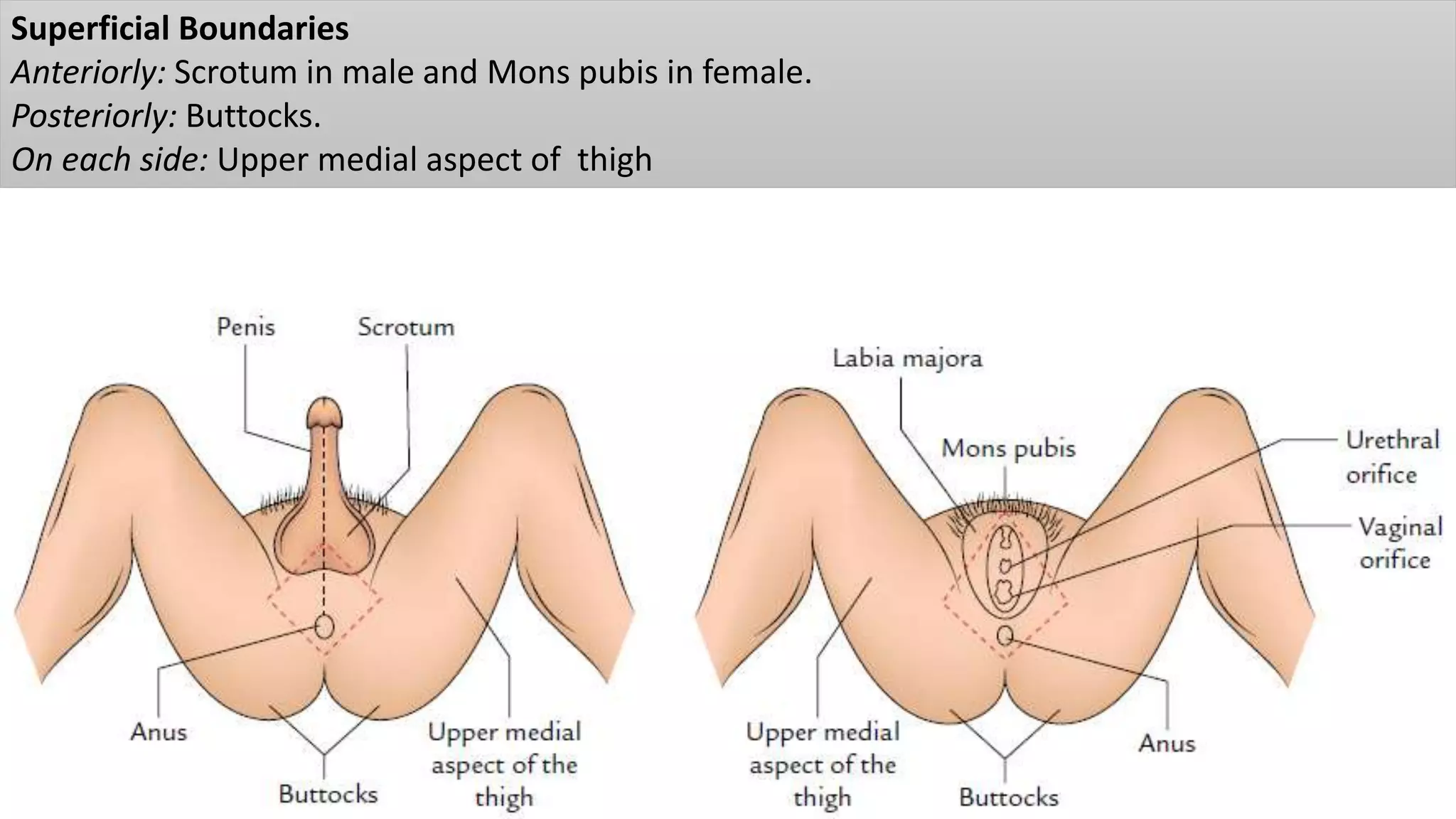
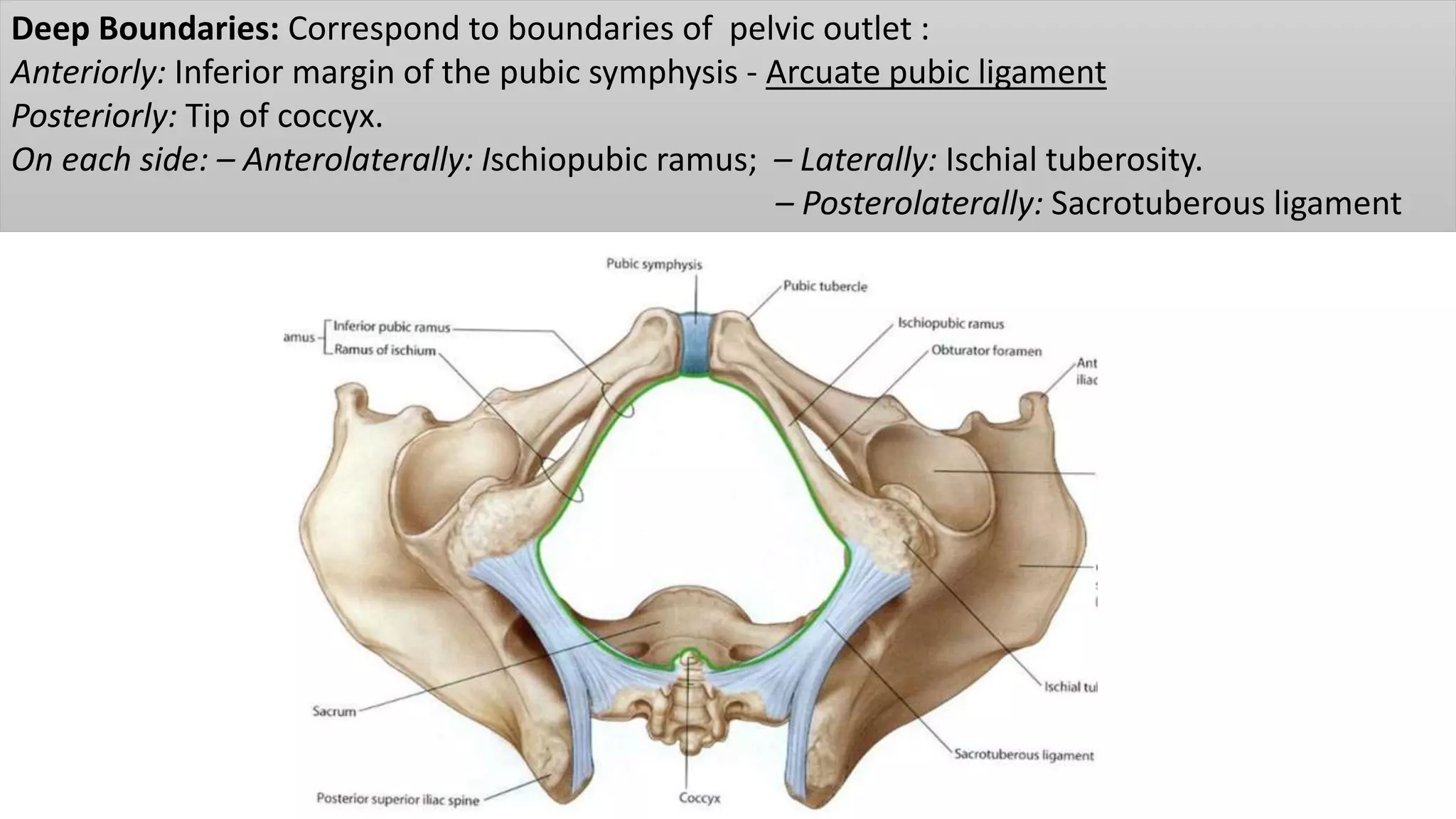
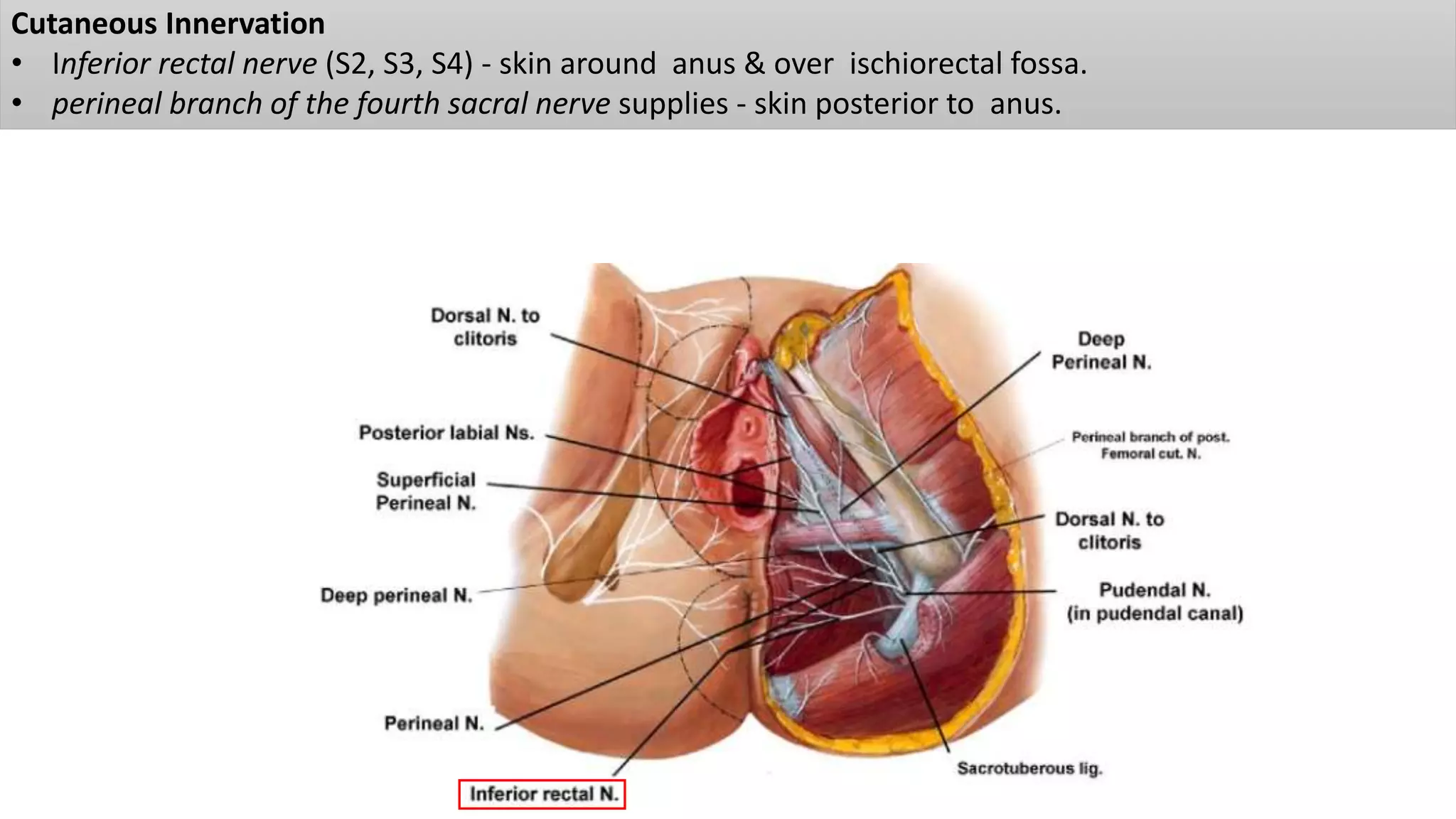
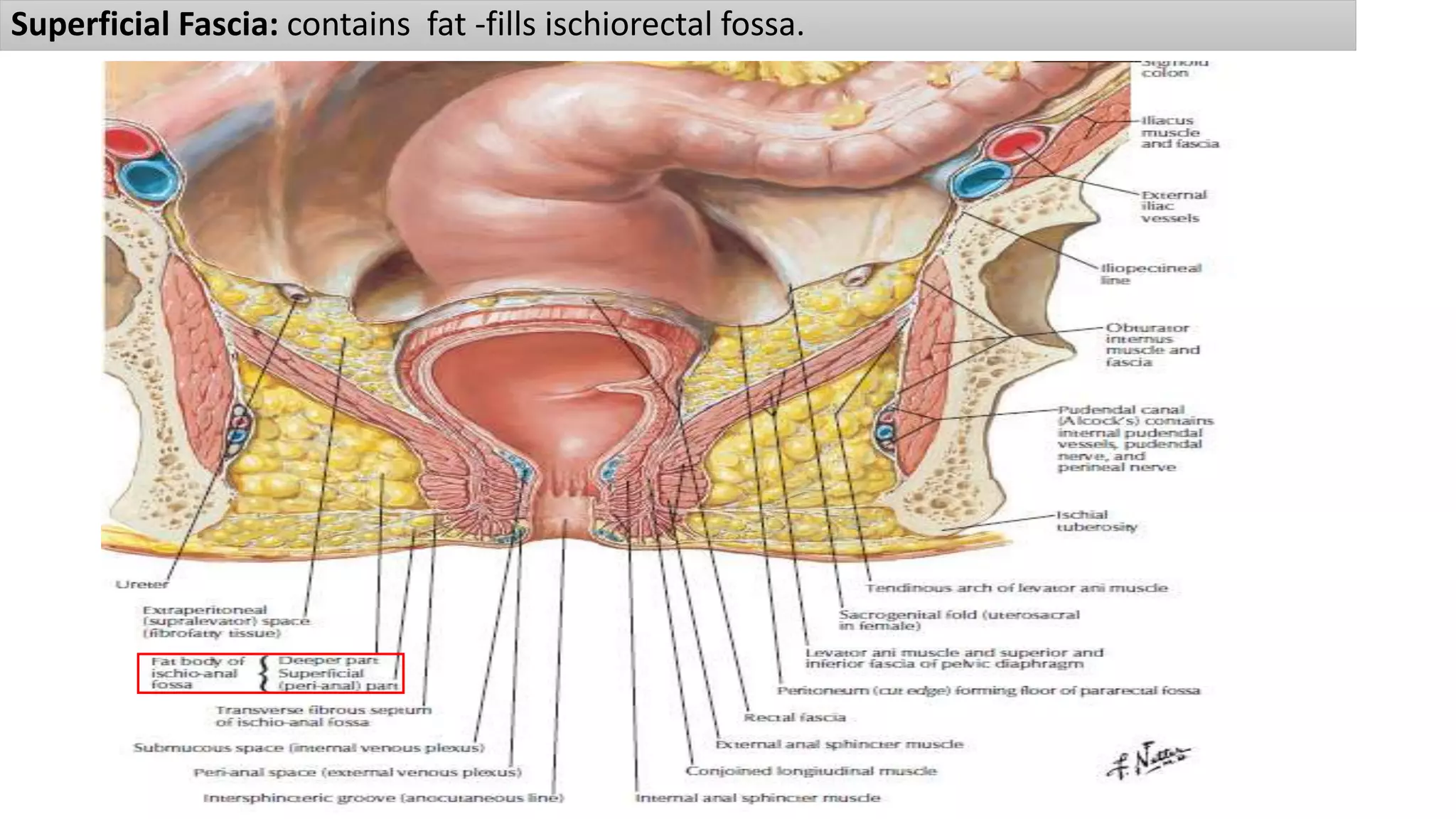
