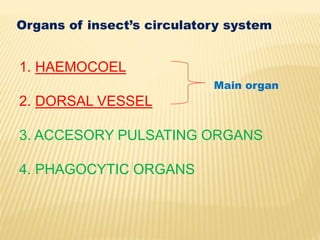
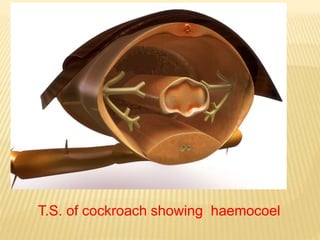
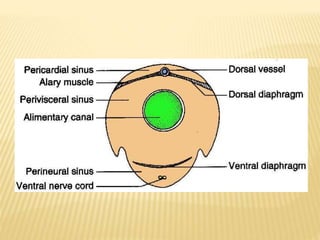
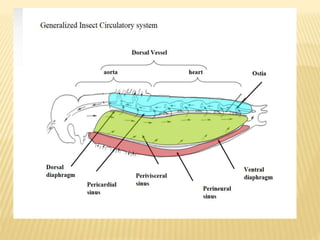
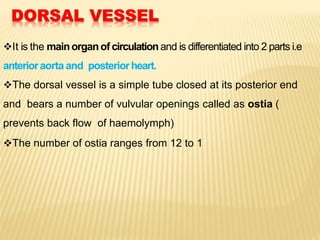
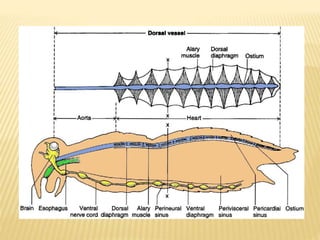
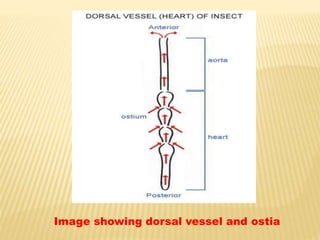
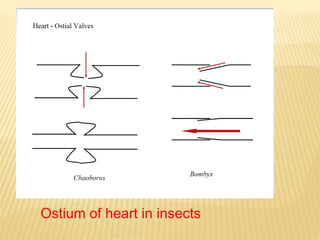
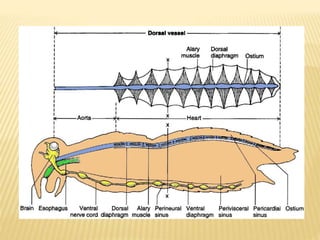
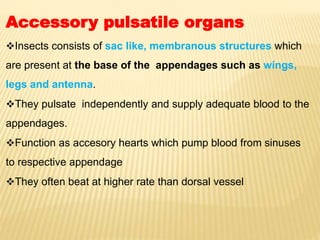
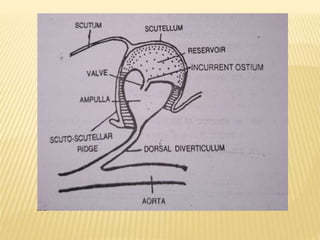
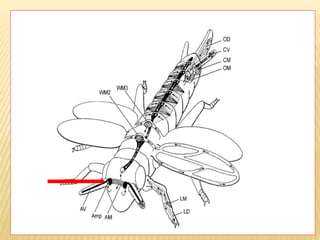
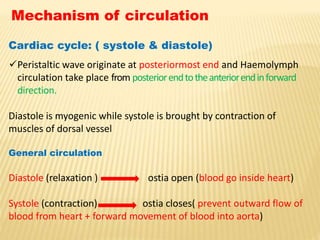
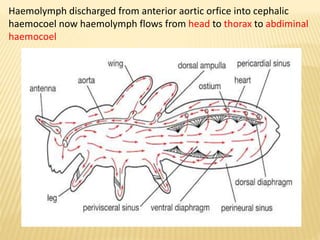
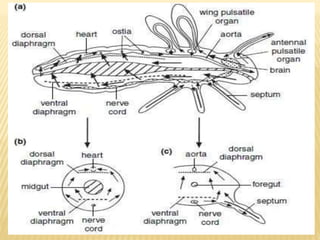
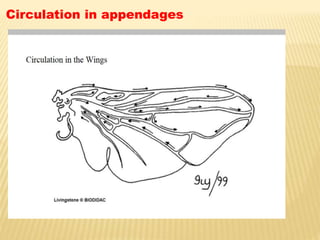
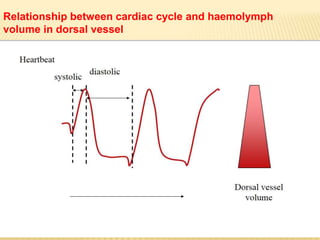
The circulatory system of insects is open and transports nutrients, waste, and aids in defense. It consists of a hemocoel body cavity and a dorsal vessel heart tube. The hemocoel is divided into three sinuses by diaphragms. Blood flows through ostia into the dorsal vessel which pumps it through the body during systole and diastole. Accessory pulsatile organs help circulate blood to appendages. Phagocytic organs filter the hemolymph. Blood moves posterior to anterior via peristalsis through the hemocoel sinuses and organs before returning to the heart.