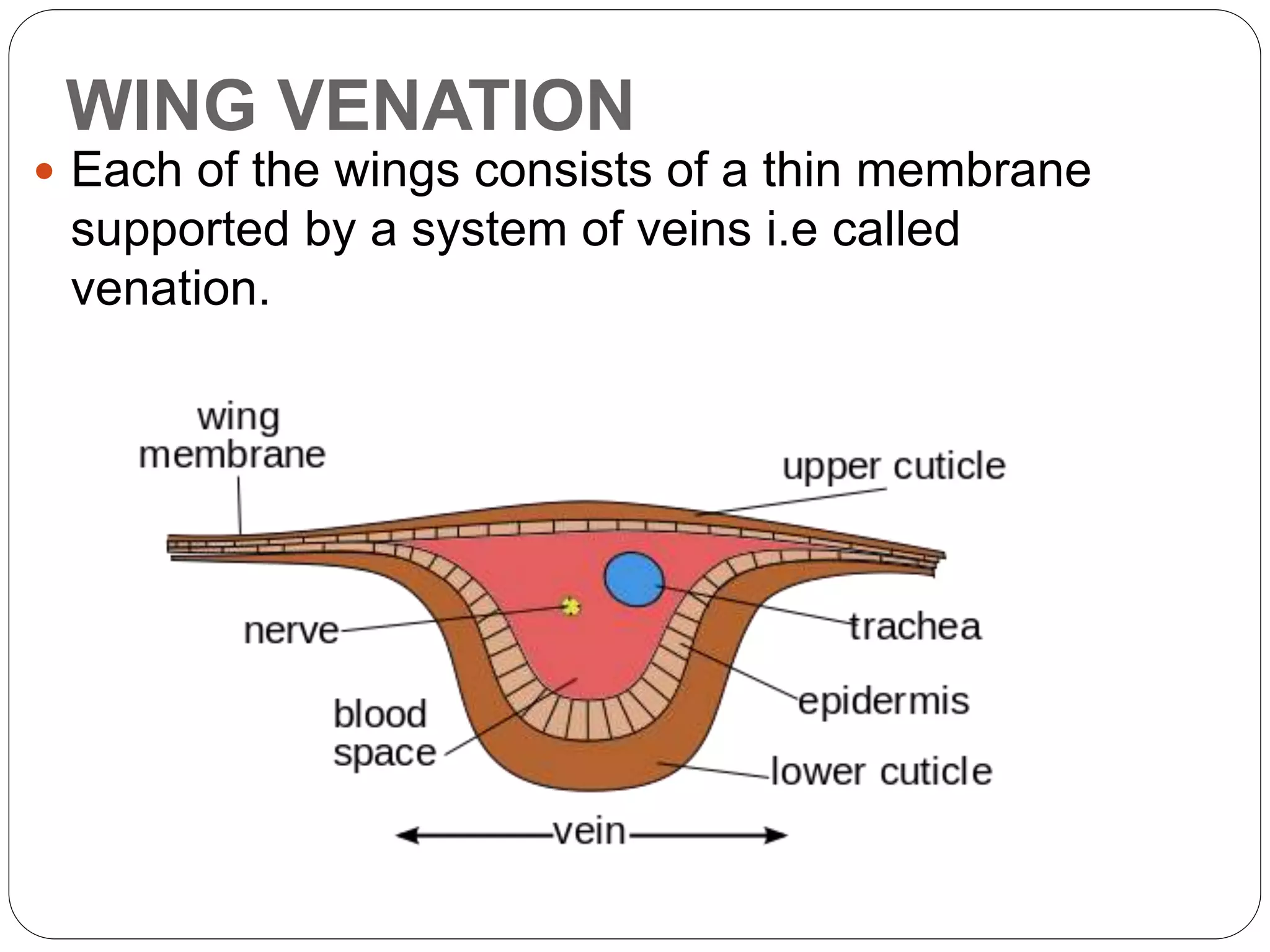
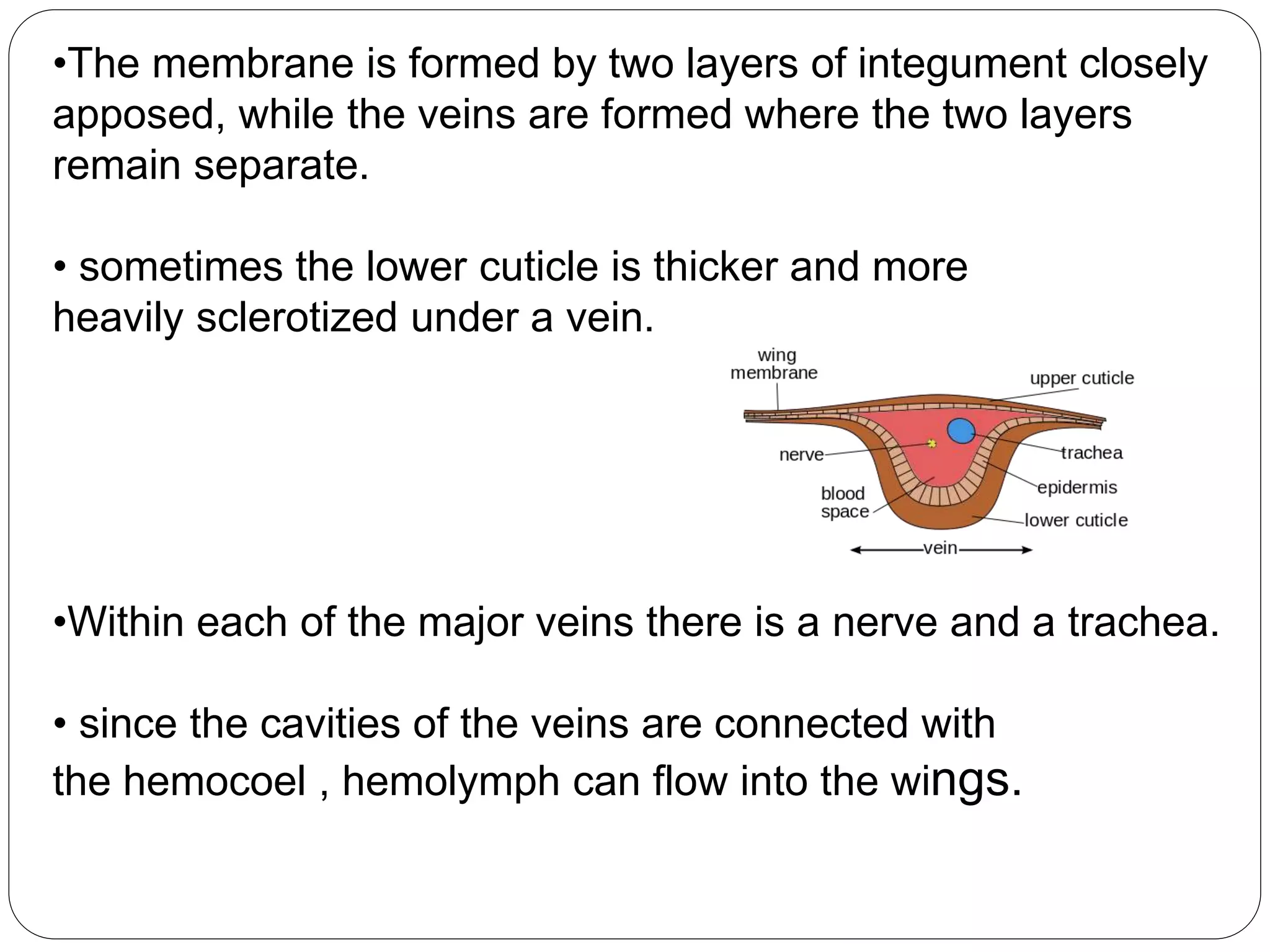
