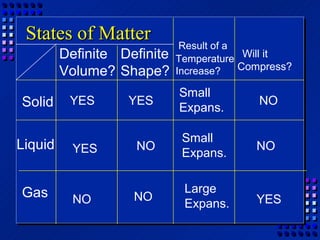
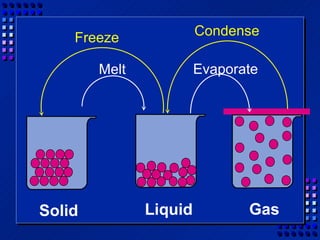
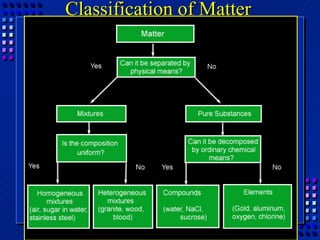
This document provides an overview of key concepts about matter and chemical changes from a chemistry textbook. It defines matter and its three main states (solid, liquid, gas). It describes properties as either extensive (depending on amount) or intensive (depending on type). It differentiates between physical and chemical changes, elements and compounds, and mixtures and pure substances. It outlines clues that indicate a chemical change has occurred and introduces the law of conservation of mass.