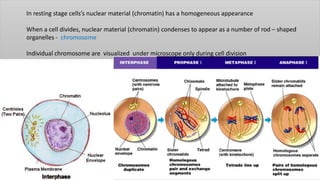
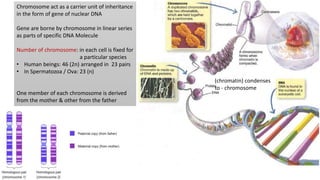
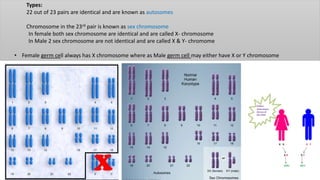
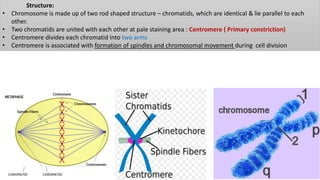
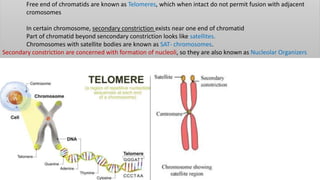
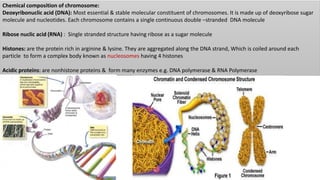
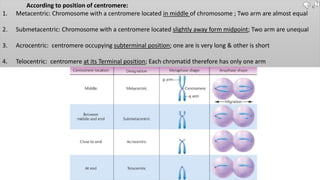
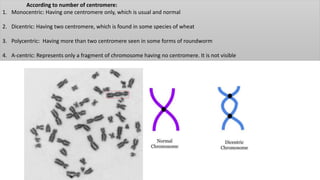
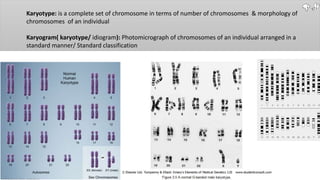
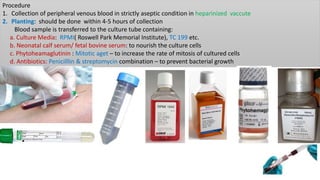
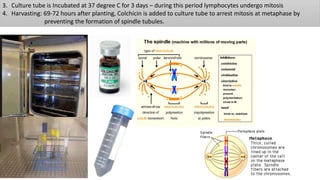
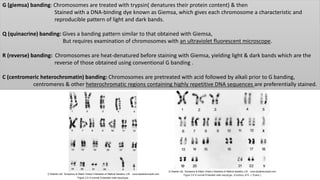
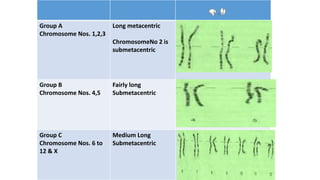
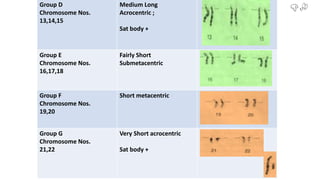
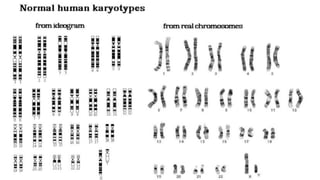
Chromosomes condense and become visible during cell division. They carry genes and act as units of inheritance. Humans normally have 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs. 22 pairs are autosomes and the 23rd pair are the sex chromosomes, which are XX in females and XY in males. Chromosomes are made of DNA, RNA, proteins and can be classified based on features like centromere position. Karyotyping involves capturing chromosome images during cell division and arranging them into a standardized layout called a karyotype based on length, centromere position, etc. This allows identifying normal or abnormal chromosome numbers and structures.