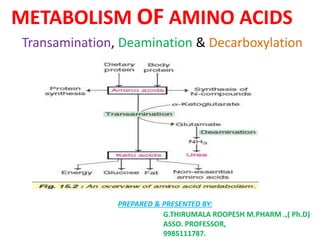
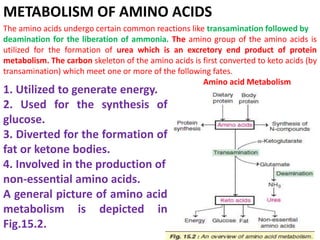
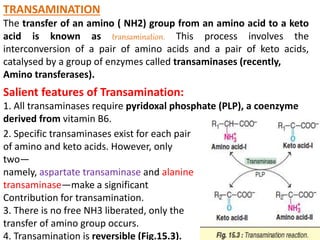
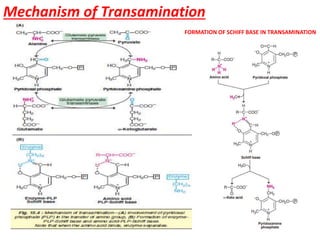
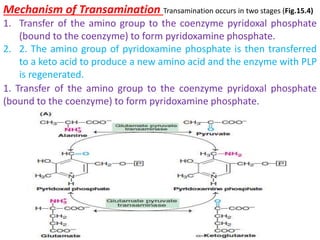
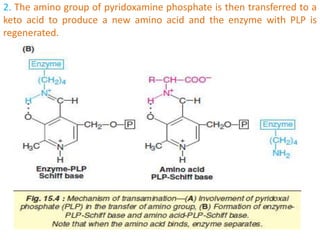
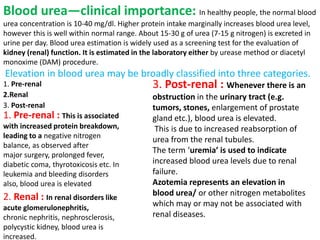
This document discusses the metabolism of amino acids. It begins by outlining common reactions like transamination and deamination that amino acids undergo to release ammonia. Transamination involves the transfer of amino groups between amino acids and keto acids, allowing for interconversion. Deamination results in the liberation of ammonia, which is used to synthesize urea via the urea cycle in the liver. The carbon skeletons of amino acids are converted to keto acids that can be used for energy production, glucose synthesis, or formation of fats/ketone bodies. The document then goes into more detail about specific processes involved in amino acid metabolism, including transamination, deamination, decarboxylation, the urea cycle,