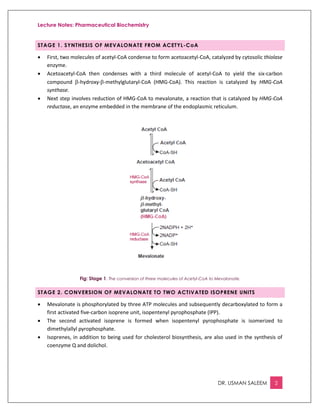
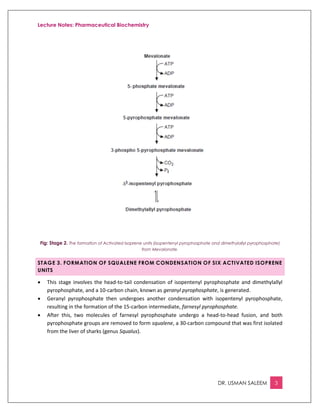
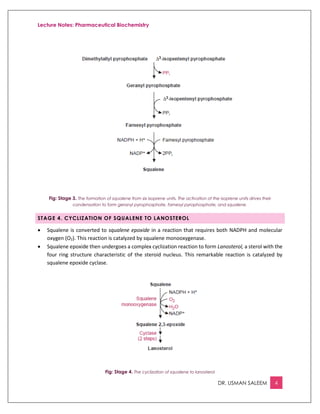
This document provides an overview of cholesterol biosynthesis, which occurs in most cells but primarily in the liver and intestine. There are 5 stages: 1) acetyl-CoA is converted to mevalonate, 2) mevalonate is converted to activated isoprene units, 3) six isoprene units condense to form squalene, 4) squalene is cyclized to lanosterol, and 5) lanosterol is converted to cholesterol over 20 steps. HMG-CoA reductase, which converts HMG-CoA to mevalonate, is the rate-limiting step and is regulated by feedback from cholesterol and bile acids as well as hormones like insulin, glucagon
![Lecture Notes: Pharmaceutical Biochemistry
DR. USMAN SALEEM 1
CHOLESTEROL BIOSYNTHESIS
OVER VIEW
Cholesterol is synthesized by a pathway that occurs in most cells of the body. Liver and intestine are major
sites of cholesterol synthesis.
The ultimate precursor of all the carbon atoms in cholesterol and in the other steroids that are derived
from cholesterol is the acetyl group of acetyl CoA. Acetyl-CoA can be obtained from several sources,
including the b-oxidation of fatty acids, the oxidation of ketogenic amino acids such as leucine and lysine,
and the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction. The reducing power for cholesterol synthesis is supplied in the
form of NADPH.
LOCATION
Most de novo synthesis occurs in the liver and intestine where cholesterol is synthesized from acetyl CoA
in the cytosol.
STAGES OF CHOLESTEROL BIOSYNTHESIS
There are 5 stages in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.
Acetate Mevalonate [Isoprene] Squalene Lanosterol Cholesterol
C2 C6 C5 C30 C30 C27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cholesterolbiosynthesis-200124095203/85/Cholesterol-biosynthesis-1-320.jpg)