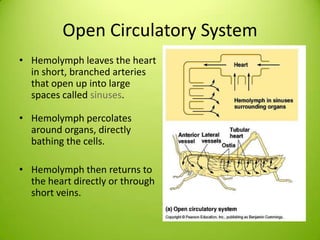
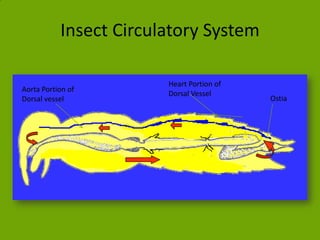
This document discusses circulatory systems, comparing open and closed systems. It focuses on the insect circulatory system, which is an open system. The insect system has a single dorsal vessel that acts as both the heart and aorta. Blood called hemolymph is pumped forward and returns via small slits in the dorsal vessel. Hemolymph directly bathes tissues. Advantages include direct exchange, while disadvantages include less control over distribution. Hemolymph is mostly water and plasma, lacking hemoglobin. Circulation is important for nutrient/waste transport, defense, development, reproduction, and thermoregulation.