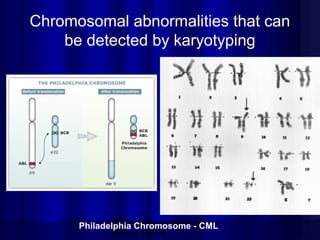
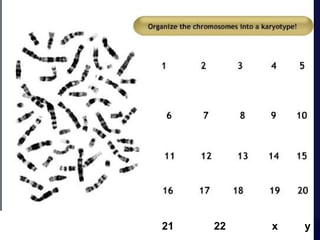
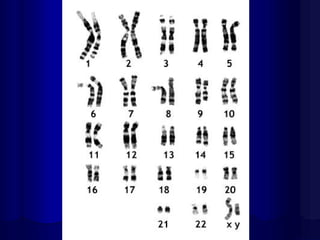
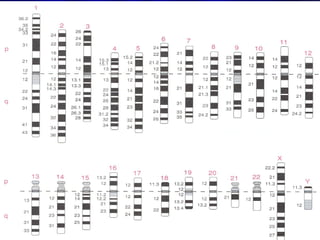
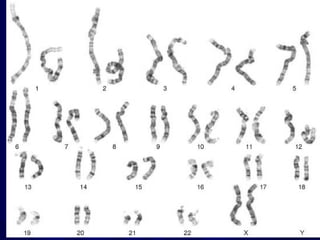
This document describes the process of karyotyping and identifying human chromosomes through G-banding. Key points include:
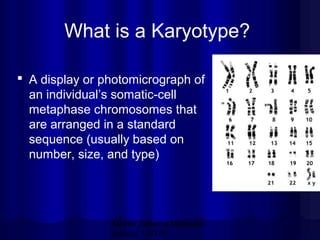
- Karyotyping involves preparing, staining, and observing human chromosomes to diagnose genetic disorders and identify chromosomal abnormalities.
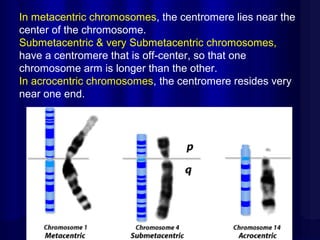
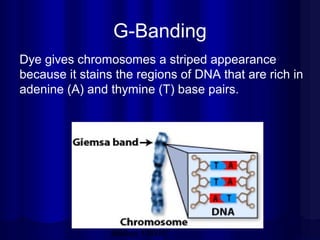
- Humans normally have 23 pairs of chromosomes, including 22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome. G-banding allows identification of chromosomes based on size, banding pattern, and centromere position.
- The karyotyping process involves culturing cells, arresting cell division, staining chromosomes, and analyzing spreads under a microscope to identify numerical or structural abnormalities. G-banding produces dark and light bands that make each chromosome pair unique.
- Common chrom