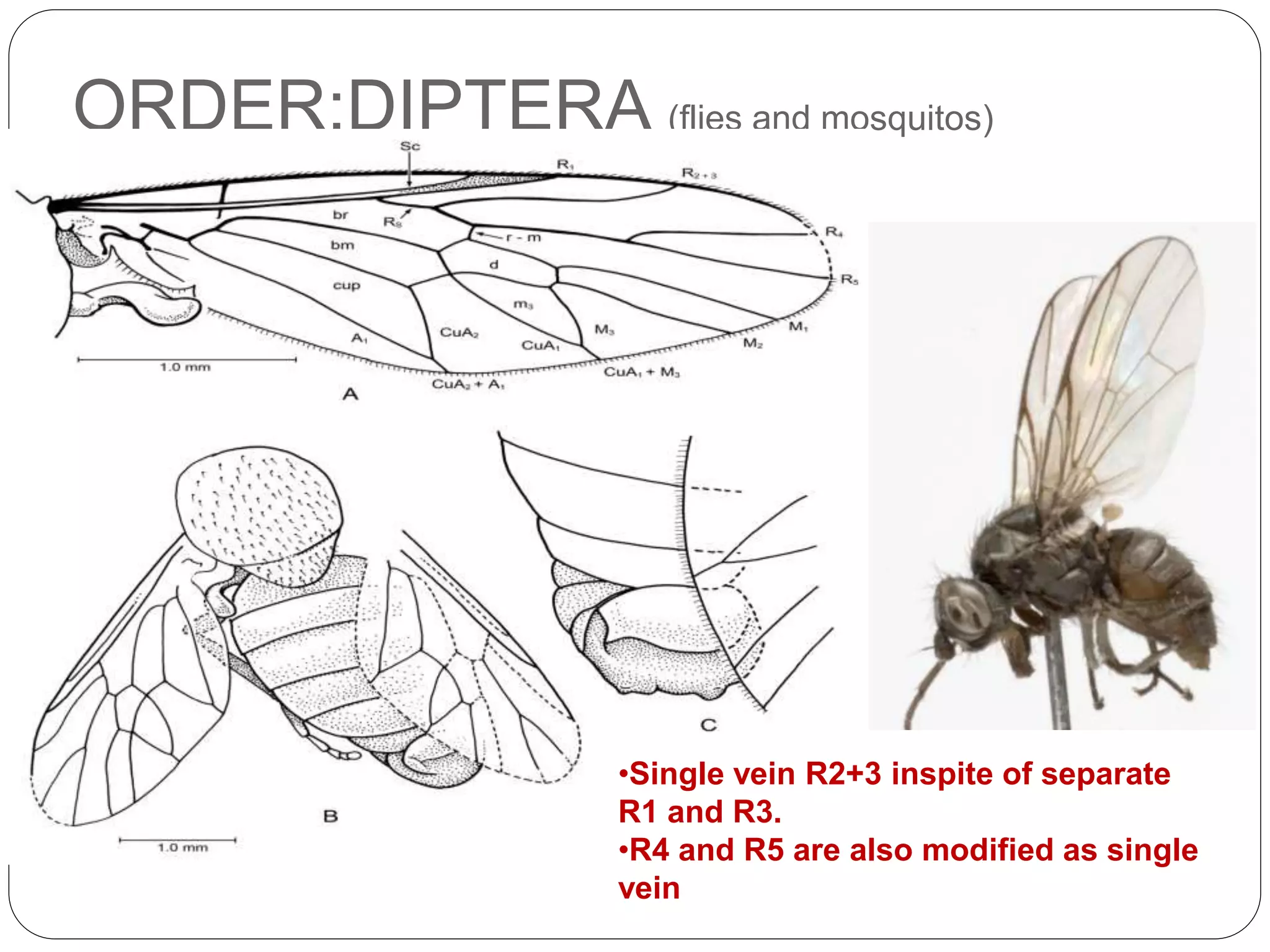
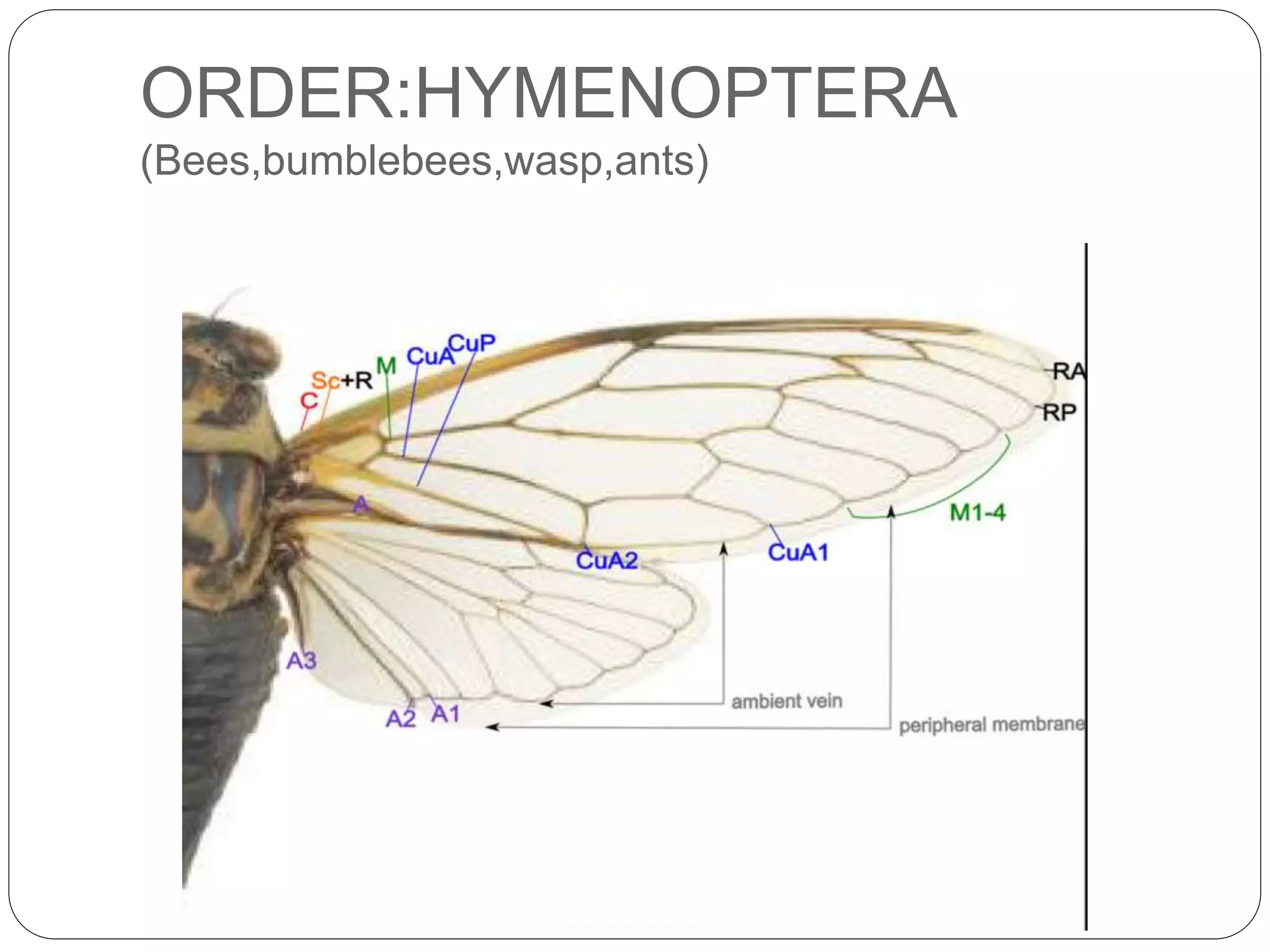
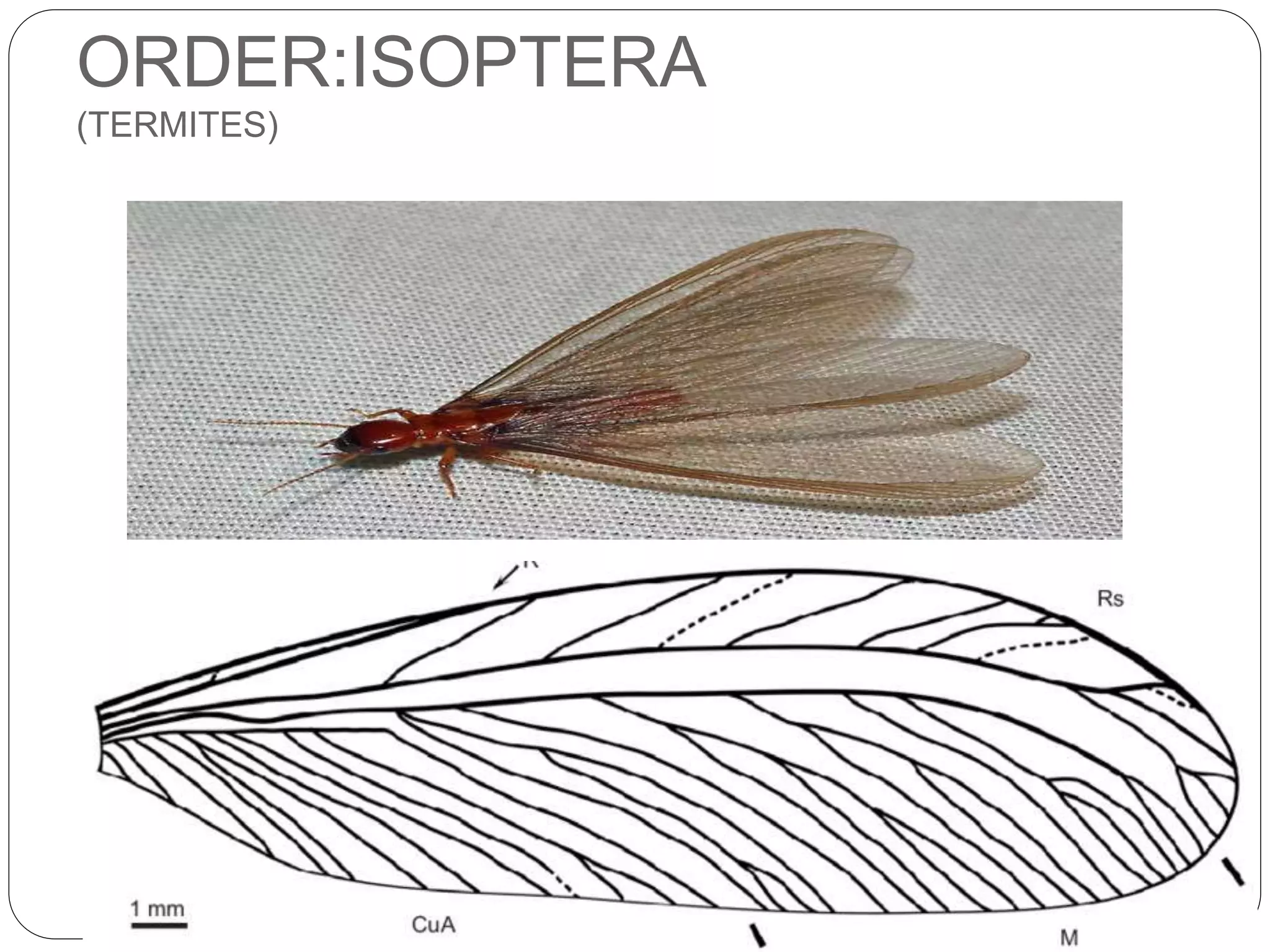
