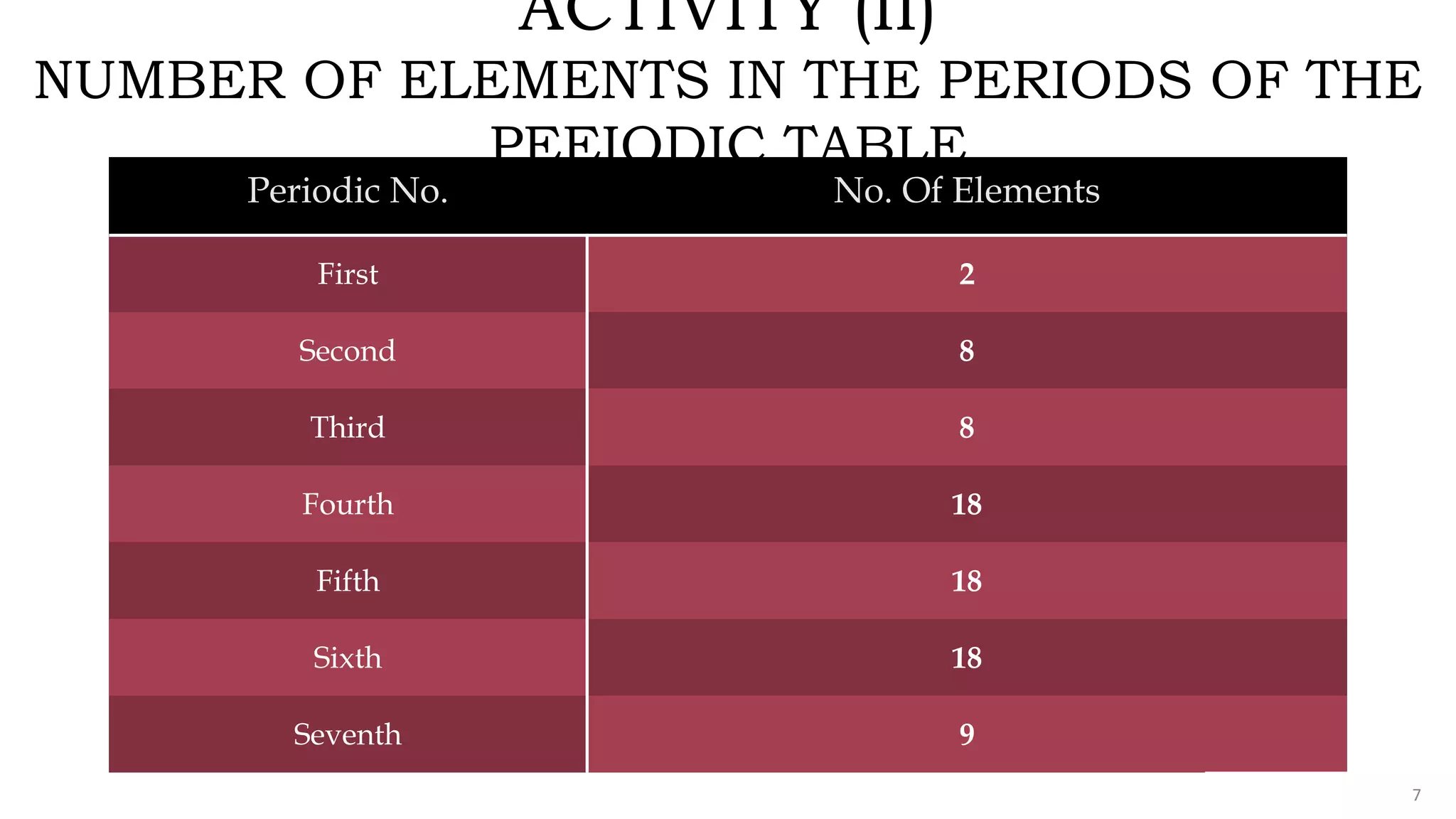
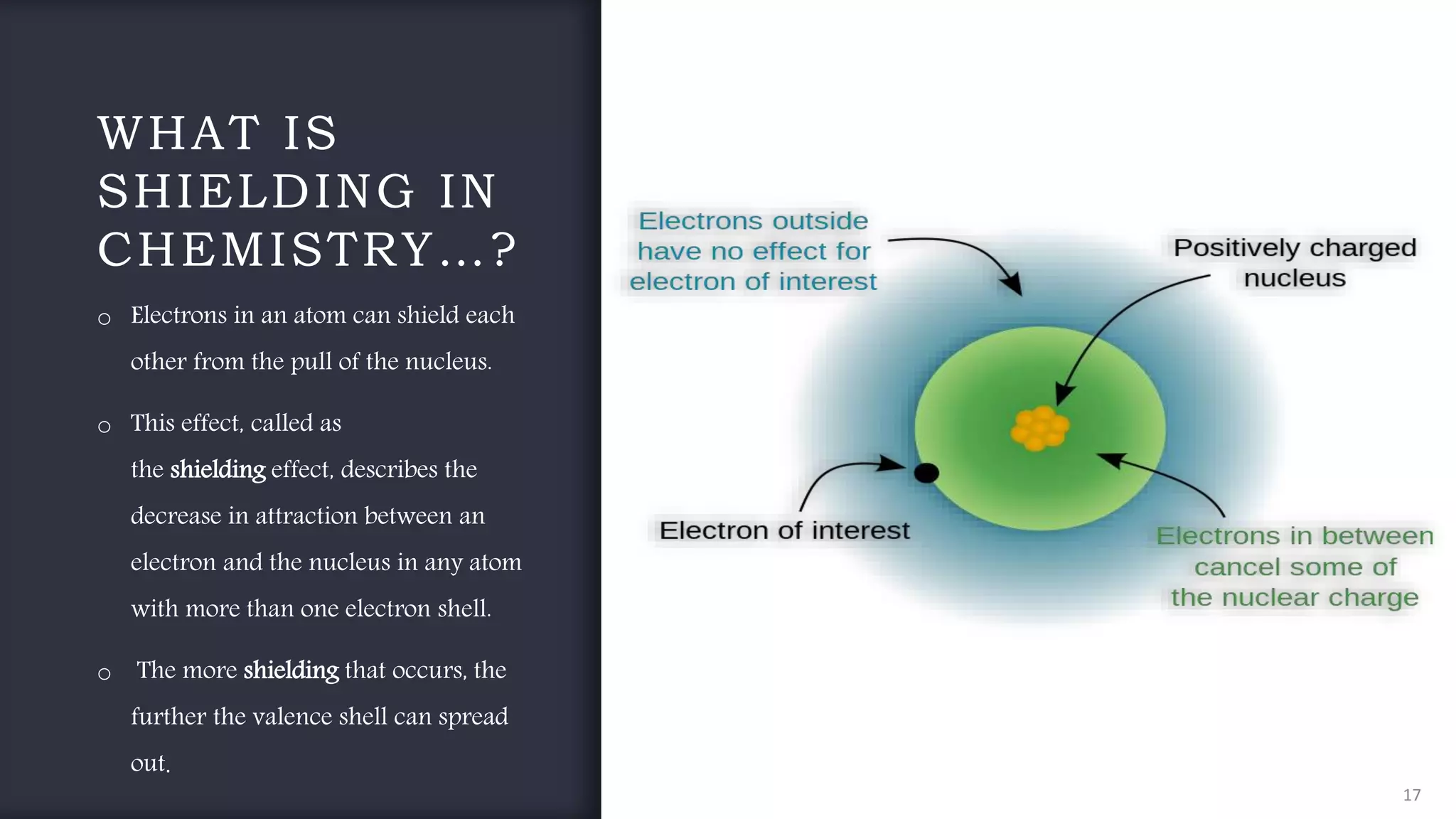
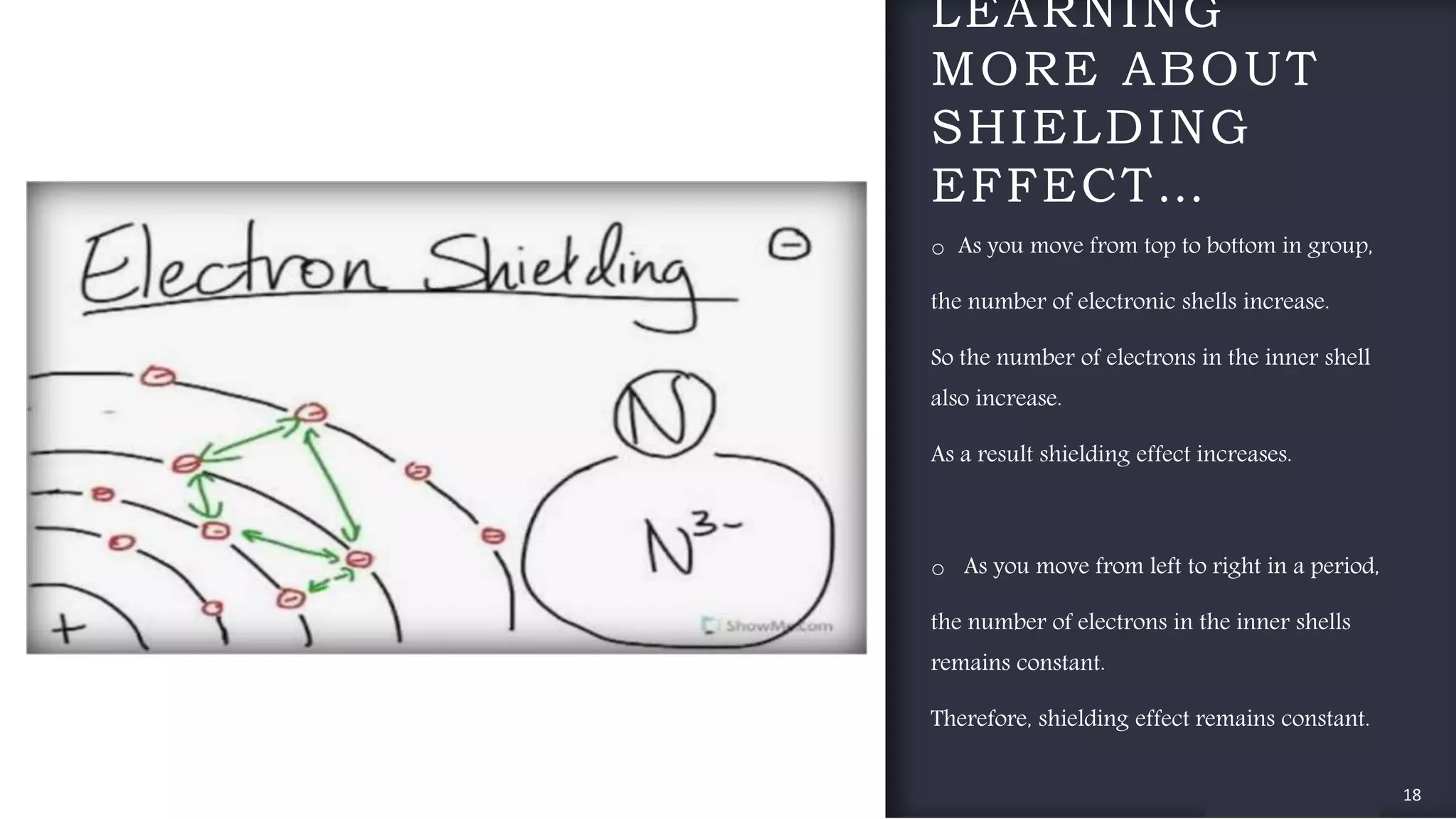
