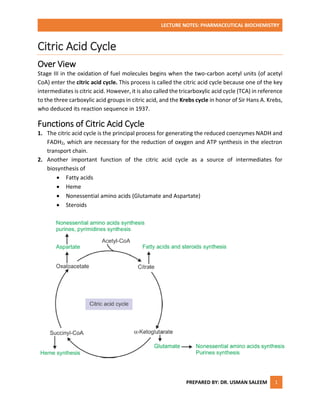
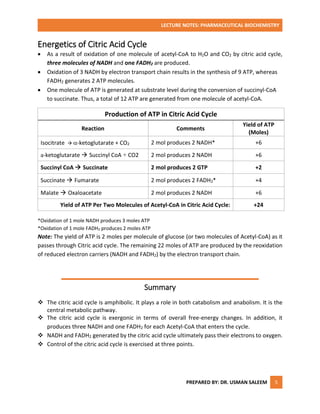
The citric acid cycle is the principal process for generating reduced coenzymes NADH and FADH2, which are necessary for ATP synthesis. It takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and involves eight steps catalyzed by different enzymes. Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle and is oxidized, producing carbon dioxide and the reduced coenzymes that fuel ATP production. Regulation occurs at three steps to precisely adjust the cycle's rate according to cellular energy needs. Overall, 12 ATP molecules are generated for each acetyl-CoA molecule that completes the citric acid cycle.