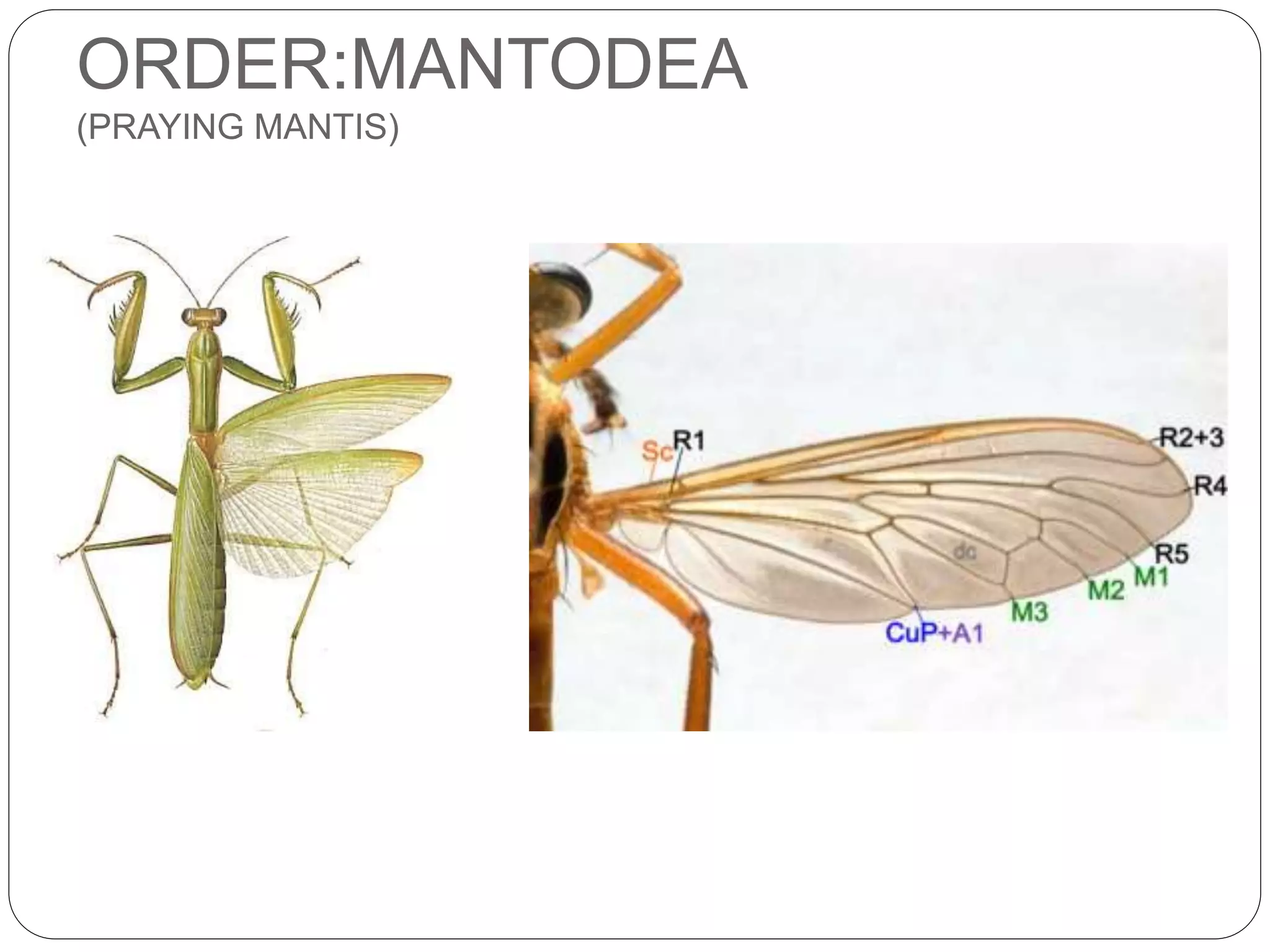
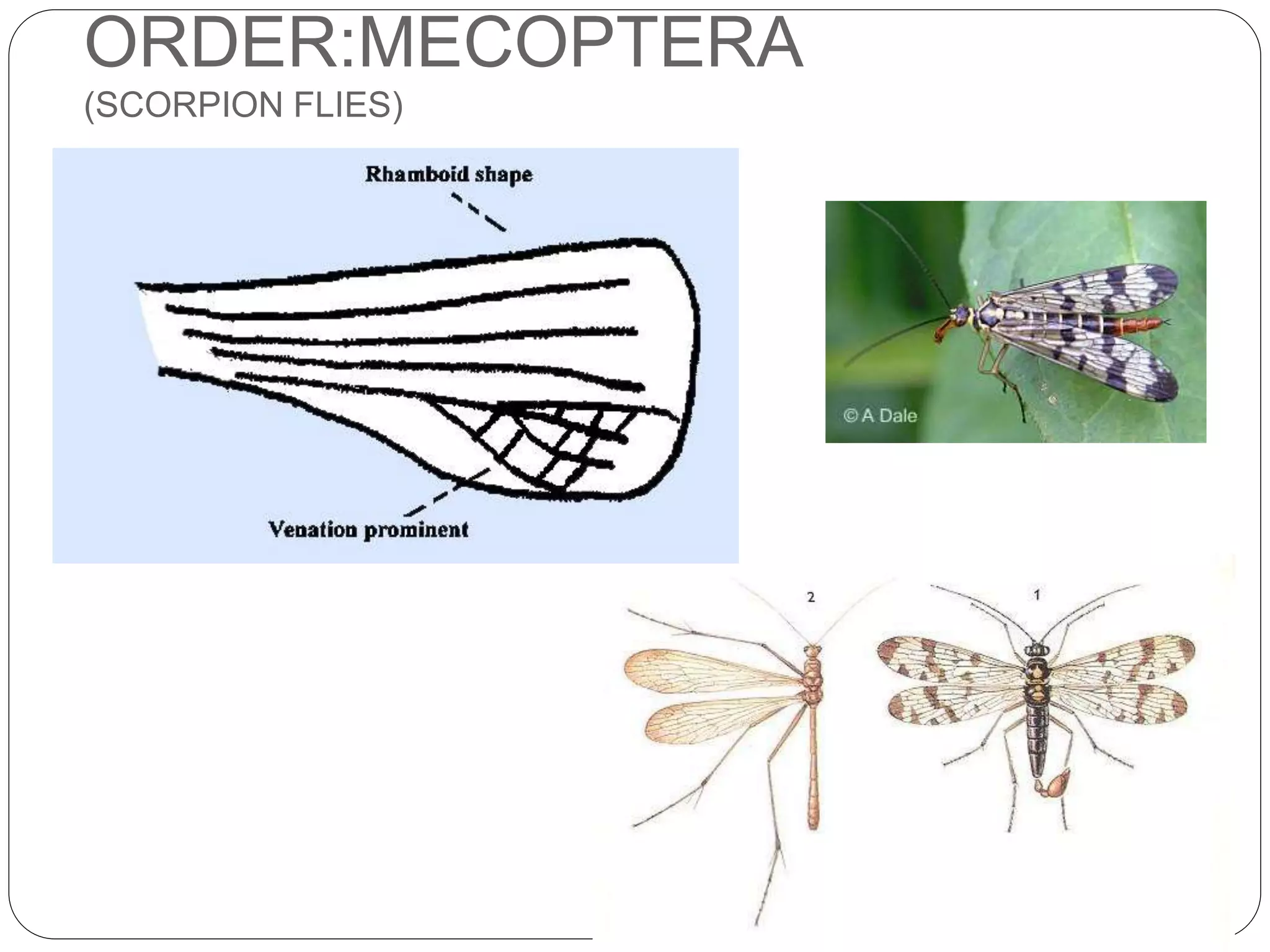