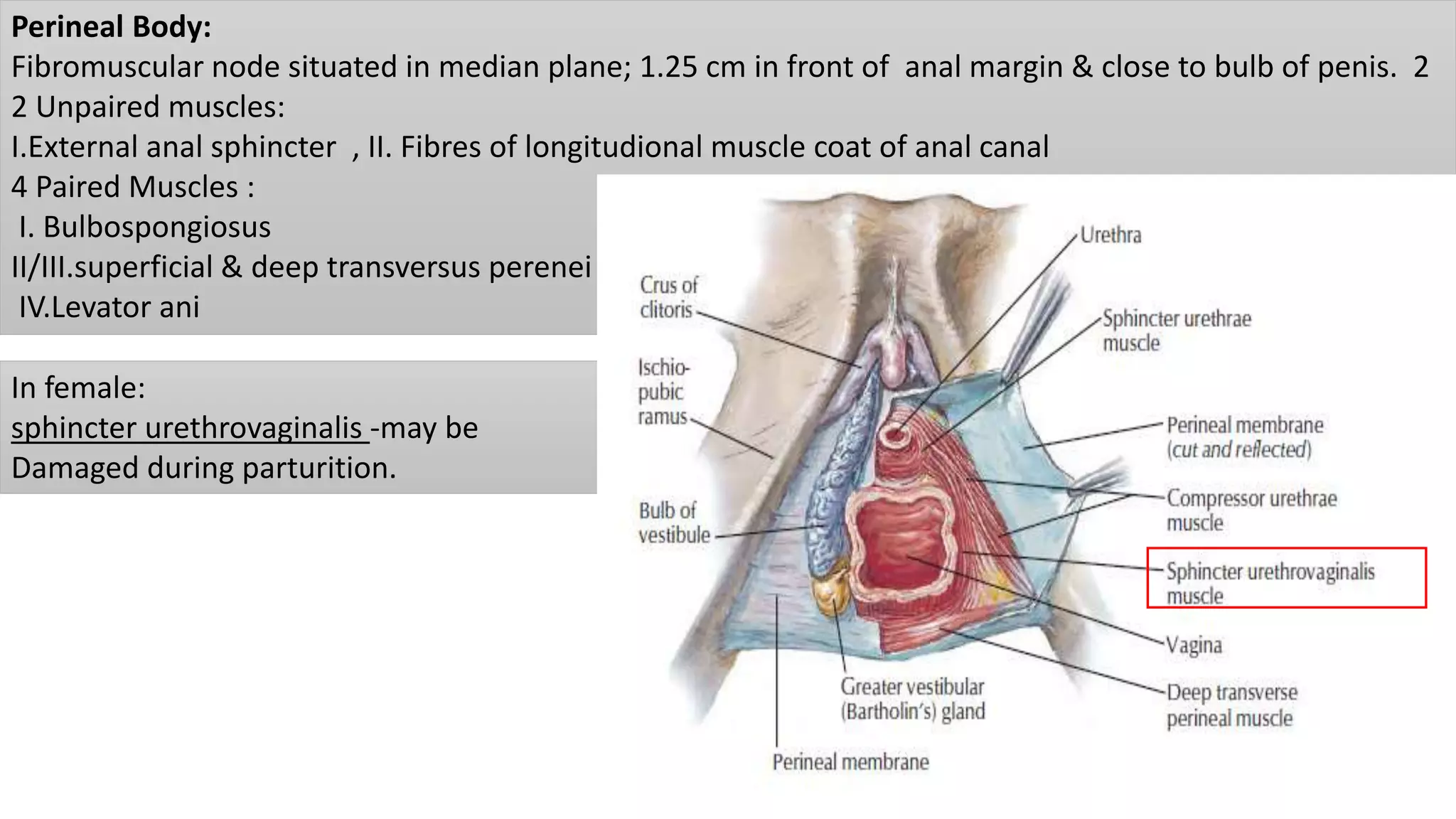
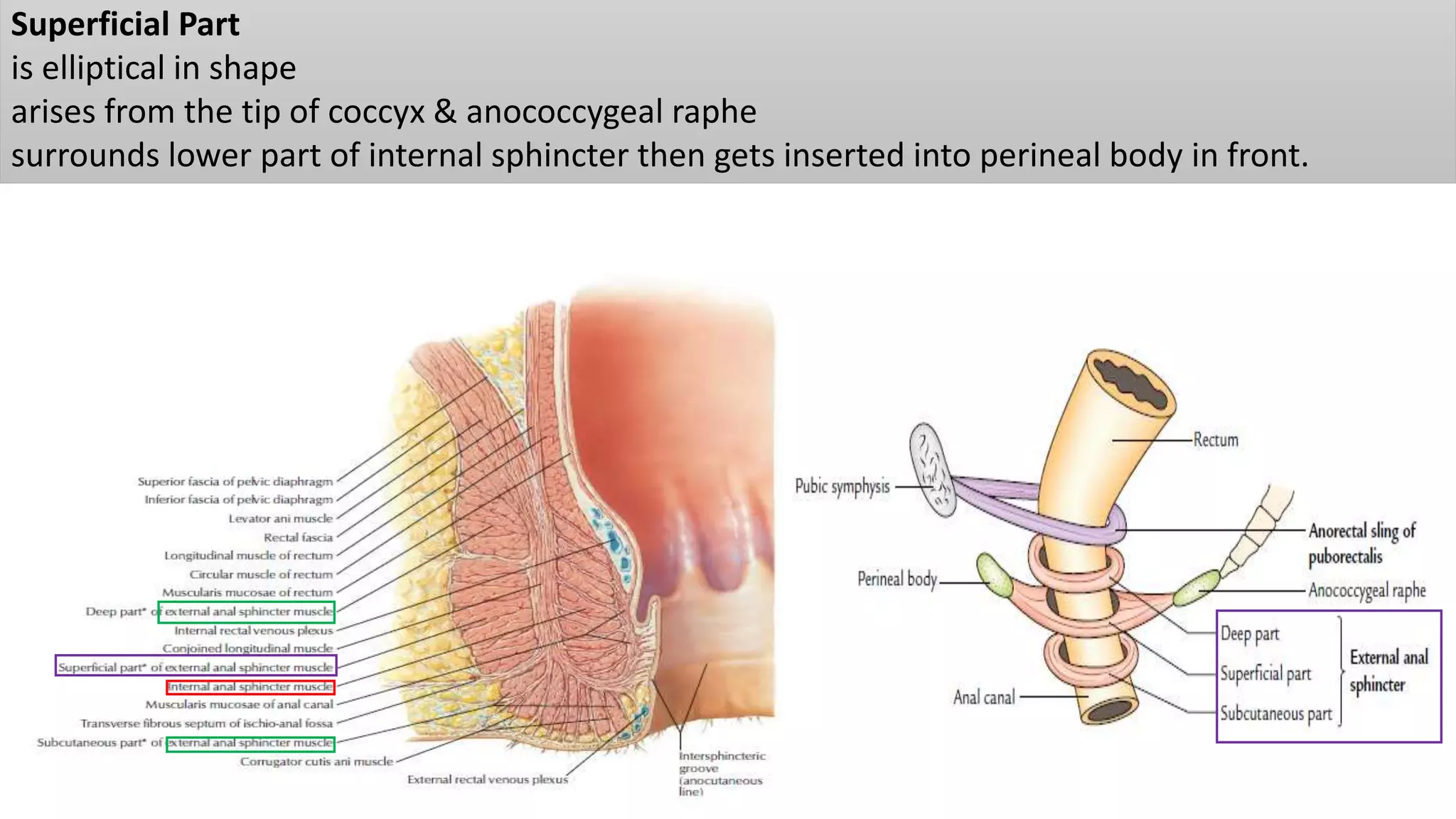
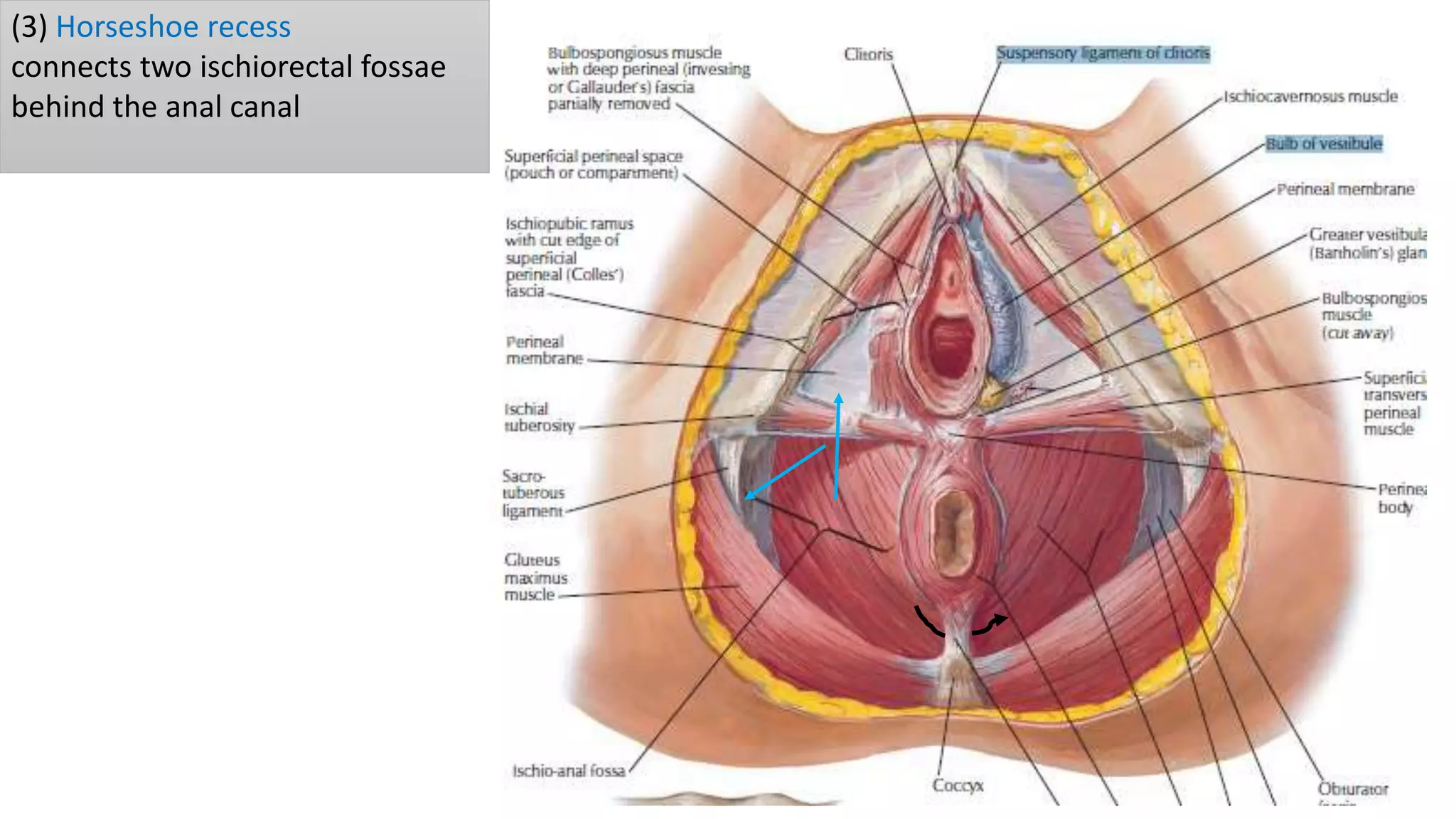
