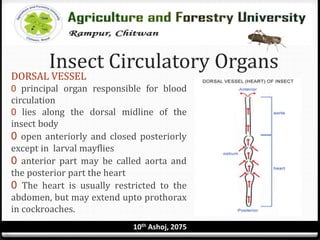
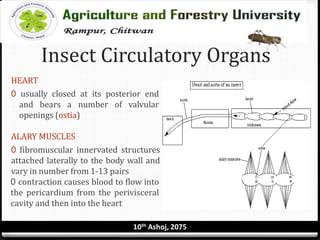
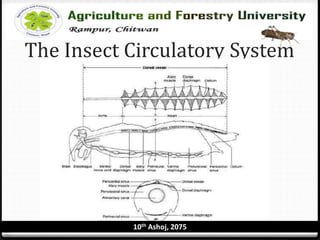
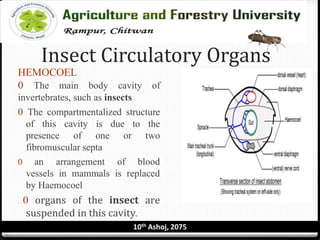
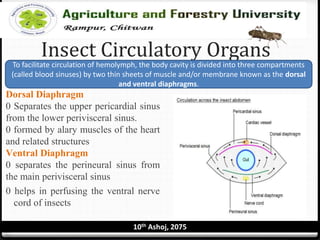
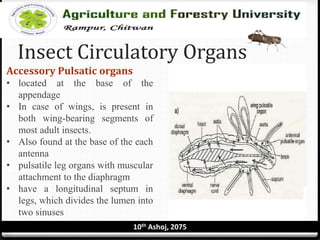
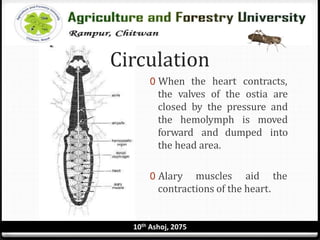
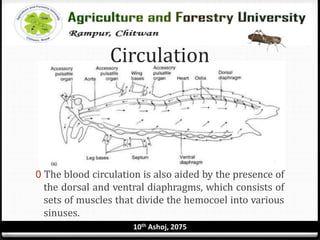
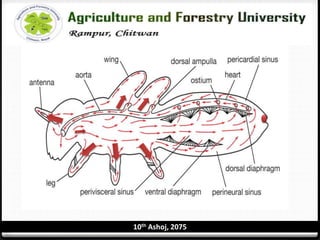
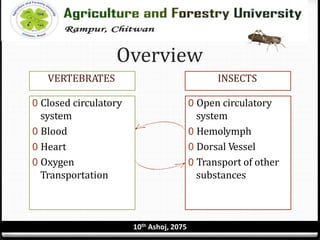
The circulatory system of insects is open and consists of hemolymph that bathes the organs rather than being contained in vessels. The main circulatory organ is the dorsal vessel, a tube located along the midline that functions like a heart to circulate the hemolymph. Hemolymph carries nutrients and wastes but does not transport oxygen. Accessory pulsatile organs help circulate hemolymph to appendages and tissues.