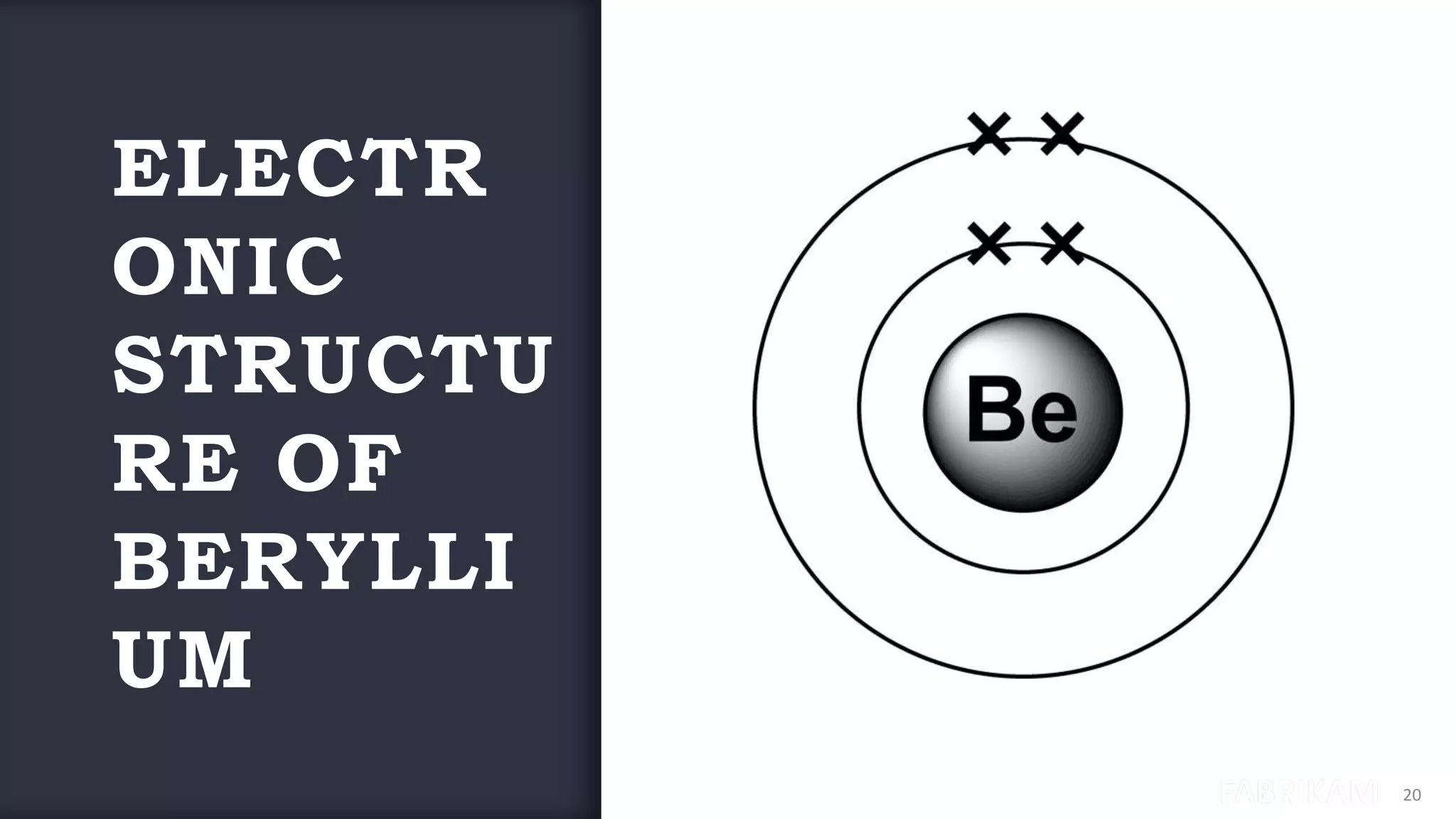
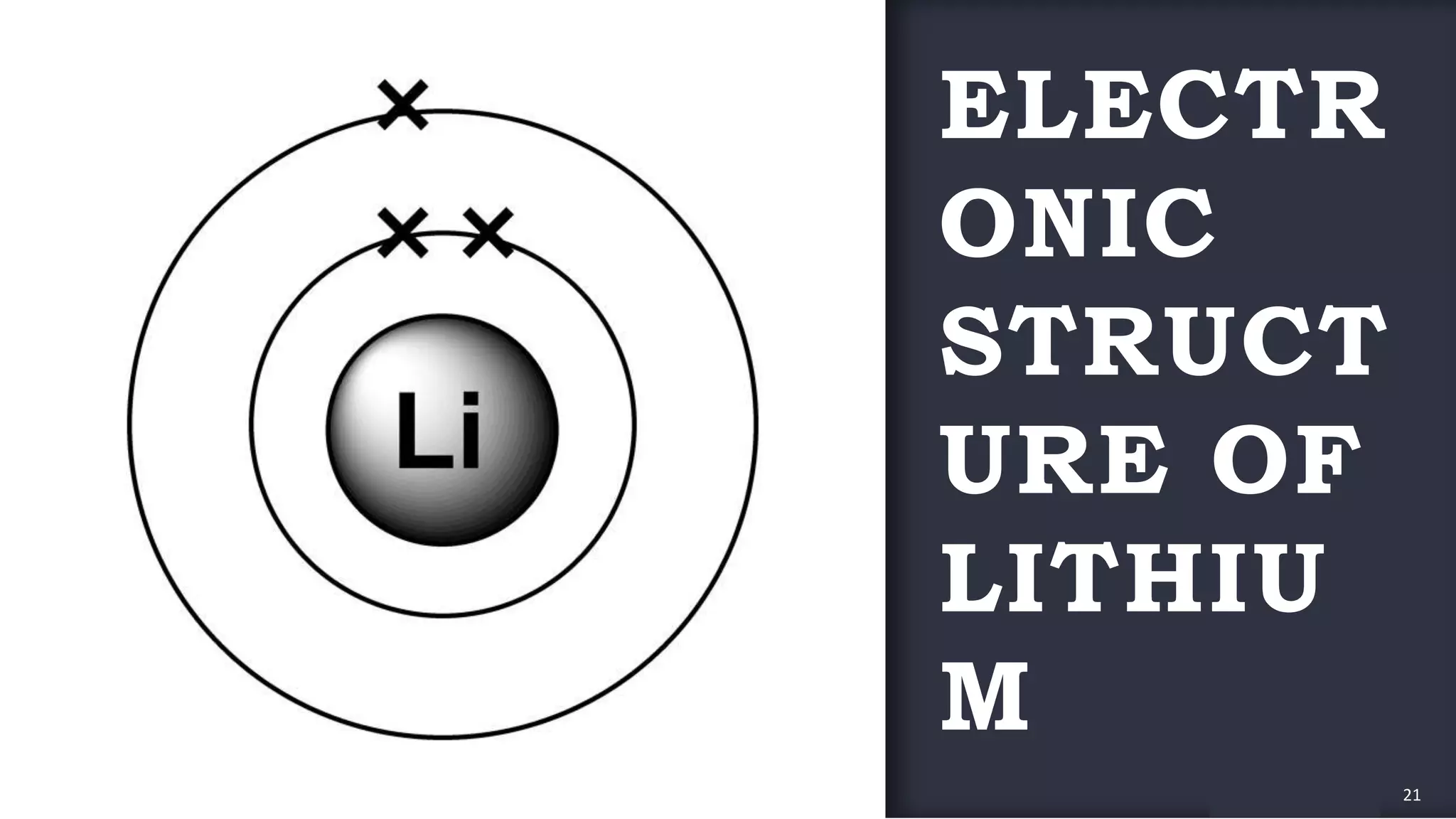
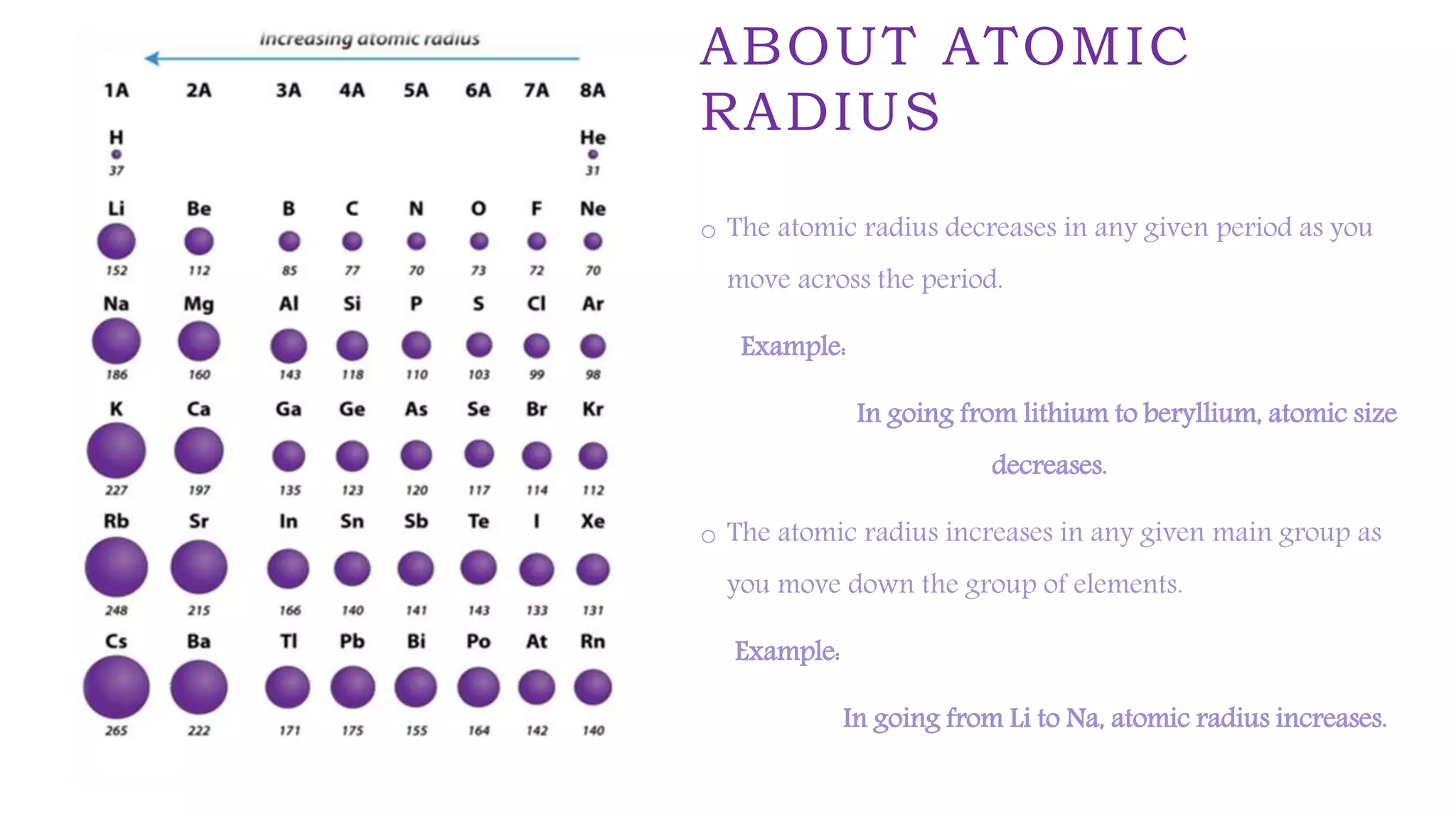
The document provides an overview of the periodic table, highlighting its significance in categorizing elements based on periods (horizontal rows) and groups (vertical columns). It discusses the properties of elements and how they change across periods and down groups, as well as the concepts of periodicity and atomic size. Additionally, it includes activities and questions to reinforce understanding of the periodic table and associated concepts.