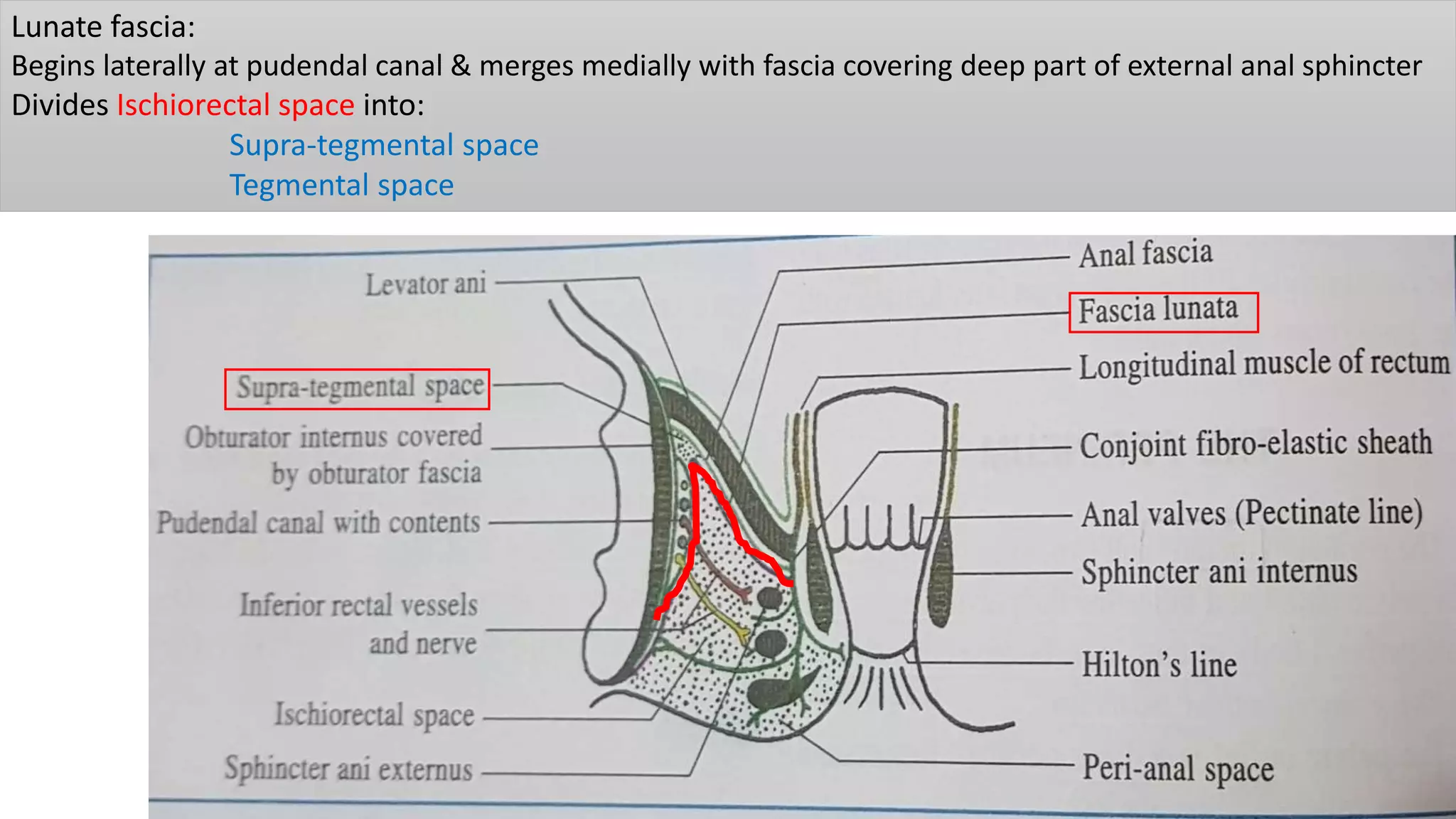
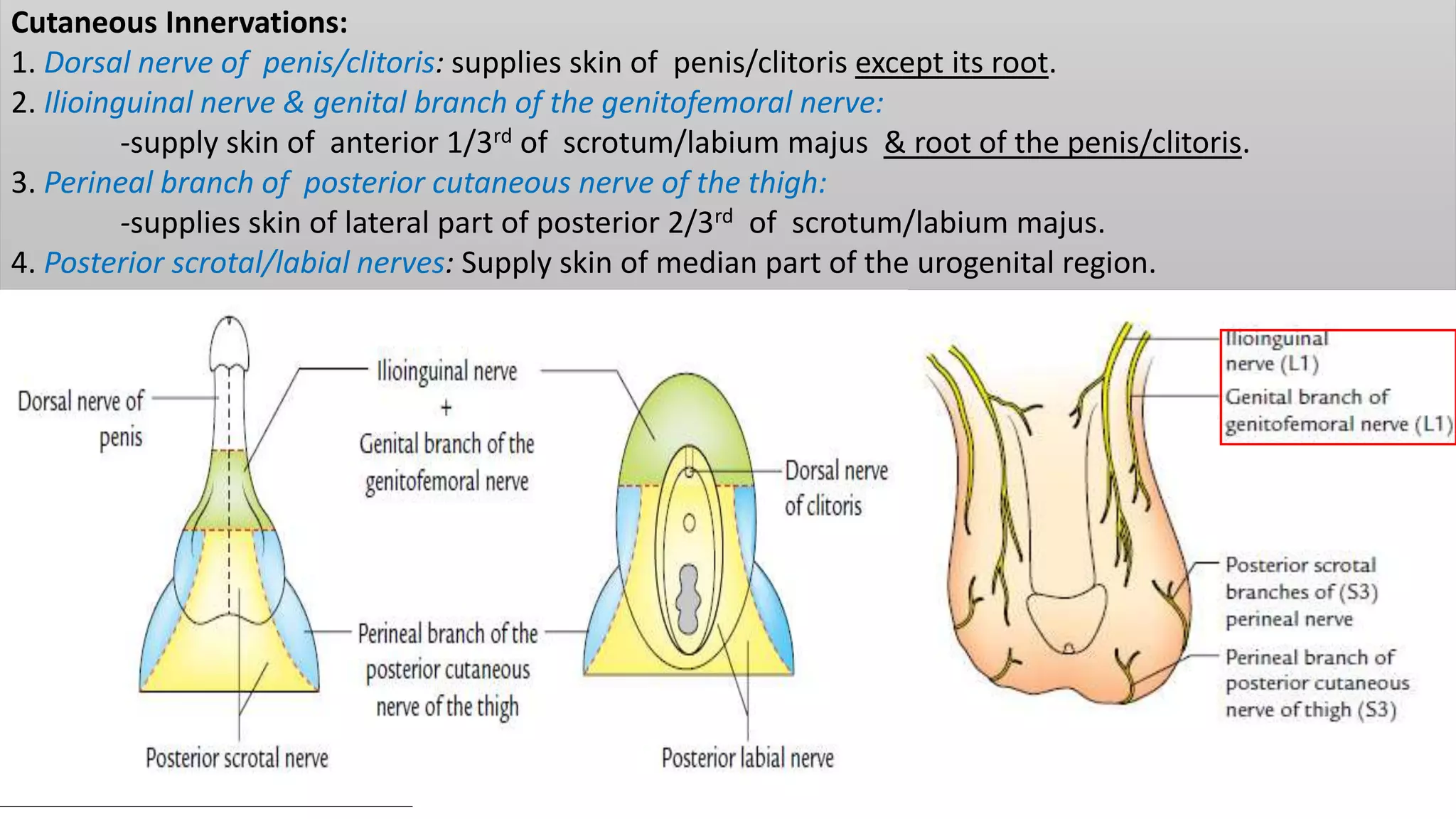
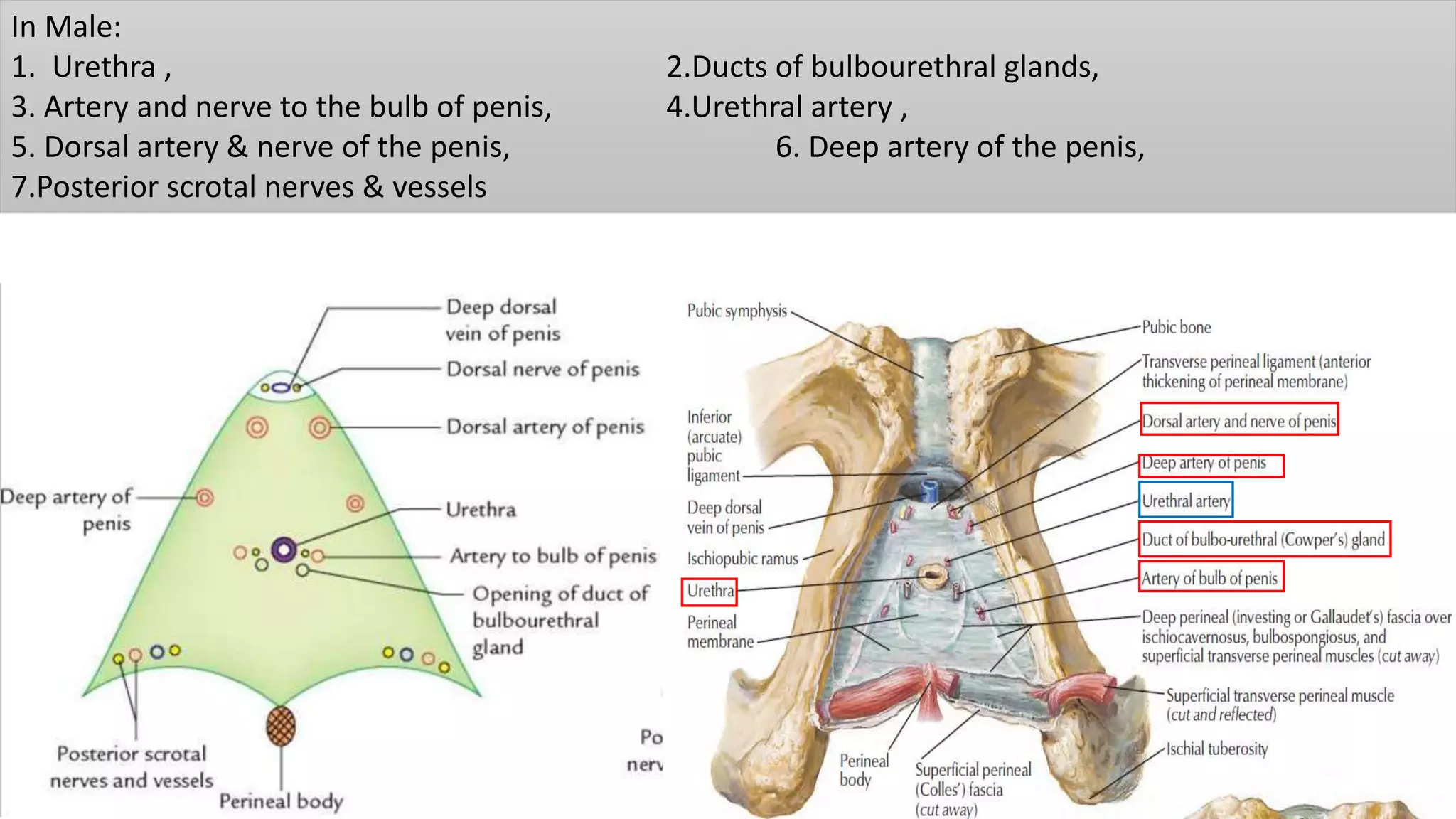
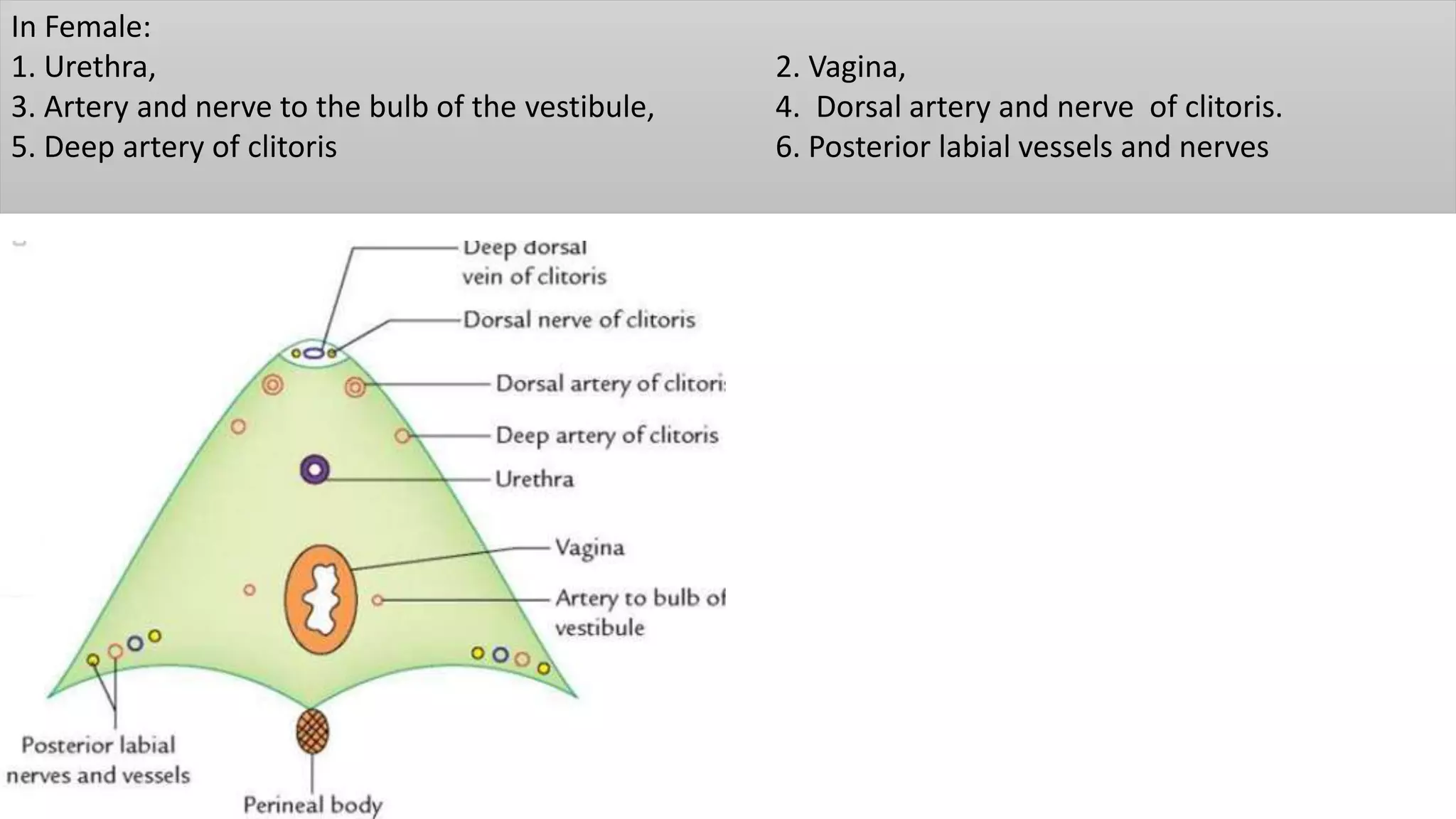