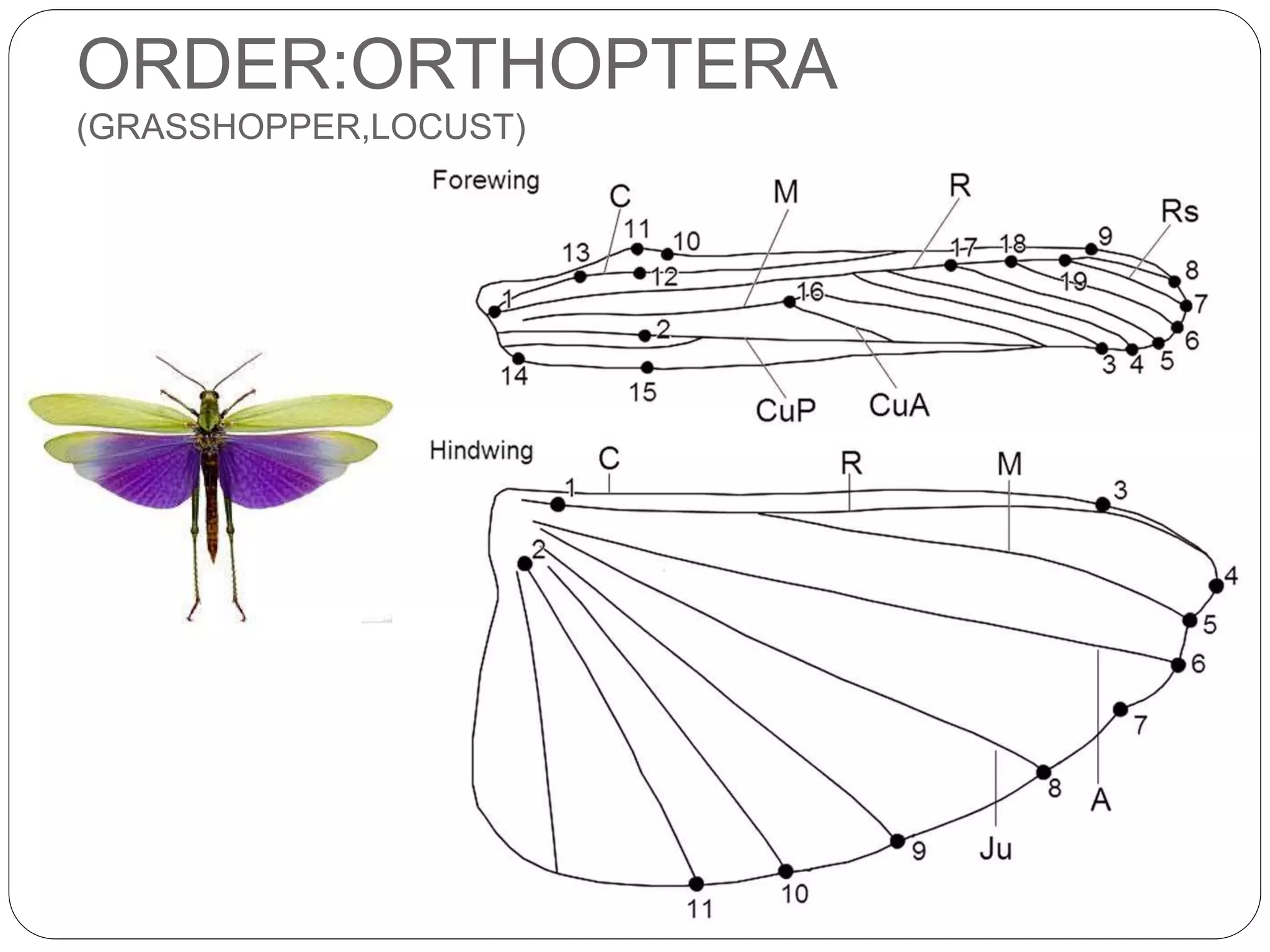
The document discusses the anatomical features of insect wings, emphasizing their structure, venation, and classification. It details the presence of wings in different insect subclasses and introduces the Comstock-Needham system for mapping wing venation. Additionally, it outlines various types of veins found in insect wings and provides examples of different insect orders based on their wing characteristics.