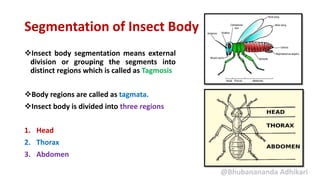
The document summarizes the structure and segmentation of the insect body. It is divided into three main parts:
1. The head, which is formed from the fusion of seven segments and contains the mouthparts, eyes, and antennae.
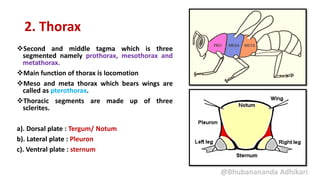
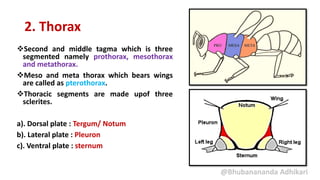
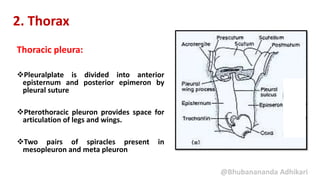
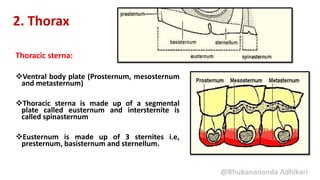
2. The thorax, which is composed of three segments - prothorax, mesothorax, and metathorax. Each segment contains a dorsal notum, lateral pleuron, and ventral sternum. The mesothorax and metathorax make up the pterothorax which bears the wings.
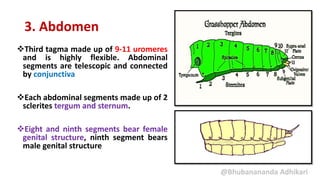
3. The abdomen, consisting of 9-11 segments. Each segment contains a dorsal tergum and ventral sternum

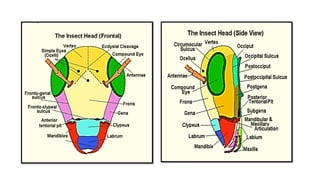
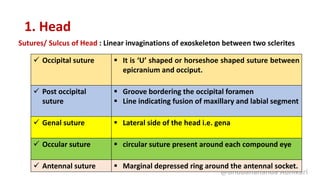
![Sutures/ Sulcus of Head : Linear invaginations of exoskeleton between two sclerites
@Bhubanananda Adhikari
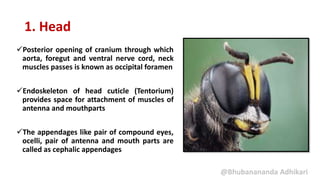
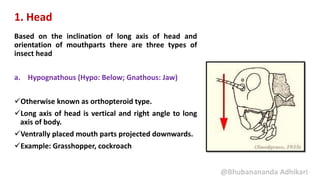
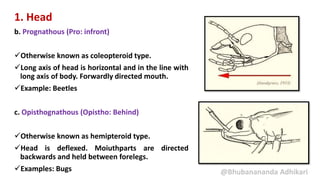
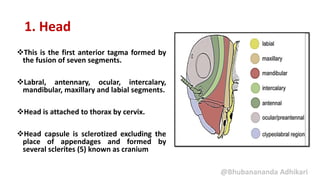
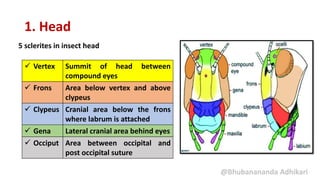
1. Head
Epicranial suture (Ecdysal line) Inverted Y shaped suture found mediallyon
the top of head [Median suture (coronal),
Lateral sutures (Frontal)]
Epistomal suture
(Fronto clypeal)
Epi: Above ; Stoma: mouth
Between frons and clypeus
Clypeo-labral suture Between clypeus and labrum
Frontogenal suture It starts from the junction of the
clypofrontal and the subgenal sutures.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lect4structuralorganisationofinsectbody-210613115211/85/structural-organisation-of-insect-body-6-320.jpg)