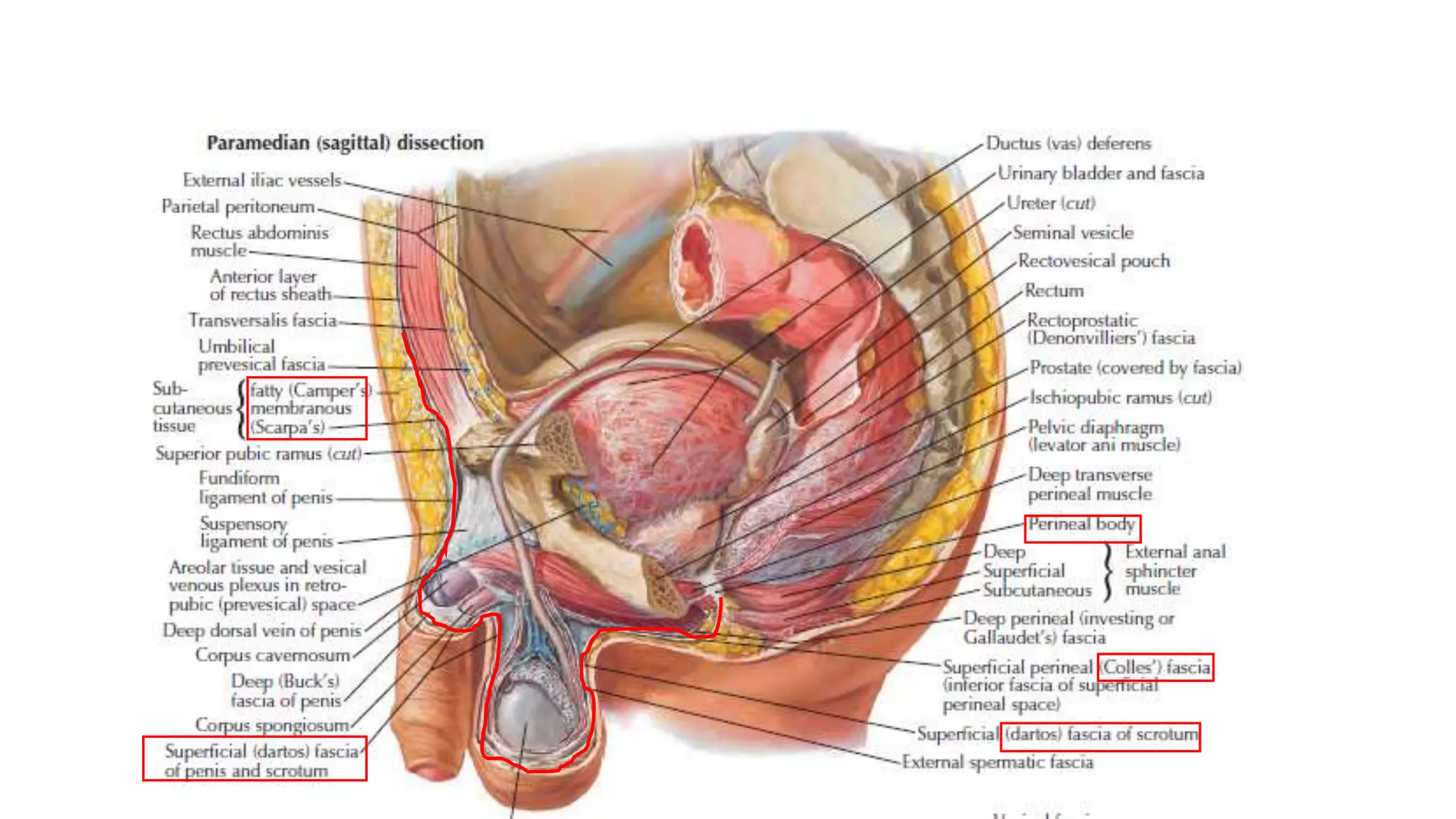
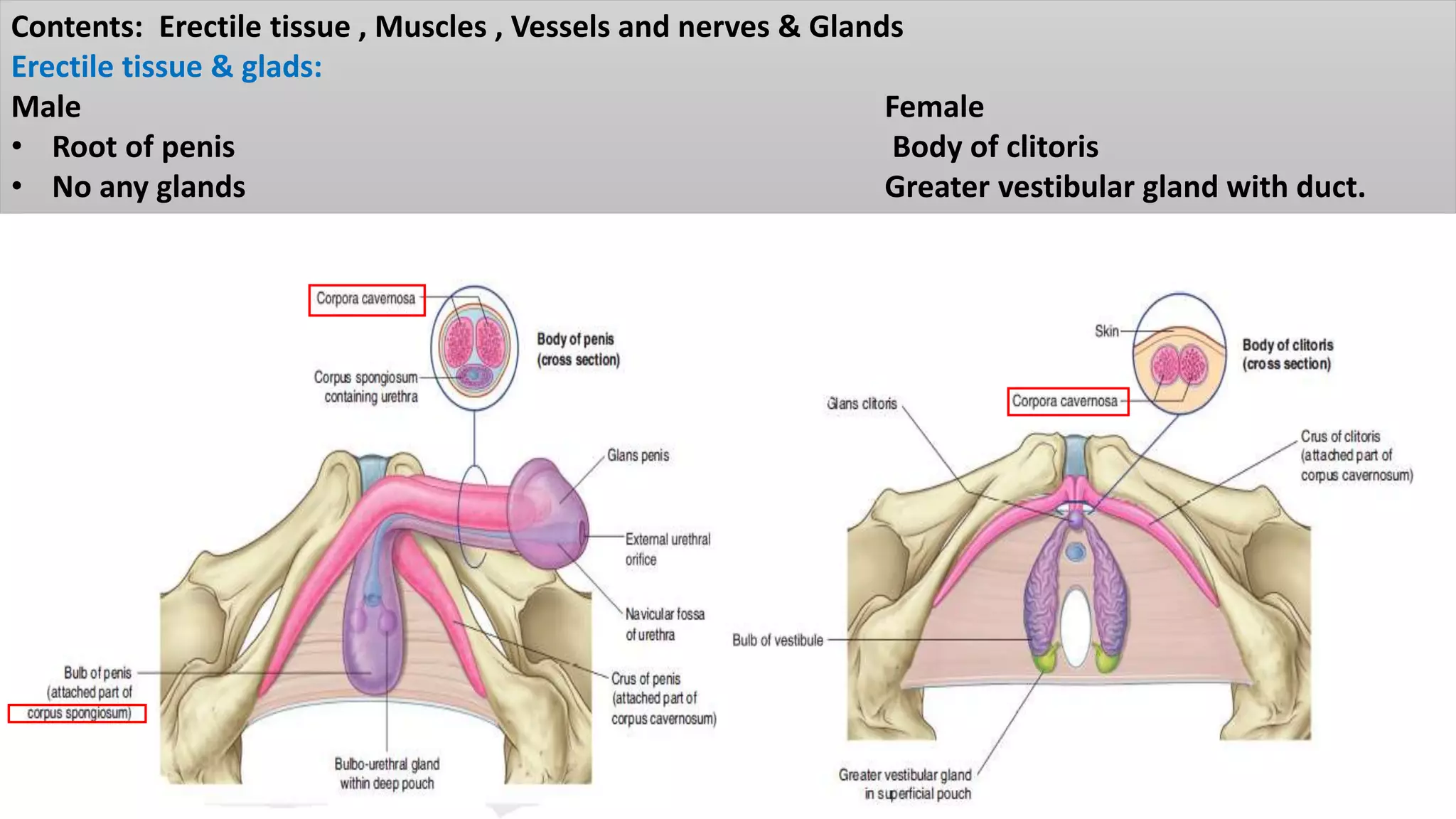
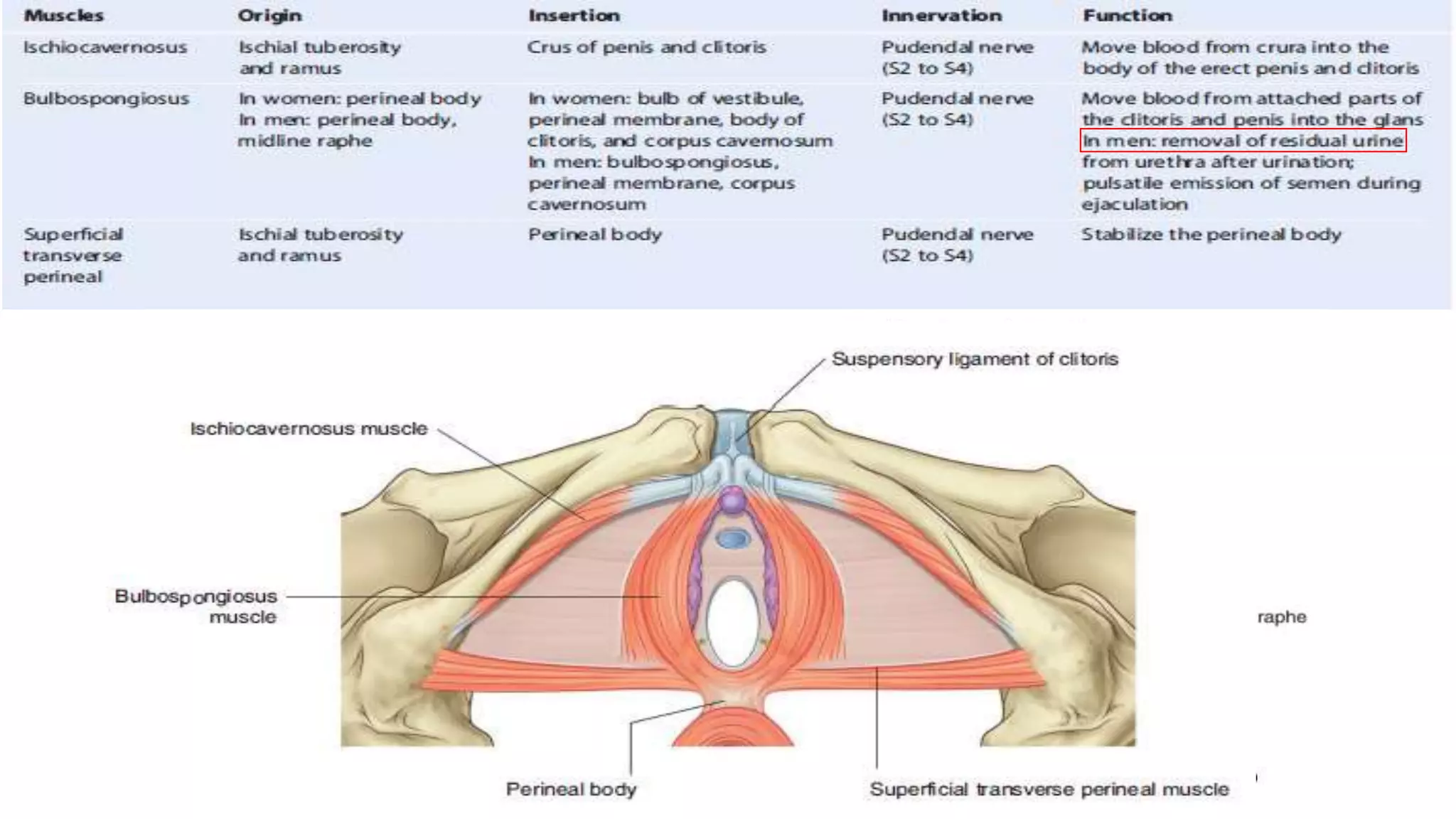
The perineum is the region between the thighs that contains the external genitalia and anal opening. It is divided into the urogenital triangle anteriorly and anal triangle posteriorly. The anal triangle contains the anal canal and ischioanal fossae on each side, bounded by muscles and ligaments. The urogenital triangle contains the external genital structures and openings of the urethra and vagina. It is bounded by the ischiopubic rami and separated into superficial and deep spaces by the perineal membrane. Various muscles, nerves, vessels and glands are located within the spaces of the perineum.