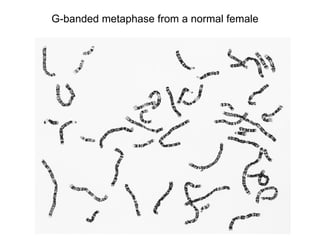
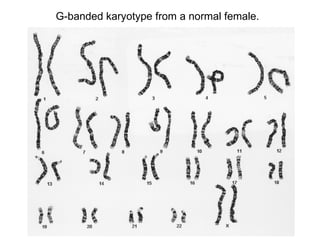
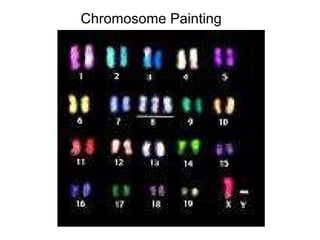
Karyotyping involves analyzing chromosomes to identify abnormalities. There are various banding techniques that stain chromosomes differently based on DNA composition, allowing identification. G-banding is commonly used, staining regions rich in adenine and thymine dark and regions rich in guanine and cytosine light. This reveals unique banding patterns for each chromosome. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) uses fluorescent probes to target specific DNA sequences, allowing analysis at the gene level.