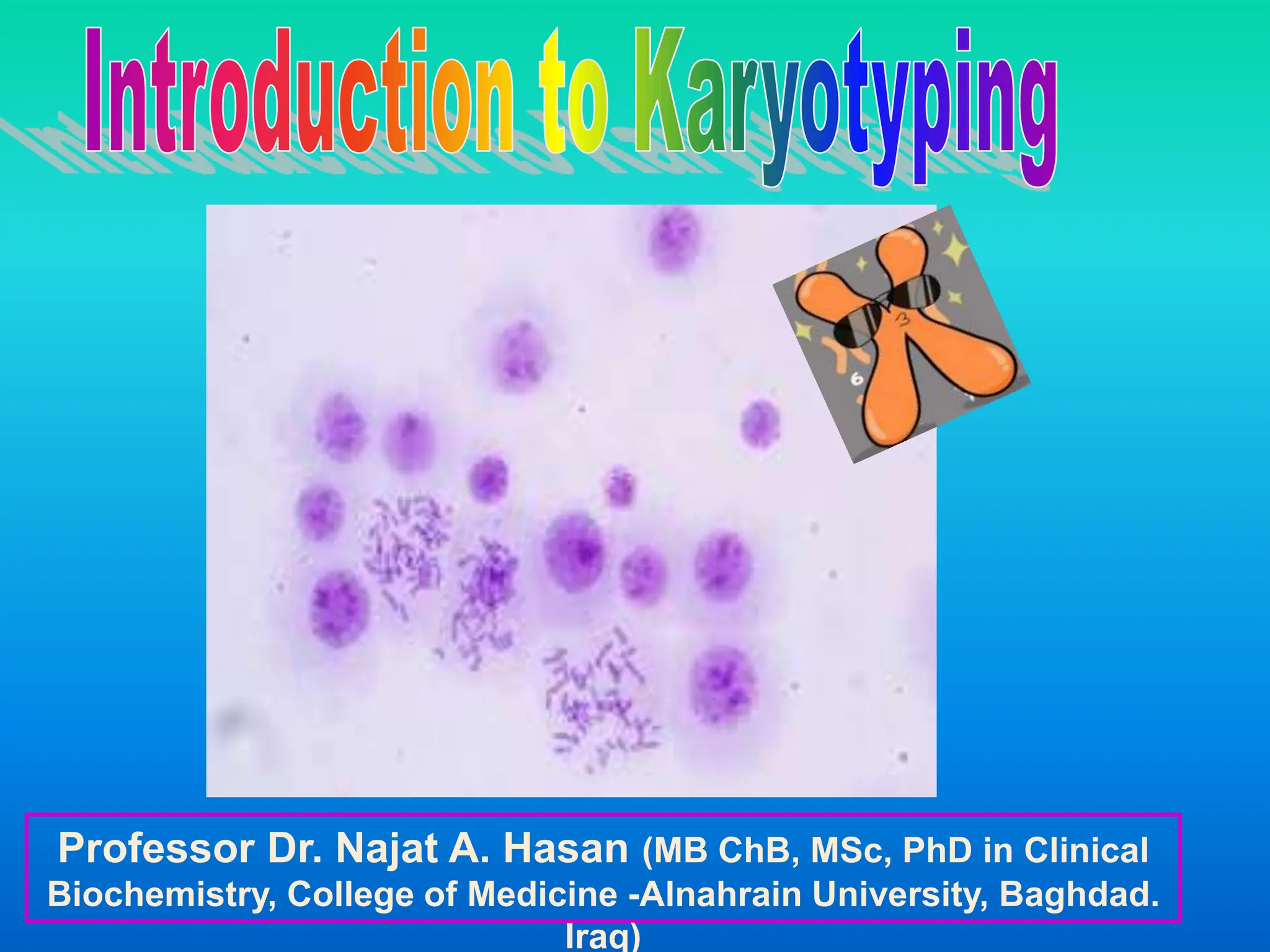
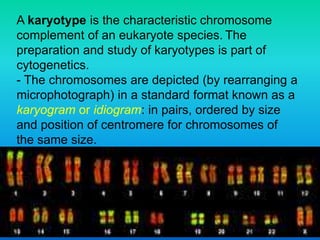
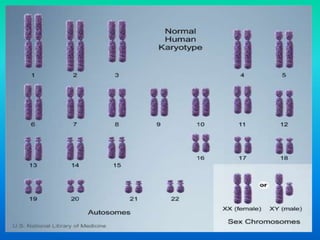
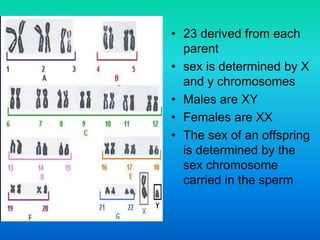
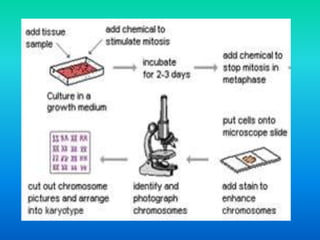
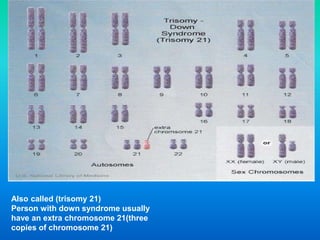
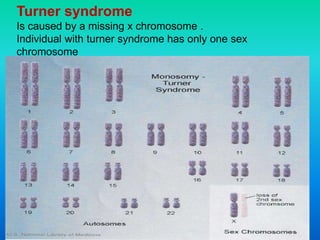
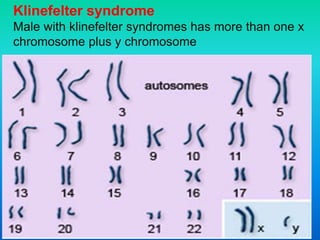
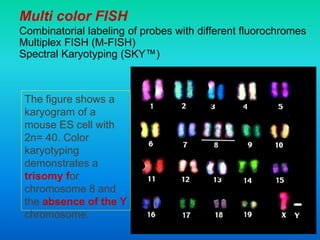
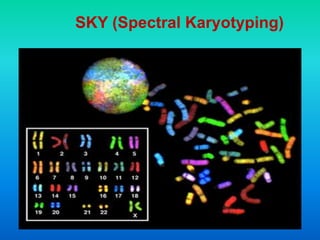
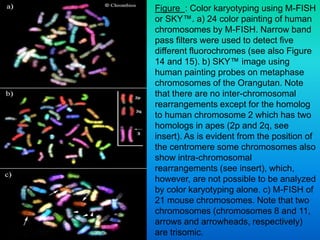
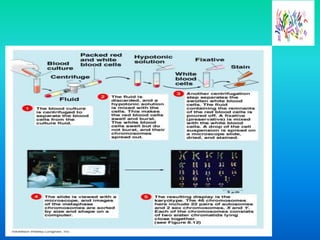
Karyotyping involves staining and analyzing chromosomes to identify any abnormalities. A normal human karyotype contains 23 chromosome pairs, including 22 autosomal and 1 sex chromosome pair. Chromosomes are categorized by centromere position and size. Karyotyping is used to diagnose conditions like Down syndrome that involve extra or missing chromosomes. New techniques like spectral karyotyping allow full chromosome visualization with color-coded labeling for detailed analysis.